Damage insurance covers a wide segment of the insurance market. A significant part of it is based on the principle of mandatory participation. It is characterized by some features.
Insurance Definition
Insurance activity is the protection of the interests of citizens and organizations in the event of adverse events. By them is meant damage or destruction of property, causing harm to life and health, causing moral harm.

The insurance system is structured as follows: the parties stipulate in the agreement circumstances in which the insurance company pays a certain amount. The insured person undertakes to pay a regularly agreed amount or makes one contribution for the entire period of the company's obligations.
In the voluntary insurance system, the parties freely enough decide on what conditions to conclude a contract.
Mandatory participation, in particular in civil liability insurance for harm, is carefully regulated by the state. Private companies take an active part in it, but exclusively on state conditions.
Contracts are concluded according to the standard form, deviation from the conditions developed by the state is minimal. This applies, first of all, to the conditions of liability and amounts of payments.
Some features of insurance as a system of services
And voluntary and compulsory third party liability insurance has a certain “ceiling”. That is, if the damage has exceeded the amount stipulated by the contract or regulation, the remaining amount is paid by the guilty person. However, in most cases insurance covers the amount of damage.
A person is included in the insurance system in several ways:
- conclusion of an agreement;
- admission to the military or to another public service.
The second option involves automatic insurance.
Legislative regulation
- GK - the basic document that laid down the principles and rules of insurance activity;
- the law "On the organization of insurance business";
- laws on certain types of insurance (social, medical, etc.);
- laws on the transport system (transport charters and codes);
- provisions on the status of certain categories of employees governing insurance of their life, health and liability;
- normative acts of central authorities issued to enforce certain provisions of laws (insurance rules, model contracts, etc.).
Rules for insurance of civil liability for harm are part of the law, subject to their approval by the state body. As a result, they are equated with legal acts in force.
The insurance rules, offered outside the compulsory insurance system, have the status of a one-way transaction, and as part of the trial, a citizen has the right to challenge its individual provisions.
Often, a company engaged in compulsory insurance develops its rules on the basis of compulsory insurance, so you should pay attention to their content and how much they comply with the law.
Compulsory insurance
Speaking of liability insurance for harm, remember first of all the responsibility of motorists. However, they are not the only ones whom the law obliges to have an insurance policy.
For example, social, health insurance. The state separately insures civil servants, in particular law enforcement officials, judges, military personnel, etc.

Insurance is provided for certain types of activities. As an example, you can specify notaries, builders, appraisers. In the case of notaries, given the importance of their activities, the insurance is double - on the part of the corporation (notary chamber) and personal.
In the case of builders and appraisers, liability insurance for harm is provided by the association (SRO), which collects a special fund in case of such expenses and also acquires insurance.
Refusal or avoidance of compulsory insurance leads to two negative consequences:
- penalties from the state for evading or refusing to insure their activities;
- the burden of damages lies entirely with the perpetrator.
Conclusion of an agreement
The conclusion of the contract is possible in several ways:
- signing a full document;
- receipt of a receipt confirming both payment of services and insurance;
- filling out an application, after approval of which, a liability insurance policy for harm is issued.
The first option is applied if a non-standard contract is concluded, and the parties have developed conditions as a result of negotiations.

The second option is found when buying a ticket for vehicles. The third option is to purchase insurance under standard conditions. This includes business risk insurance.
Part of the contract are copies of documents. For example, each driver knows the list of documents, without which there is no way to get an insurance policy. Without them, the conclusion of an agreement with an insurance company is impossible.
In the voluntary insurance system, companies providing services independently develop the rules for concluding a contract, in particular:
- application form and procedure for its submission;
- list of documents required in each type of insurance.
The website of any such company contains information about the list of services and the package of documents that must be provided.
Insurance policy
The result of the agreement is the issuance of the policy. This is the main document confirming the conclusion of an insurance contract.
The law makes a number of requirements for the content of the policy:
- it is always called a policy and nothing else;
- company name, location and bank account information;
- Full name of the person to whom the insurance is issued;
- object (vehicles, cargo, etc.);
- amount of contributions, procedure and terms of payment;
- size of insurance payment or formula for its calculation;
- insurance risks (for example, death or damage to property);
- policy validity period;
- rules for changing insurance conditions or terminating the policy;
- date of issue and signature of the person issuing the document;
- other conditions that the parties consider necessary.
An example of issuing policies is the OSAGO system, which provides liability insurance for harm to third parties.
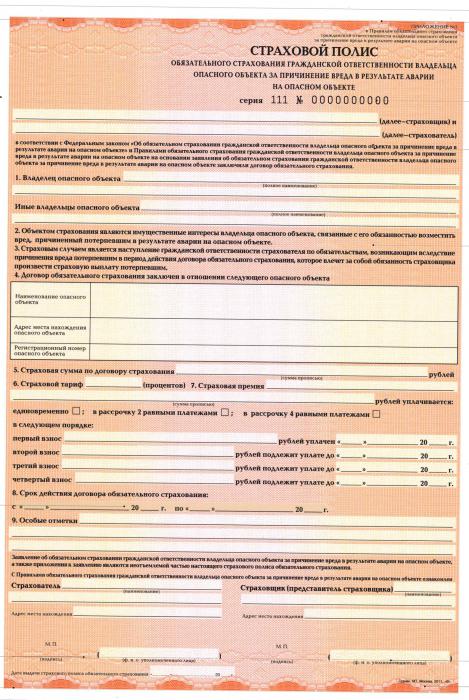
The law allows the issuance of a policy for one or more objects or several operations.
Beneficiary
The legislation contains the concept of a beneficiary - a person in whose favor the insurance company makes payments upon the occurrence of an insured event.
In the usual case, either the insured person or someone else indicated by him acts as his, if this is expressly indicated in the text of the agreement. In civil liability insurance in case of harm, the beneficiary is always the person who suffered the damage.
Receipt of payments
Compulsory third party liability insurance works as follows: the insurance company pays money on condition that a package of documents is received from the client.

It is determined by the specifics of legal relations. For example, CTP. The basis for receiving money is a protocol from the police or a “European protocol” signed by the parties.
Then, an assessment is made of the damage caused by specialists associated with the company.
Insurance rules provide for deadlines for submitting documents and their composition. If the documents are not submitted in full or with a delay, payments may be refused, or they will be received also with a delay.
Features of CTP
The amount of payments in favor of the insurance company is calculated from the technical characteristics of the vehicle (engine size, number of passengers) and the driver’s driving experience.
- Compensation for damage caused to life, health and property of citizens;
- the marginal amounts of payments in favor of victims periodically change upwards;
- the duration of the policy is usually 12 months; the law also allows for shorter periods (up to 3 months).
Carrier liability
The civil liability insurance contract for damage caused by the carrier is concluded for 12 months. There is a difference between carriers operating within the country and beyond its borders. There are more requirements for international carriers, but the list of risks has also been expanded.

In particular, insurance covers:
- destruction and damage to goods;
- harm caused to the health of citizens;
- harm caused by company employees.
Insurance is usually paid based on a court decision.
Company insurance
Since 2012, Russia has been insuring the activities of enterprises whose activities can harm the environment. And as a result of life, health and property of citizens. The tariff system is gradually improving, and there is an increase in the amounts paid to victims.
Product Responsibility
Now provided for liability insurance for harm resulting from shortages of goods. They are caused both by defects in the production system, and shortcomings and low quality of raw materials used in the production process.
The liability of producers is insured for the duration of the guarantee, the company has the right to extend the validity of the insurance by paying at a higher rate.
Insurance, as in other cases, extends to harm, health, life and property, compensation for non-pecuniary damage, payment of legal expenses, expenses for clarification of all circumstances and services of the appraiser.
Compensation is paid:
- subject to the consent of the insured and the insurer;
- subject to the adoption of all necessary measures to ensure the level of quality;
- the operating instructions are reasonably clear and comprehensive.

The lack of consent of the producer or insurance company to pay compensation can be circumvented if there is a decision of the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare or a court, which is more effective.
The insurance company has the right to refuse payments if the harm is associated with the following factors:
- aging of the material caused by natural processes;
- production features;
- hidden material flaws that could not be foreseen.
Risks of professional activity
Examples include notaries, lawyers, private detectives, and representatives of other professions.
The insurance is valid for 12 months, payments on it are made on the basis of a court decision confirming the fact of harm.
The insurance company will refuse to pay if the insured person:
- showed gross negligence;
- committed a deliberate crime resulting in the occurrence of an insured event;
- there is a conspiracy of the insured person with the victims.
It does not matter whether a contract was formally concluded with the injured person or not.
Finally
Thus, today the system of compulsory liability insurance covers a significant number of citizens and organizations.
It is carefully regulated by the state, but the main players are private companies.
Insurance rules are developed according to a single scheme, while there are significant differences.