The Russian railway is the longest in the world. To date, more than 20 thousand locomotives run on it. In its scale, the Russian Railways fleet is second only to the American one (by about 3 thousand units).
Locomotive Definition
All locomotives carrying goods and passengers on the country's railways are classified into electric and diesel locomotives. The first are used where power lines are laid. Diesel locomotives are mainly used for transporting goods to remote non-electrified areas. The draft engines of the locomotives of this group also operate on electricity. However, at the same time, such machines are completely autonomous. The fact is that electricity in this case is transmitted to the engines from a generator mounted on a diesel shaft. Diesel locomotives, in turn, are classified into train, industrial and shunting.
Purpose of shunting machines
Locomotives of this group are used for:
- servicing passenger and industrial stations;
- supply of cars to driveways;
- work in the submarine parks;
- disbanding and formation of trains;
- thrust wagons on hills sorting.
In total, the Russian Railways fleet has about 6 thousand locomotives of this variety. Shunting diesel locomotives are usually by one person. However, soon Russian Railways plans to automate such machines. They will be controlled by the operator remotely over the air. Thus, Russian Railways wants to solve the problem of staff shortages.
general description
The emphasis in the design of locomotives of this variety is on maneuverability and draft power. Locomotives of this group are able to move along lines with a very sharp bend (up to 80 g). Such locomotives cannot develop too much speed, unlike passenger ones. However, at the same time they are capable of rapid acceleration and smooth braking.
Repair of shunting diesel locomotives and their maintenance are carried out through a special door located on the hood. The roof of such locomotives has a hatch door, and the driver’s cab is equipped with large windows.
Locomotives of this group are controlled by a special remote control located in the cab. To communicate with dispatchers in locomotives, a radio station is used. Locomotives of this variety operate on diesel fuel and, depending on the scope of application, can have different power. The shunting locomotive driver has the ability to work in fairly comfortable conditions. In any case, the cabin is heated.

Series of domestic locomotives
Shunting diesel locomotives can have a different design. You can identify the variety by the designation of the series. This is usually a TEM. Also in the Russian Railways park there are shunting diesel locomotives ČME produced in Czechoslovakia. Separately, freight locomotives of this group - TGM - are distinguished. There are other series of shunting diesel locomotives. However, TEM, ChME and TGM constitute the main fleet of locomotives of this type.
Diesel locomotives of the TEM series: technical specifications
TEM shunting locomotives, in turn, are classified into:
- designed for heavy shunting (TEM7, 7A and 14);
- universal (TEM2 and TEM18).
Models in this series make up the bulk of the Russian Railways shunting locomotive fleet.
TEM7, 7A and TEM14 cars
Shunting diesel locomotives TEM7 and TEM14 are produced by the Lyudinovo diesel locomotive plant. The main distinguishing feature of their design is the eight-axis crew. On locomotives of modifications 7 and 7A, one diesel engine is installed.More modern diesel locomotives TEM14 are equipped with two. However, the power of all these modifications is the same. The second diesel engine at TEM14 is installed mainly in order to save. For some types of shunting, the power of one diesel engine is enough. The second one can be disabled. TEM14 diesel locomotives in the Russian Railways fleet are still few. In 2013, only three units of such equipment were engaged in shunting operations.

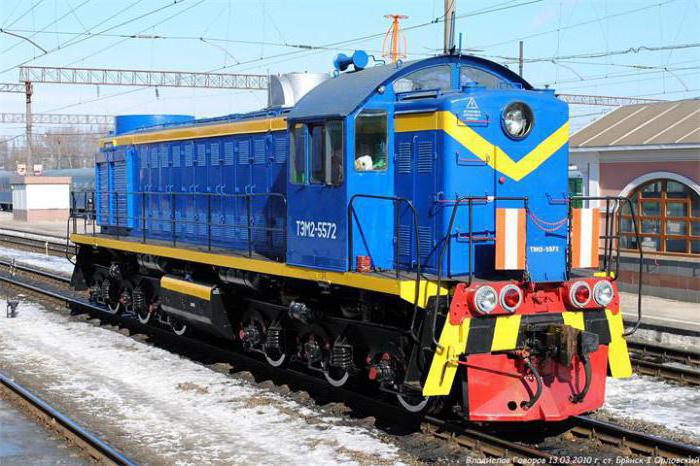
Locomotives TEM2 and TEM18
Shunting diesel locomotives TEM2 and TEM18 of different indices are suitable for almost all types of shunting operations. For the first time locomotives of this design began to be produced back in 1941 in America. During the Second World War, they were delivered to Russia. In the USA, such locomotives were labeled RSD1, in our country - YES.
After the war, locomotives of this design began to be produced at the Kharkov plant. The first series was called TE1. Later, more advanced TEM1 machines were developed at the Bryansk plant. At the moment, various shunting operations are carried out by even more powerful and productive TEM2 and TEM18. Such locomotives operate on a D50 diesel engine and direct current transmission. There is also a modification of TEM18V, equipped with a installation of the Finnish company Wartsila. The TEM2U diesel locomotive is designed specifically for operation in the Far North and Siberia. This modification is capable of performing tasks at temperatures below -50 gr.

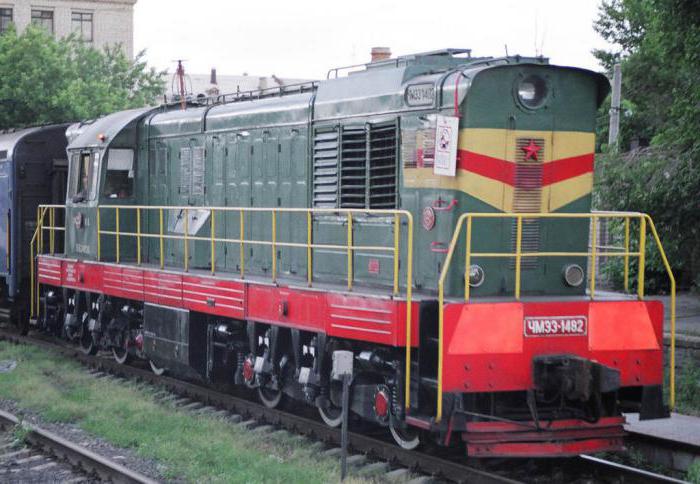
Czech cars CME2 and CME3
These locomotives are also quite often used by Russian Railways for shunting operations. According to their technical characteristics, they are similar to domestic TEM2. Current transmission, like TEM, ChME are outdated - constant. Such locomotives have been delivered to our country from the Czech Republic since 1967. In most cases, these shunting diesel locomotives are equipped with one Czech engine. However, in 2013-2017. The management of Russian Railways plans to modernize 60 such locomotives by installing two or three diesel engines produced by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant on them. ChME2 diesel locomotives are most often used for normal shunting operations. ChME3 is used for heavy and export operations. This series of machines, as well as TEM, is mainly used at railway stations. They rarely serve industrial enterprises and mainly only on a lease basis.

Modifications of the TGM shunting diesel locomotive series
The main distinguishing feature of the design of TGM locomotives is the presence of hydraulic transmission. The most popular modifications of this series are TGM23, TGM21 and TGM1. Shunting diesel locomotives TGM are used mainly at industrial enterprises. For a long time, 1D12400BS2 diesel was installed on the locomotives of this series. Recently, however, Russian Railways has been modifying such shunting diesel locomotives with the replacement of 1D12400BS2 MTU diesel engines, whose power can be 450, 500 and 600 liters. with. These installations differ not only in their remarkable operational characteristics, but also in their small size.
Diesel locomotives of modern modifications
Most of the above models of shunting locomotives were designed in the middle of the last century. Fundamentally, nothing new, unfortunately, was invented by the engineers. However, over the years, advanced modifications of shunting locomotives have been produced, characterized by greater productivity. These include, for example, cars produced in recent years:
- Experienced shunting locomotive TEM 35. Currently, only one such locomotive has been built. This modification was released at the Bryansk plant in 2013. The locomotive is equipped with a 777 liter Caterpillar C18 engine. with.
- TGM40. This diesel locomotive was first launched in 1981. To date, its modifications TGM40-S (1987-2002), TGM40-01 (1988-2000), and TGM40-02 (1989-1992) have also been developed.
- Experienced TEM19. This powerful shunting diesel locomotive weighing 126 tons is equipped with a 491GD engine of 1200 liters. with. It was released in 2013 at the Bryansk plant.

Trunk locomotives: description
Locomotives of this group may be:
- Passenger
- freight and passenger;
- freight.
When designing passenger trunk diesel locomotives, the main emphasis is on speed, freight - on traction characteristics. Such diesel locomotives are distinguished from shunting ones primarily by their lower maneuverability.
There are many series of such diesel locomotives. Among the passenger ones, TEP10, TEP60 and TEP70 can be distinguished first. The most popular freight main-line locomotives are TEZ, 3TE10M, 2TE116, 2M62, 2TE10L. The number before the series name indicates the number of sections of the locomotive. If it is not, then the model consists of one section.
By the number of the series of main diesel locomotives, you can also determine at which enterprise it was manufactured. So, the numbers from 1 to 49 indicate the models of the Kharkov plant, 50-99 - Kolomensky, from 100 - Lugansk.
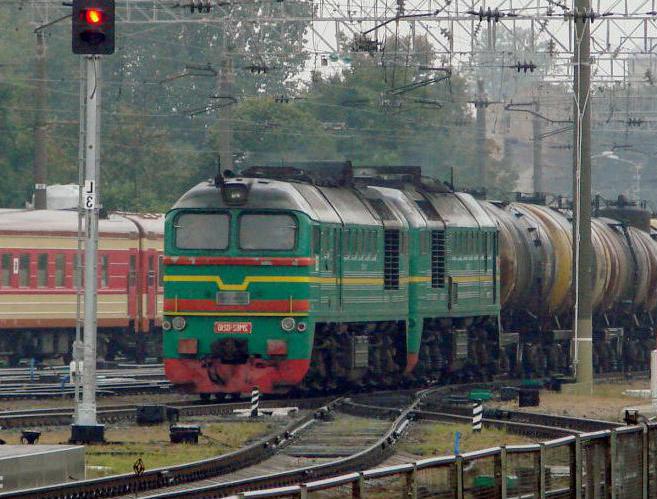

The main and shunting locomotives used today by Russian Railways are notable for their good performance and reliability. However, many experts agree that the Russian Railways fleet still requires speedy modifications. This is especially true for obsolete DC transmission.








