Many articles of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation offer a new type of main or additional punishment for a criminal - forced labor. Such a preventive measure implies the involvement of a convicted person in paid work. Moreover, a certain percentage of salary is withheld in favor of the state or the victim.

Principle of punishment
A preventive measure may partially or completely replace such punishment as imprisonment. Forced labor means paid labor of the convicted person without fail in places determined by a specialized institution.
Punishment can act as a harsh preventive measure or for preventive purposes aimed at preventing further offenses. The timing and types of work depend on this.
Part of the salary is withheld and credited to the account of the state, the territorial body of the executive system or to pay damages, payment of monetary debt. The amount to be collected is determined and determined by the court. Its size depends on the nature of the act and the damage caused, it can be from five to twenty percent of the salary.
Forced labor in criminal law is dealt with in article 53.1. The procedure for the execution of sentences is regulated by the Criminal Executive Code of the Russian Federation (chapter 8.1).
The procedure for sentencing
- Convict sentenced to imprisonment. If the term is less than five years, the court may consider replacing imprisonment with forced labor.
- The author considers the identity of the offender and the real possibility of correcting him without serving a term in prison. It is also necessary to prove that such a preventive measure is really necessary as a punishment.
- If the court comes to the conclusion that deprivation of liberty can be replaced with labor, then a corresponding decision is issued. At the same time, the duration of the sentence does not change - each day of serving a term in prison is equivalent to a working day. The time that a citizen spent in detention for the duration of the investigation and clarification of the circumstances of the case is added to the general term.
- The amount of deduction from the wage of the convicted person is assigned. It can not be more than twenty percent of the total amount received. In case of collection of several debts, the size of the deduction of salary is not added. Compensation money is shared among all victims.
Work place
The correctional center in which the convict will work is determined by the court and the bodies of the penal system. If possible, distribution is carried out within the area where the defendant lives.
However, there are far from specialized institutions in all regions of the country, therefore forced labor can be carried out far from the hometown. The court can make the same decision if there are no places in local correctional centers, or at the request of the convict.

Duration of punishment
If the defendant was supposed to imprisonment for no more than five years, there is a chance that the conclusion will be replaced by forced labor. The terms of such punishment can vary from two months to five years. It all depends on the severity of the committed act, its material and moral damage. The goals of the preventive measure are also taken into account - preventive, as the main punishment or as a supplement.
The court considers the identity of the defendant. If the violation is single, and the social characteristics of the citizen are positive, the term of work, as a rule, does not exceed six months.
It should be noted that if the punishment is imposed for the purpose of collecting monetary debt, the duration of labor will be delayed until the full material compensation of harm to the state or the victims.
Who is assigned to such work?
The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for this type of criminal punishment for persons convicted for the first time of committing a crime of light or medium gravity. Forced labor can be the main or additional punishment, as well as an alternative to imprisonment.
In practice, such a measure is assigned mainly to debtors and non-payers of alimony. First, violators receive a warning with the possibility of urgent repayment of monetary debt. After ignoring the requirement, the convicted person is sentenced to forced labor. Part of the earnings of the violator will be transferred to the account of the victim until the full payment of material debt.
Prohibition of Forced Labor
This type of criminal punishment is not imposed on persons to whom heavy physical labor can harm or is simply inaccessible. The preferential category of citizens include:
- children and minors;
- pregnant women;
- elderly people - women from fifty five years old and men from sixty years old;
- single mothers who have children under three years old;
- military.
In addition to this work is not assigned to those who have committed repeated crimes of moderate gravity or more than one especially serious act.
Article 37.2 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, articles 2 and 4 of the Labor Code, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and international conventions signed by Russia, provide for the prohibition of involuntary labor and slavery. However, work performed by a court decision in connection with a sentence that has entered into force is an exception.
If the punishment in the form of forced labor is still impossible, compulsory labor is assigned to the citizen. It is usually associated with the performance of civil duties in emergency situations or with the introduction of martial law.

Alternative
A distinctive characteristic of this punishment is the alternative. It consists of several positions.
- In the case of a crime of moderate or minor gravity, imprisonment can be replaced by forced labor. Even the criminals who committed the act, regarded as grave, have a chance to avoid imprisonment. But only if it is single.
- The court that issued the sentence of imprisonment may change its decision. If there is a possibility that the convicted person will recover without serving a term in prison, then his alternative would be the execution of punishment in the form of involuntary labor. But if the term of imprisonment is more than five years, this option is unacceptable.
- In judicial practice, there are cases when the defendant refuses to perform forced labor. This happens especially often with criminals who have repeatedly violated the law - a similar sentence upsets them, and even humiliates those who are especially sensitive. In this situation, the opposite is true. Every day of work is replaced by imprisonment.
Types of jobs
The workdays of the defendants begin with a trip to the correctional inspection. Here they receive instructions on planned work, mark the beginning and end of daily tasks.
All employees are supervised by employees of the responsible organization, so it is not possible to relax or “hack”. The lunch break provided for criminals is also monitored by inspection officials. Any disobedience or evasion of duties amounts to a violation of order and may lead to an increase in the sentence.
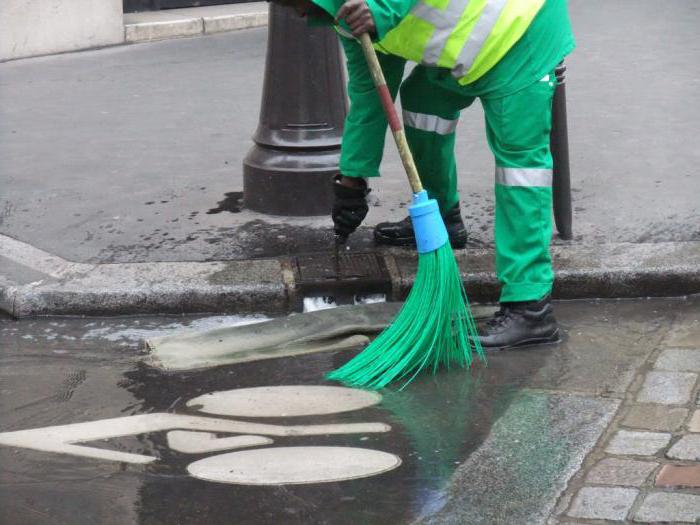
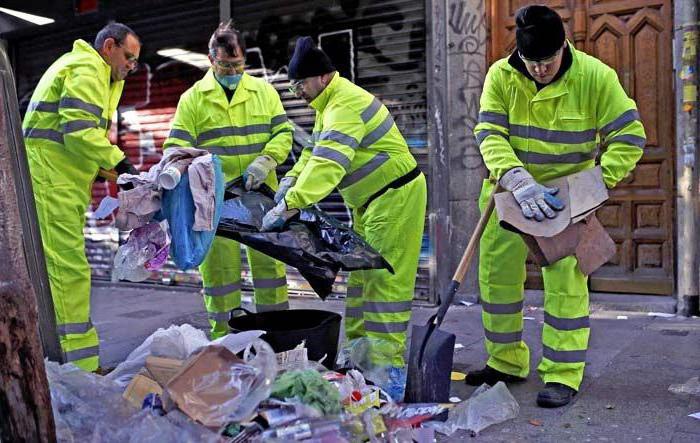
The types of forced labor entrusted to convicts usually consist of performing heavy physical work or ennobling the city:
- sweeping streets, porches;
- painting borders and trees;
- garbage collection, cleaning bins;
- restoration of buildings;
- care for the sights of the village;
- care of vegetation in parks, malls.
How often is punishment found in practice?
Despite the fact that the punishment “forced labor” is found quite often in the Criminal Code, it is rarely prescribed. There are several explanations for this.
- The preventive measure was included in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation only in 2011, while the law was in no hurry to enter into force. That is, such work is relatively young, and not all judges want to experiment.
- To carry out the execution of punishment, specialized institutions are needed. The construction and organization of such inspections is too expensive for the state. Today, not every city and even a constituent entity of the Russian Federation has a correctional center.
- Until what such work are assigned to a too narrow circle of convicts. As a rule, these are citizens who have caused only material damage to the state or society. In other cases, the conclusion of the offender remains preferable.
- A significant drawback of the measure is the inability to track the process of correction of the convicted person. But the purpose of such punishment is to become “on the true path.” In addition, often curators cannot cope with criminals or make them work.
Differences from other types of work
Forced labor in the Criminal Code is one of the youngest forms of punishment. It is considered a strict preventive measure in comparison with other types of work and is assigned less often. Differences of species are concluded with a view to punishment, place and method of execution.
- Schedule. Correctional work carried out during working hours, mandatory - in the period free from the main employment, forced labor takes all day.
- Salary. Forced labor, unlike other types, is paid. Compulsory labor is aimed at public benefit and is equated with volunteer work.
- The timing. The duration of compulsory and corrective labor is no more than nine months.
- Goals. The main task of forced labor is to punish the offender. The remaining types of work are aimed at correcting convicts.
This is the main difference.