Radiation, radioactivity and radio emission are concepts that even sound dangerous enough. In this article, you will learn why some substances are radioactive and what it means. Why is everyone so afraid of radiation and how dangerous is it? Where can we find radioactive substances and what does it threaten us with?
The concept of radioactivity
I call radioactivity the “ability” of atoms of some isotopes to split and create radiation by this. The term "radioactivity" did not appear immediately. Initially, such radiation was called Becquerel rays, in honor of the scientist who discovered it in work with the uranium isotope. Already now we call this process the term "radioactive radiation".

In this rather complex process, the initial atom turns into an atom of a completely different chemical element. Due to the ejection of alpha or beta particles, the mass number of the atom changes and, accordingly, this moves it along the table of D. I. Mendeleev. It is worth noting that the mass number changes, but the mass itself remains almost the same.
Based on this information, we can slightly rephrase the definition of a concept. So, radioactivity is also the ability of unstable atomic nuclei to independently transform into other, more stable and stable nuclei.
Substances - what is it?
Before talking about what radioactive substances are, let's define what is called a substance. So, first of all, this is a kind of matter. Logical is the fact that this matter consists of particles, and in our case it is most often electrons, protons and neutrons. Here we can already talk about atoms, which consist of protons and neutrons. Well, atoms, molecules, ions, crystals, and so on.
The concept of a chemical is based on the same principles. If it is impossible to isolate the core in matter, then it cannot be reckoned with chemicals.
About radioactive substances
As mentioned above, in order to exhibit radioactivity, an atom must spontaneously decay and turn into an atom of a completely different chemical element. If all atoms of a substance are unstable to such an extent that they decay in this way, then this is a radioactive substance. In a more technical language, the definition would sound like this: radioactive substances, if they contain radionuclides, and in high concentration.
Where in the table of D. I. Mendeleev are radioactive substances?
A fairly simple and easy way to find out whether a substance is radioactive is to look at the table of D. I. Mendeleev. All that is after the lead element is radioactive elements, as well as promethium and technetium. It is important to remember which substances are radioactive, because it can save your life.
There are also a number of elements that have at least one radioactive isotope in their natural mixtures. Here is a partial list of some of the most common elements:
- Potassium.
- Calcium.
- Vanadium.
- Germanium.
- Selenium.
- Rubidium.
- Zirconium.
- Molybdenum.
- Cadmium.
- Indium.
Radioactive substances include those that contain any radioactive isotopes.
Types of radiation
Radioactive radiation can be of several types, which will now be discussed. Alpha and beta radiation have already been mentioned, but this is not the whole list.
Alpha radiation is the weakest radiation, which is dangerous if the particles enter directly into the human body. Such radiation is realized by heavy particles, and that is why it is easily stopped even by a sheet of paper.For the same reason, alpha rays do not fly more than 5 cm.

Beta radiation is stronger than the previous one. This is the radiation of electrons, which are much lighter than alpha particles, so they can penetrate several centimeters into the skin of a person.
Gamma radiation is realized by photons, which quite easily penetrate even further to the internal organs of a person.
The most powerful penetration radiation is neutron. It is quite difficult to hide from it, but in nature it, in fact, does not exist, except in the immediate vicinity of nuclear reactors.
Human exposure to radiation
Radioactive substances can often be fatal to humans. In addition, radiation exposure has an irreversible effect. If you have been exposed, then you are doomed. Depending on the extent of the damage, a person dies within a few hours or for many months.

At the same time, it must be said that people are continuously exposed to radioactive radiation. Thank God it’s weak enough to be fatal. For example, watching a football match on television, you get 1 microrad of radiation. Up to 0.2 happy per year - this is generally natural radiation background of our planet. 3 gift - your portion of radiation with an x-ray of teeth. Well, exposure to over 100 rad is already potentially dangerous.
Harmful radioactive substances, examples and warnings
The most dangerous radioactive substance is Polonium-210. Due to the radiation around him, a peculiar luminous “aura” of blue color is even visible. It is worth saying that there is a stereotype that all radioactive substances glow. This is not at all true, although options like Polonium-210 are found. Most radioactive substances are apparently not at all suspicious.
The most radioactive metal at the moment is considered a liverworm. Its isotope Livermore-293 only needs 61 milliseconds to decay. This was found out back in 2000. Ununpentium is slightly inferior to him. The decay time of Ununpentia-289 is 87 milliseconds.

Another interesting fact is that one and the same substance can be both harmless (if its isotope is stable) and radioactive (if the nuclei of its isotope are about to collapse).
Scientists who studied radioactivity
For a long time, radioactive substances were not considered dangerous, and therefore they were freely studied. Unfortunately, the sad deaths taught us that caution and an increased level of safety are needed with such substances.
One of the first, as already mentioned, was Antoine Becquerel. This is the great French physicist, who belongs to the fame of the discoverer of radioactivity. For his services, he was awarded membership in the Royal Society of London. Because of his contribution to this area, he died quite young, at the age of 55. But his work is remembered to this day. In his honor, the unit of radioactivity was named, as well as craters on the moon and Mars.
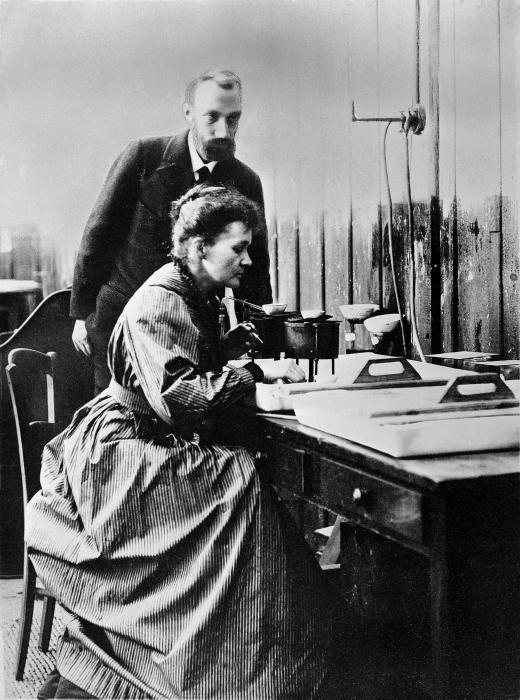

No less great was Maria Skłodowska Curie, who worked with radioactive substances with her husband Pierre Curie. Maria was also French, albeit with Polish roots. In addition to physics, she was engaged in teaching and even active social activities. Marie Curie is the first woman to receive a Nobel Prize in two disciplines at once: physics and chemistry. The discovery of such radioactive elements as Radium and Polonium is a merit of Maria and Pierre Curie.
Conclusion
As we can see, radioactivity is a rather complex process that does not always remain controlled by humans. This is one of those cases when people can be completely powerless in the face of danger. That is why it is important to remember that really dangerous things can be outwardly very deceiving.
To know a substance is radioactive or not, most often you can already come under its influence. Therefore, be careful and attentive.Radioactive reactions help us in many ways, but also do not forget that this is practically not a force under our control.
In addition, it is worth remembering the contribution of great scientists to the study of radioactivity. They have given us an incredible amount of useful knowledge that now saves lives, provides whole countries with energy and helps treat terrible diseases. Radioactive chemicals are a danger and a blessing to humanity.








