In banking and finance, clearing is the aggregate of all actions from the moment a payment obligation is received until the transaction is directly processed. The duration of this operation is equal to the time it takes to transfer money from one account to another. Currency clearing in international settlements is necessary because the trading speed is much greater than the period that is required to complete the entire cycle of operations. It includes cash transaction management, monitoring, tax processing, reporting and credit risk management. The latter ensures that the entire transaction is completed in accordance with the rules of the markets. Risk management even considers the possibility of bankruptcy of one of the parties.
Nationally and regionally
Systemically important payment systems (SIPS) are those whose failure can potentially lead to problems throughout the economy. They carry out interbank clearing in real time within individual states in large volumes. Pan-European TARGET2 and STEP2 are classified as systemically important payment systems. The US Federal Reserve is also SIPS.
The concept of clearing checks
This security is a payment order one side to pay a certain amount in favor of the other. This is the very first form of clearing. With this calculation, the check moves from the institution where it was handed over to the bank where it was drawn up. Money is moving in the opposite direction. Checks appeared in the 17th century. Initially, this operation took several days. This was the case before the transfer of checks into electronic form in the early 1990s. Now it can pass almost instantly. If there are not enough funds on the payer's account, a corresponding message will be received in response to the request for payment. That is, the seller can immediately understand that the check is not accepted for payment, and avoid many risks.
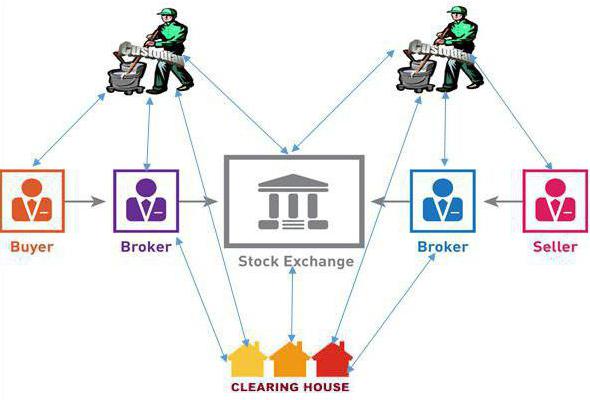
Securities Clearing
Amsterdam Stock Exchange was founded in 1602. Since that time, there is a need for clearing transactions, because the trading speed becomes much greater, and the time to complete transactions remains the same. This meant that there were several days of delay. Thus, clearing is an element of risk management. The buyer and seller need to be sure that the first will receive a certificate for the goods, and the second - the money laid to him. Therefore, a third party is often involved in clearing.
The impact of modern technology
In the 1700s, the Amsterdam Stock Exchange had close ties with the London. It took time to transport goods from one city to another and send and receive money. There was even a standard clearing period of 14 days. During this time, the courier could travel from London to Amsterdam (or vice versa) by horse or ship. Over the next two hundred years, a similar scheme was used on all exchanges existing at that time. With the advent of new technologies in the mid-20th century, the standard clearing period was reduced to three days. This innovation has further increased international trade.
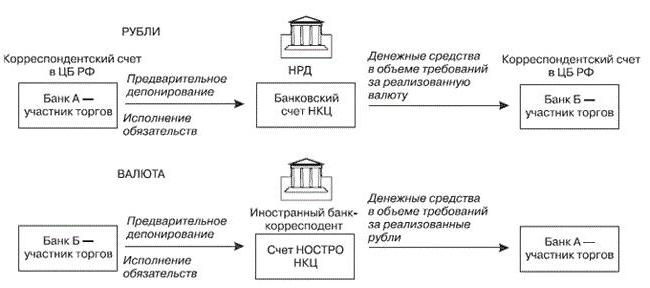
Today, clearing is primarily electronic systems. In connection with the dematerialization of securities, the introduction of new equipment, software, special depositories and registers was required. Until that moment, the exchange itself could act as a settlement and clearing organization for itself.However, the introduction of computer systems has opened the financial markets of many countries, so the volume of trade has increased significantly. Therefore, many exchanges transferred their clearing functions to third parties. This trend manifested itself in the middle of the 20th century. Examples are the London Clearing Organization and the Yuroklir structure.

US billing system
Millions of transactions involving the purchase of goods, services, and financial assets worth several trillion US dollars occur in the United States every day. Most of these payments go through depository institutions that have accounts with banks of the Federal Reserve System. Thus, clearing is an important function of the Fed. She plays the role of an intermediary in the settlement of international bank payments. Efficiency is ensured by the presence of deposit accounts on both sides. Central U.S. Bank insured against liquidity problems. He always has enough funds to fully pay for the transaction. The Fed provides real-time settlements between 9,500 participants. In 2013, she processed 123 million transfer payments. Their total value exceeded 436.7 trillion US dollars.

Types of Clearing During the Financial Crisis
Of particular importance is this operation during a downturn in business activity. During this period, many enterprises may experience problems with current liquidity. Therefore, they may need a deferred payment. Clearing can become an auxiliary tool in interbank payments, which can compensate for the lack of money in some enterprises. For the first time, it was used by a Swiss bank (Swiss WIR Bank) in the early 20th century, and internationally by the Panamanian financial division of the European Standard Bank. This set a precedent for many enterprises and allowed them to avoid some of the negative effects of financial crises. Such non-traditional use of clearing can also help organizations increase turnover and profit margins during a downturn due to the use of new opportunities at the expense of additional time.



