Modern management is based on a fairly wide range of teachings and approaches to management. For more than a hundred years, entrepreneurs have created many theories that are constantly being tested in practice. And this wealth of alternatives often confuses managers: they don’t know which management approach to use in different situations.

Basic control systems
Modern theorists and practitioners distinguish three main management systems: a process approach, a systematic and situational. All others upon closer examination turn out to be derivatives of one of these methods.
What is the difference? Approaches to the management process are based on a different attitude to the organization itself, to the time and moment of application of the control action and to pressure from the environment. So, the process system considers management as an endless chain of interrelated management functions. The system version focuses on the fact that the organization consists of many units, one way or another interacting with each other. And the situational approach to management concentrates on momentary decision-making based on events taking place on the market.
Management is a process
A process approach to management was proposed by representatives of the administrative school of management theory. He considers the functions of a manager as a single interconnected system. Achieving the goals of the company, according to this teaching, is a consistent solution to small problems. In itself, each such decision does not play a role in the activities of the company, but, being a link in the chain, is an integral element of achieving success.
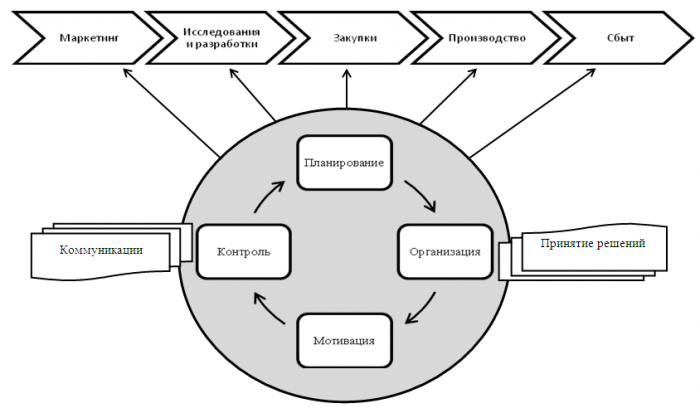
The process approach to management is ensured by the implementation of four critical functions: planning, organization, motivation and control. Each of them also represents a system. Therefore, the success of the organization is considered as the sum of all managerial decisions made at all levels of the hierarchical ladder of the enterprise.
In addition, to combine the activities of all elements of the company, the so-called connecting processes are necessary. Or communication.
Management functions
The first function is planning. At this stage, the management is engaged in setting goals and objectives and determines the direction of the business units of the company. We can say that planning allows you to develop a single system of actions of the elements of the organization to achieve the goals.
Planning is an ongoing activity of the leader. The fact is that both the external environment and internal variables constantly make adjustments to the chosen strategy. Therefore, the manager should constantly monitor the compliance of current activities with the goals set.
The function of the organization involves the development of the organizational structure of the enterprise, the development of an algorithm for the interaction and transfer of information between different departments. Another objective of the organization is to create a hierarchy of subordination. The head not only selects staff to perform specific work, but also delegates part of the responsibility and authority to him.
But for the success of a delegation of authority is not enough. It is necessary to find an approach to each employee in order to increase labor productivity.If earlier it was believed that it was enough for all employees to promise a material reward, now researchers claim that there are many different motivators. AND manager's task - choose the right one for each employee.

Modern management theory has developed several approaches to personnel management. One of them offers the manager to determine the true needs of employees in order to find a decent incentive.
Any force majeure situation may affect the following course. That is why the control function is considered as continuous. The sooner a deviation is detected, the faster and with less losses it will be possible to restore the company. The most common are three type of control. The first is the development of standards. All company plans are carefully developed and exact deadlines for completing tasks are set. The second is measurement. It is assumed that the result of the activity obtained for a certain period of time is compared with the expected (planned) result. And finally, the third stage of control is adjustment. The enterprise’s work is amended according to new environmental data or internal violations.
The market situation dictates the conditions
The situational approach to management suggests that decision-making should be based on an analysis of the current state of things on the market. Only by studying a specific set of conditions for a given moment can one make the only right decision. The theorists of this school do not consider all other management techniques to be incorrect or erroneous. On the contrary, they are trying to integrate the partial approaches of other teachings. The most promising in this regard is considered a systematic approach to management.
Managing an enterprise based on an analysis of the market situation presupposes that the head of situational thinking has the ability to concentrate on specific tasks and search for their solutions. In this case, the manager must not harm the implementation of the strategic goals of the company. This combines situational and systemic approaches to enterprise management.

It is also surprising that management theorists as early as the 1920s said that the situation governs everything. A well-known adherent and creator of the theory of organizations, Mary Parker Follet argued that "different situations require different knowledge."
Situation Management Methodology
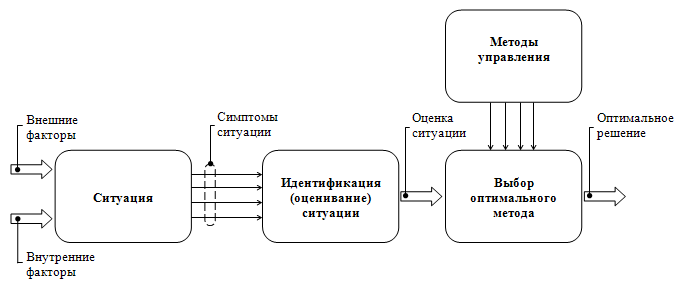
Specialists in the field of situational management consider the accumulated experience and effectiveness of decision-making by other managers in similar conditions. The methodology itself is a four-step process.
First, the manager must be familiar with effective management tools. He needs to understand the theory of behavior of subordinates and consumers, to know the basics of system analysis, to be able to identify the most significant factors (both within the company and beyond), to monitor the progress of the tasks.
Secondly, the manager needs to be able to predict the development of the situation depending on the decision made and be able to consider several alternative solutions at the same time. Since all modern management approaches have positive and negative sides, this skill is the most valuable for the leader.
Thirdly, it is necessary to be able to correctly identify causal relationships between events. Only an adequate assessment of the situation will make the right managerial decision. Unfortunately, this skill only comes with experience.
And finally, fourthly, this approach to management requires the ability to link together various methods of influencing the activities of the enterprise. It is necessary to build a program of action that would give a minimal negative effect (i.e.would not entail negative changes in other factors) in the existing circumstances.
Variables
Such an approach to management is effective only if the manager is able to correctly and efficiently determine and evaluate the variables of the current situation and the degree of their impact on the enterprise. If the situation can be analyzed, then there is very little room for all kinds of conjectures and the use of the “trial and error” method.
That is why the theoreticians of this technique distinguish the experience and experience of the leader as the most important elements of the success of the company. Only in recent years, studies have allowed us to highlight some situational variables that significantly affect management decision making.
Nevertheless, it is impossible to determine all the variables (and especially the degree of their impact on the situation). Everything, from the temperament and mood of each employee of the company and ending with geopolitical changes in the world, can to one degree or another affect the correctness of the decision. Experienced professionals consider two categories of factors:
1) having a direct impact on the company;
2) potential.
System management
All organizational management approaches focus on one aspect of the business. And this is their fault. After all, the effectiveness of management depends on many factors. The development of all management schools allowed managers to verify the integrity of the organizational system, the importance of the interconnections between individual departments and the unity of the enterprise and the outside world.
That is why system management theorists seek to integrate elements of different management approaches. For the first time, they started talking about the need to consider management as a single continuous process in the middle of the 20th century. And since then, a systematic approach to management has become more popular every year.
Concept
The idea to consider organization as a system came to management from the exact sciences. To understand the basic ideas of this school, it is necessary to determine what a system in general is.
A system is a whole consisting of unequal but interconnected elements; each such element contributes to the description and properties of the whole. Organizations are also systems consisting of people (personnel), technology, equipment, finance, etc. Due to the interaction of people and machines, firms are classified as socio-technical systems. In this case, approaches to personnel management should be developed by each organization independently, since the psychological compatibility of employees is as important as the availability of expensive equipment or modern technology.
Types of systems
Theory distinguishes between two different types of systems - open and closed. Closed is strictly limited and practically independent of the outside world. A striking example of such a system is the clockwork. Among enterprises, there are practically no completely closed systems.
More often we come across open systems. They are characterized by the fact that they actively interact with the world. Such systems need energy, information, materials and resources (both physical, financial and human). All this is found in the external environment. In addition, open systems can adapt to constantly changing conditions. This is a prerequisite for a long life open system.
Subsystem
We already remember that the system consists of elements. Most often, each such component is itself a system. To simplify understanding, they are called subsystems. The division of the organization into such sections is very important, especially when it is necessary to develop approaches to quality management. After all, a failure in the operation of a subsystem will lead to the adoption of erroneous decisions in the system itself.Therefore, malfunctions in the work of even the smallest structure can affect the result of all production activities.

It is the understanding that the enterprise is a complex composite open system that explains why it is impossible to unconditionally apply the postulates of any one school of management for effective management. After all, each of them focused on a single subsystem. So, the school of scientific management studies the technical subsystems, and behaviorism deals with the social side of the organization’s work.
Modern researchers argue that the success of the company is determined by environmental factors. They predetermine the conditions and capabilities of the company. And only after studying the state of affairs in the external environment, the manager can choose the most rational and effective solution to the problem.
Organization is an open system
The organization can be considered as a kind of machine or combine. Selecting and mixing components (environmental information, technology, personnel, equipment, etc.), the enterprise processes them into a final product and puts them on the market. Actually information, people, capital and materials are called the inputs of the organization. And the goods and services produced are called the organization’s output.
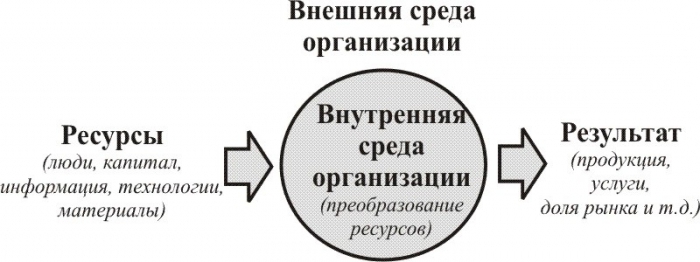
If the enterprise management process is organized correctly, then during the processing of resources added value is formed. As a result, in addition to goods at the organization’s output, there are profit, market growth, production growth (due to increased sales).
This is how modern basic management approaches look. We repeat once again: there is no one right management style, just as there can be no one right decision by a manager. The pace of information transfer and the development of the modern environment is so great that the leader can only look for the least "harmful" solutions. That is, those that do not entail serious fluctuations in the state of the external and internal environment of the enterprise.








