Direct submission and direct submission are links of one chain. For those who are not sure whether he uses these terms correctly, it is useful to read this article. Descriptions of organization structures can also be of interest. After all, they can be compared with the device of the work teams of readers.
Terminology
The concepts of "submission" and "management", "leadership" are closely related. They are close, like a face and a wrong side in a woven or knitwear. One without the other does not make sense, it simply does not exist.
A subordinate is a person who executes orders and instructions received from his supervisor.
Head - a person who has the right to give instructions to subordinates.

Types of Subordination
There are two types of subordination:
- Functional. As a rule, they encounter it quite rarely. Examples include the recommendations of a methodologist, expert advice, instructions from a sanitary and epidemiological station, a firefighter, a tax administrator, and an employee of his own security department. Although there are, for example, active technologists who literally stand behind the employee for the entire shift.
- Organizational, administrative. In this case, the subordinate is completely and constantly in the grip of his official duties. Each step is governed by the instructions of the organizational (linear) manager.
The structure of the service hierarchy is well seen when considering managerial structures. For clarity, it is worth highlighting the duties of the chief.
The role of the leader in the implementation of the labor process
The functions of the boss are diverse and depend on many factors, such as:
- specialization;
- extent of liability;
- team size;
- a sense of responsibility for the well-being of a subordinate.
Common features for all managers are:
- documented or unofficially defined leadership position;
- responsibility for the discipline of team members, the quality and timeliness of work performed;
- duty of distribution of functions between subordinates.

Structure creation
The organizational structure of the company is the construction of the enterprise and the interaction between its individual elements in such a way as to achieve success in achieving the goal. At the time of its building, the following characteristics are considered:
- list of work that the organization will need to perform;
- the number of employees and specialists for the implementation of each type of activity;
- organization of reporting;
- forms of interaction between different functional groups.
The formation of the correct organization structure is very important. A bad device leads to big problems:
- cast confusion;
- conflicting orders from superiors at the same level;
- lack of functional coordination;
- lack of demand for productive ideas;
- slow decision making;
- tension in the team.
Types of Organizational Structures
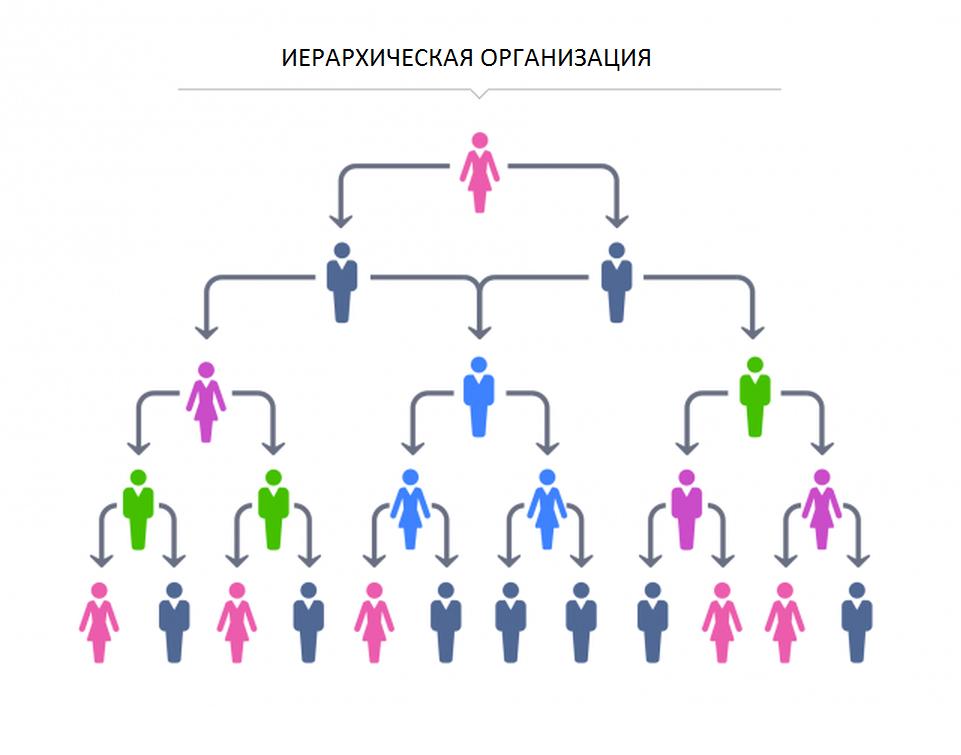
1. Hierarchical. Has a great story. Nowadays, it is most suitable for paramilitary organizations. Disadvantages:
- neglect of innovation;
- lack of activity of subordinates;
- isolation of the functioning of each unit;
- all information and power is concentrated above.
This model is firmly entrenched in the design of companies around the world. They seek to get rid of it. In diagram 1, direct submission and direct submission are clearly visible. People communicating in person, without intermediaries, are depicted in contiguous rows.
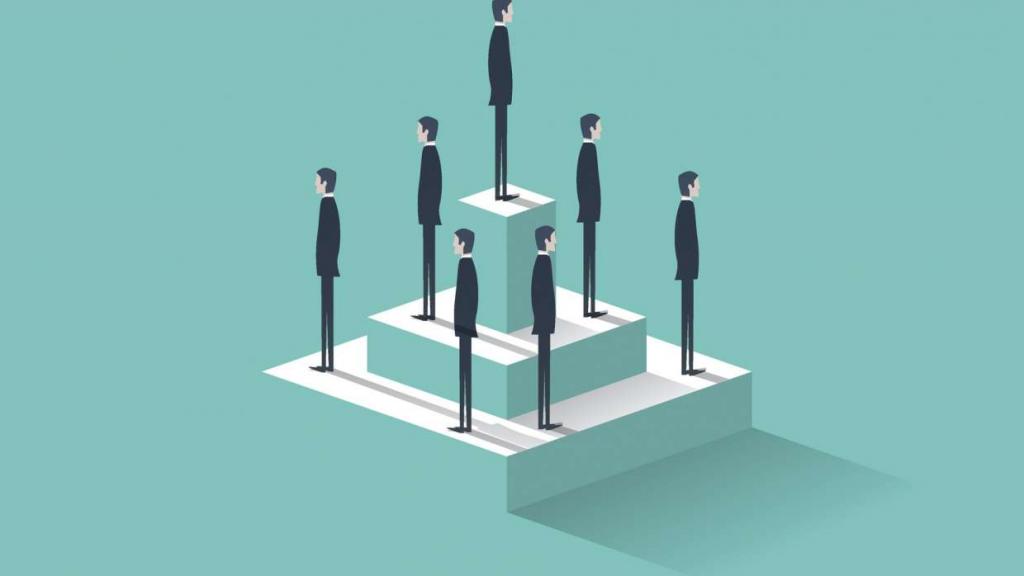
2. Horizontal. Hierarchical ruler shortened. Key positions are not directly subordinate to the director, but report to a group of interacting directors or shareholders. Open horizontal connections. Improving the qualifications of employees. Goals are achieved much faster and easier. Such a device is trying to create most organizations on the planet. Especially suitable for large companies. Important conditions for the effective functioning of such a system are:
- the desire of employees to work not out of necessity, but because of interest;
- the presence of proven technologies for maintaining ties in the team;
- free access to the required information and to communication with colleagues;
- democratic principles of work of managers who care about their moral authority;
- the existence of employees who track changes in consumer demand and methods of organizing work, developing constructive ideas for improving work.
3. Self-government. Everyone is equal here. As a rule, there are no posts and leadership. No one gives out tasks. Workers have access to the projects that need to be completed, and everyone chooses a task to his liking. To implement his own project, the employee himself finds financing and recruits a team. Disadvantages:
- psychologically more influential are older employees;
- can be used only in small teams;
- possible problems with the reliability and distribution of income;
- the desire of individuals to facilitate tasks;
- lack of coordination in work due to the failure of communicative functions.

4. Matrix. Coordination bodies responsible for the quick interaction of the horizontal functional blocks existing in the organization are introduced into the hierarchical system. Such a modification is formed during the implementation of a particular project. Workers employed in the program are on various issues with at least two bosses in direct subordination and direct submission is visually temporarily compressed to the project manager. The functional leader sets the tasks, linear distributes them.
Pros:
- the efficiency of interactions increases;
- functional managers more competent in specific issues are involved;
- units are granted economic independence;
- take advantage of teamwork.
Minuses:
- functional and organizational leadership of a high level is required;
- need a team with communication skills;
- key issues are slowly being agreed;
- the possibility of conflicts between the two types of leaders over the use of common subordinates.
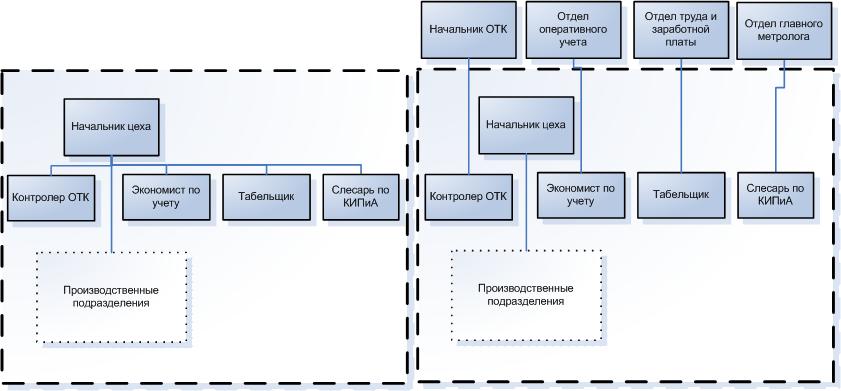
A lot of organizational structures have already been invented, apart from the ones listed. The most important point in the design of any of them is the separation of executive and control bodies. Scheme 2 depicts the posts whose jobs are located in the shop. However, they must be directly subordinate and directly subordinate to entities outside the production area.
Communication in the organization
At the workplace, a person voluntarily or involuntarily has to communicate with peers equal in official position and with his boss. The direct subordination of the employee completely exhausts all the requests and questions that arise during the labor process. Although everyone on Scheme 1 is taller than the employee, they are his direct superiors, their orders are transmitted through the immediate supervisor. If a subordinate manages to get an appointment through the head of the closest boss to a superior, he is likely to be hinted that he should understand the workplace. It is possible to see the top (direct) leadership at meetings, rallies and May Day demonstrations. This is the main difference between direct and immediate subordination.

More about the difference
The dissimilarity of direct and immediate leadership is expressed in the fact that the immediate boss:
- usually does not solve the material problems of the subordinate himself;
- Does not have a decisive voice in shaping company policy;
- personally knows each of his subordinates;
- develops small details of the assignment;
- each employee usually has one;
- nearest direct boss.

The 2 upper paragraphs describe the boss of the lower levels in an organization with a long hierarchical ladder. For the 6th paragraph, the following situation illustrates: the security service is directly and directly subordinate to the general director.
Heads of the 1-3rd upper levels:
- consider innovations;
- solve material issues;
- can change the functional orientation of the enterprise;
- produce personnel rotation and the selection of personnel of a high managerial level.
The reality of this division depends on the size and structure of the organization.
Conclusion
At first glance, it seems that direct organizational subordination in the service does not affect the well-being and daily activities of employees. However, the veiled effects of the organizational structure of the institution are undeniable.









