Performing work using products that are powered by current can be a threat to the health and life of the worker. In order to make the use of electrical equipment safer, it was invented to classify. After studying the classes of power tools, an employee can navigate what equipment he needs for a particular job. Cases of human damage are not uncommon. The electrical safety classes of the electric tool contain information about the degree of protection this product can provide to the employee.
What is subject to classification?
The power tool classes contain data on resistance to heat and the level of insulation in case of accidental contact of a person with live parts. In addition, the marking indicates the protection of the product from ingress of water and foreign solid particles.
What information does the isolation class contain?
Operation of any electric tool leads to heating of its engine. This, in turn, leads to the vulnerability of the material used as insulation, and the safety of the employee.
The insulation class is an important parameter of electrical equipment, since it characterizes the quality of the engine winding and the degree of its heat resistance.
It indicates the temperature limit, exceeding which leads to the combustion of the engine. Classes of electric tools according to the insulation parameter are indicated by Latin letters, each of which corresponds to a certain temperature condition.
Resistance to heat
Classification of a power tool by heat resistance depends on the characteristics of the material used as a winding.
- Y: the lowest rates. Cellulose fibers, natural silk and cotton are used as windings. The limit of resistance to heat is 90 degrees C.
- BUT: cellulose fibers, silk and cotton treated with dielectric are used as wrapping material. The temperature limit is 105 degrees.
- E: Organic film and resin (120 degrees.) are used for winding.
- AT: used organic - mica (130 degrees.)
- F: synthetic and asbestos applied (155 degrees.)
- H: is an organosilicon impregnation, elastomers and fiberglass (180 degrees.)
- WITH: highest class. The winding is able to withstand temperatures exceeding 180 degrees. A combination of mica, glass, quartz and ceramics is used. Inorganic material is used as a binder.
Classification by the parameter of resistance to heat of the product also depends on the scope. Power tools for their intended purpose are domestic and professional.

The difference between the two is that the household appliance was not originally designed for long-term operation. He needs regular breaks necessary to cool the engine. Every 20 minutes of work should alternate with 15 minutes of rest.
Security Classification
Classification of power tools and hand-held electric machines is carried out depending on their safety level:
- «0». This class is characterized by the presence of a rated voltage. No grounding. There is only working insulation. Intend for rooms without increased danger.
- «01». In the presence of working insulation and a grounding device in the absence of a grounding conductor to a power source.
- «1». A power tool of class 1 contains working insulation, a grounding device, a wire core and a ground-contact plug.These are computers, washing machines, microwave ovens. The instruction manual indicates that when connecting the plug to a special outlet containing a grounding contact, the use of such electrical equipment is not limited. In the absence of grounding, these devices are equated to class zero.
- «2». Does not contain grounding elements. Double isolation of all parts with which contact is possible is characteristic.
- "3". The power tool is powered at a voltage not exceeding 42 V, and does not need grounding.
How to operate the equipment depending on its class?
Each Hazard Class the power tool dictates clear rules that must be strictly followed when operating the equipment. So, a tool of class “0” and “01” is allowed for operation if it is mounted in a device with a grounded case. A power tool of class 1 is suitable for industrial conditions (the exception is particularly hazardous areas). To work with equipment of this class, it is necessary to use such insulating agents as a rubber mat and gloves.

For the 2nd class additional safety measures are not provided, except when work is done in wells and metal tanks. Electrical products with safety class 3 are suitable for all conditions.
Marking
The hazard class of the power tool is marked with special icons.
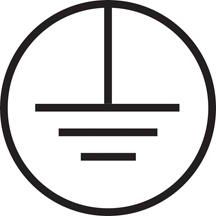
- 1st grade marked with three horizontal bars and one vertical, located at the top. All are circled.
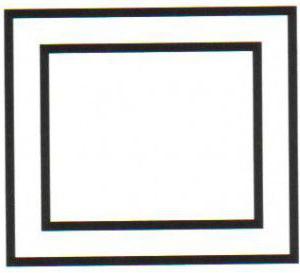
- 2nd grade it is marked with two squares (one large square contains a smaller figure).
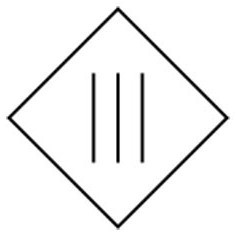
- 3rd grade has a marking depicting a rhombus, inside of which there are three vertical stripes.
Using IP-xx Labeling
IP-xx marking is used to classify power tools according to their degree of protection against penetration into foreign elements. It is two digits.
First digit
Indicates the degree of protection against solid foreign particles. It reflects both the level of risk of injury to an employee and the likelihood of a breakdown of the appliance itself.
- «0» - lack of any protection.
- «1» - the power tool is protected from particles whose diameter exceeds 5 cm. Equipment of this class is recommended for rooms without people.

- «2» - protected from bodies with a diameter of 12.5 mm (worker fingers). This is a power outlet and distribution board.
- «3» - the product is protected from 2.5 mm bodies (tools or thick cable).
- «4» - the equipment is isolated from bodies with a diameter above 0.1 cm.
- «5» - the tool is fully protected.
- «6» - absolute protection (even from dust).
Electrical equipment of the 5th and 6th class are used in rooms with a high level of dust.
Second digit
Indicates moisture protection for electrical equipment.
- «1» - protection against drops that fall from above.
- «2» - protection against drops falling at an angle of 15 degrees.
- «3» - the angle of protection is 45 degrees.
- «4» - comprehensive protection against water.
- «5» - comprehensive protection against water entering under pressure. 5th grade electrical equipment can be used outdoors even in the rain.
- «6» - the power tool is invulnerable to short flooding. The equipment is recommended for use on ships. It does not deteriorate even in stormy weather.
The IP-xx marking indicates that the components of the electrical equipment are reliably protected from exposure to moisture and mechanical elements.
Hand Power Tool Classes
These power tools are equipped with a cord (cable needed for power). It belongs to the hose type and contains a protective tube that prevents bending of cores, punctures of insulation and any contacts of wires to the body.

Depending on the method of protection against electric shock, three classes of electrical equipment intended for manual use are distinguished:
- First grade. The cable is equipped with a zero (ground) core, which connects the housing and the protective contact located in the plug (with a plug connection). The tool is intended for industrial use only. Provides for the presence of at least one electrical insulating agent (rubber gloves, rubber shoes or rug). For private use, equipment of this class is prohibited.
- Second class. The equipment is used in rooms with a high level of danger in the presence of dielectric gloves.
- Third class. Electrical equipment is suitable for use in hazardous areas without the use of protective equipment.
Work with a manual power tool is carried out by workers who have qualifications not lower than the second group.
Safety precautions
When working with manual electrical equipment, it is very important to comply with safety regulations:
- It is forbidden to work if during inspection of the instrument defects are found in it.
- It is advisable to suspend the power cables during operation.
- Care must be taken that the power cord does not come into contact with hot, damp, wet or oily objects and surfaces. Such contact may lead to mechanical damage to the cable and electric shock to the worker.
- Do not pull, bend or twist the cable. Also, you can not put weight on him and confuse him with other cords.
- If any violations are detected, the operation of electrical appliances should be stopped immediately.
Portable Power Tool Classes
- «0» - equipment with working insulation without grounding devices.
- «1» - a class of power tools with working insulation and a grounding element. The power cable is equipped with a grounding conductor and corresponding plug, which contains the image of a circle with the inscription "ground". It can also be marked PE or white - green stripes.
- «2» - double insulation without grounding. It is designated by a double square.
- «3» - power tools are designed for safe extra-low voltage. It is marked with a rhombus and three stripes.
Conclusion
Before you start using the power tool, you should check the operation of the power cable, plug, insulating handle. To do this, it is recommended that experienced electricians turn on the device and test it idle. Such a launch will allow for the detection of defects by the characteristic sounds inherent in engine components with unreliable parts. An ohmmeter is needed to verify the grounding integrity of first-class instruments.

You should also familiarize yourself with the class of the device, which is indicated in his passport. Orientation in the classification of electrical equipment is necessary to ensure operational safety. When operating electrical appliances, the rules corresponding to each class must be strictly followed.