Today, the firefight is an acute issue throughout the country security facilities construction. This includes housing, public buildings, administrative buildings, shopping centers, etc. Both at the design and construction stage, and for carrying out major, ongoing repairs, it is necessary to create maximum measures to create compliance with fire safety. This applies to systems providing the communal sphere: power supply, heating, all kinds of heating, the use of electrical appliances.
It is worth noting that building materials also come under close control and require attention in terms of their quality, reliability and safety. Often, it is the materials used that become the cause of the fire, because their use was incorrect and ill-conceived. Therefore, a combustibility class is used for them.

General classification
In order to proceed directly to the breakdown of certain materials into classes, it is necessary to understand what is the composition and classification of their fire hazard. The combustibility class depends on the properties of the building material used and on its ability to cause a fire during operation. Therefore, to determine the safety and hazard stage it is necessary to appeal a number of properties. These include flammability and flammability, as well as the speed of spread of fire on the surface. Important factors are the toxicity emitted during combustion and the level of smoke during combustion. According to regulatory documents, combustibility is divided into two types: combustible (G) and non-combustible (NG).
Non-combustible materials
This category does not become a complete guarantee of safety, because the combustibility group does not imply a complete absence of changes in the characteristics of the material during combustion. This means that when a fire is exposed to it, it is less active and retains resistance to high temperatures for longer.

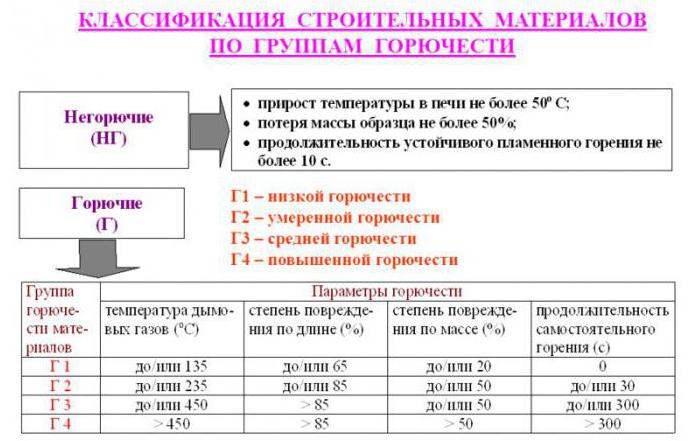
There is a specific method for determining incombustibility. If during combustion the temperature increase is at least 50 ° C, and the total weight loss does not exceed 50%, then such a material can be attributed to non-combustible. At the same time, the stability of continuous burning should not exceed 0 seconds.
How does the composition of the material affect the combustibility
Non-combustible materials can be safely attributed to those that are made from mineral substances and become the basis of the entire product. These are brick, glass, concrete, ceramic products, natural stone, asbestos cement and other building materials that have a similar composition. But in production, other substances are used as additives, the combustibility group of which is different. These are organic or polymeric compounds. Thus, non-combustible material is already becoming vulnerable in the combustion process, which means that confidence in its non-combustibility is significantly reduced. Depending on the proportions that make up the preparation of a particular product during production, the material can go from the non-combustible category to the group of refractory or combustible ones.
Types of combustibility classes

Regulatory documents impose requirements on the need to ensure fire safety, and GOST 30244-94 establishes the class of flammability and methods of testing building materials for flammability. Depending on the indicators and its behavior, when exposed to fire, 4 classes are distinguished.
Low combustible

The group includes materials, during combustion of which the temperature of the flue gas does not exceed 135 ° C. Flammability G1 should have a degree of damage to the material along the entire length of the sample not more than 65%, and the degree of destruction not more than 20%. In addition, self-combustion should be 0 seconds.
Moderately combustible
The group includes materials, during combustion of which the temperature of the flue gases does not exceed 235 ° C. The 2nd combustibility class has a degree of damage to the material along the entire length of the sample not more than 85%, a degree of destruction not more than 50%, and self-burning should not exceed 30 seconds .
Normally flammable
The group includes materials, during combustion of which the temperature of the flue gases does not exceed 450 ° C. Flammability G3 should have a degree of damage to the material along the entire length of the sample not more than 85%, the degree of destruction not more than 50%, and self-combustion should not exceed 300 seconds .
Highly combustible

The group includes materials, during combustion of which the flue gas temperature begins to exceed a threshold of 450 ° C. The combustibility class G4 has a degree of damage to the material along the entire length of the sample more than 85%, a degree of destruction of more than 50%, and self-combustion exceeds 300 seconds.
The combustibility materials G1, G2 are subject to additional requirements. When burning, they should not form melt drops. For example, linoleum. The flammability class of a given floor covering cannot be 1 or 2 due to the fact that it melts very much during combustion.
Material Safety Parameters
In addition to the combustibility class, in aggregate, additional parameters are used to classify the level of safety of building materials, which are determined by testing. This includes toxicity, which has 4 subsections:
- T1 - low hazard.
- T2 - moderate degree.
- T3 - increased hazard indicators.
- T4 is an extremely dangerous degree.
The smoke generating factor, which is contained in regulatory documents of the 3rd class, is also taken into account:
- D1 - low ability.
- D2 - average ability.
- D3 - high ability.

Flammability is also important:
- B1 - flammable.
- B2 - moderately flammable.
- B3 - flammable.
And the final criterion that makes the safe use of products is their ability to spread the flame over the combustion surface:
- RP-1 - non-propagating.
- RP-2 - low distribution.
- RP-3 - moderately spreading.
- RP-4 - highly spreading.
The choice of building materials
The combustibility class and additional criteria for evaluating safe materials are a significant indicator when choosing. The structure, regardless of scope, place of use should be safe for humans and, moreover, eliminate the risk of harm to health. First of all, it is necessary to competently approach the appointment of building materials in a specific field of work. In construction and repair, structural, finishing, roofing, insulation materials are used, which means that each of them has its place of application. Improper use may cause fire.
When purchasing building materials, it is necessary to study the label with characterizing indicators. Manufacturers that adhere to the technology indicate information containing codes reflecting the degree of fire safety. In addition to marking, the seller, upon request, must present a certificate of conformity for the goods. It also reflects indicators regarding safe use. Clandestine production or production in violation of technology compliance significantly reduces the quality, level of resistance to the effects of certain loads, and also does not meet the fire safety requirements.
Separately, it is worth noting the objects of social infrastructure, where different structures, shapes, and composition of the product are used for decoration.Special control is exercised over educational organizations, preschool institutions, medical buildings. Conditionality takes place, since a large concentration of children in one place should completely exclude any risk for them. In this regard, the relevant regulatory authorities conduct ongoing checks of these facilities. As a result, designers and developers are guided by the standards taking into account the object of the proposed work, taking into account, among other things, the combustibility of materials.








