Any state on the planet that is washed by certain seas has in its composition internal sea waters. As well as territorial waters, which are also state property. In these zones, their own rules and laws are established; external borders are the borders of states. That this territory and what laws operate in them will be described in this article.
Inland Sea Waters: Concept
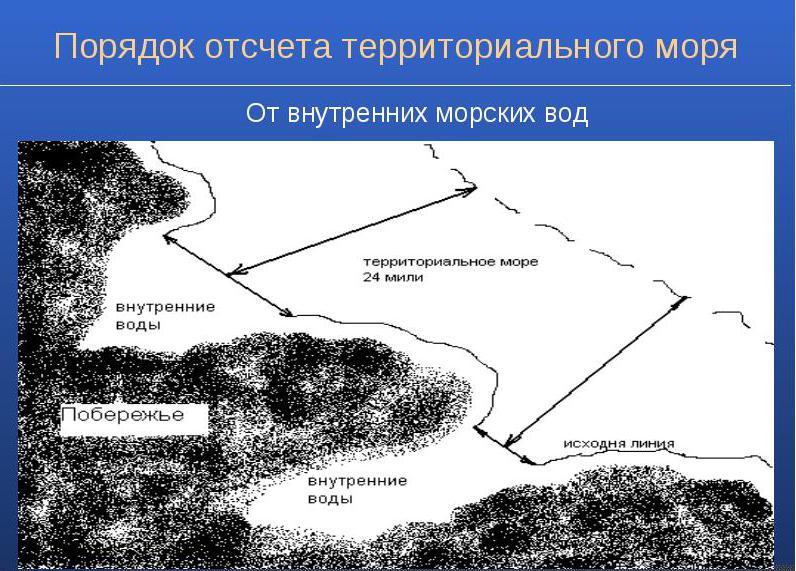
This is the water area, which is located between the coast and direct baselines. These lines are needed to measure the internal sea waters and to count from them the strip of territorial waters. How exactly these lines are drawn will be described below.
Inland Sea Spaces
Which territories and sections of the sea are classified as inland sea waters:
- Sea space in ports, limited by the line that runs through those port facilities (including hydraulic) located farthest from the coast.
- Any sea that surrounds one state on all sides. In addition, inland waters include completely marginal seas, all coasts of which are located in one country. An example is the White Sea in northern Russia.

- Small and small bays, bays of the seas, lips or estuaries that form rivers when they flow into the sea, the banks of which are part of the territory of one country, if the width of the ships in them is at most 24 nautical miles. If this value is larger, then to determine the internal waters inside the bays from one coast to another, a direct reference line of 24 miles is drawn so that the maximum possible water area is limited. There may be exceptions to this rule. It does not apply to bays that, according to historical tradition, belong to one or another state.
Historic Inland Maritime Territories
An example of one of the historical bays is the Far Eastern Gulf of Peter the Great in Russia. This bay extends to the line that connects the mouth of the Tyumen-Ula (river) and Cape Povorotny. The size of the entrance to it is more than 24 miles and is 102 nautical miles.

The status of this bay was established back in 1901 and is indicated in the rules for fishing in sea waters belonging to the Amur Governor General. It is also defined in the agreements of Russia, and then the USSR (1907, 1928, 1944) with Japan on fishing.
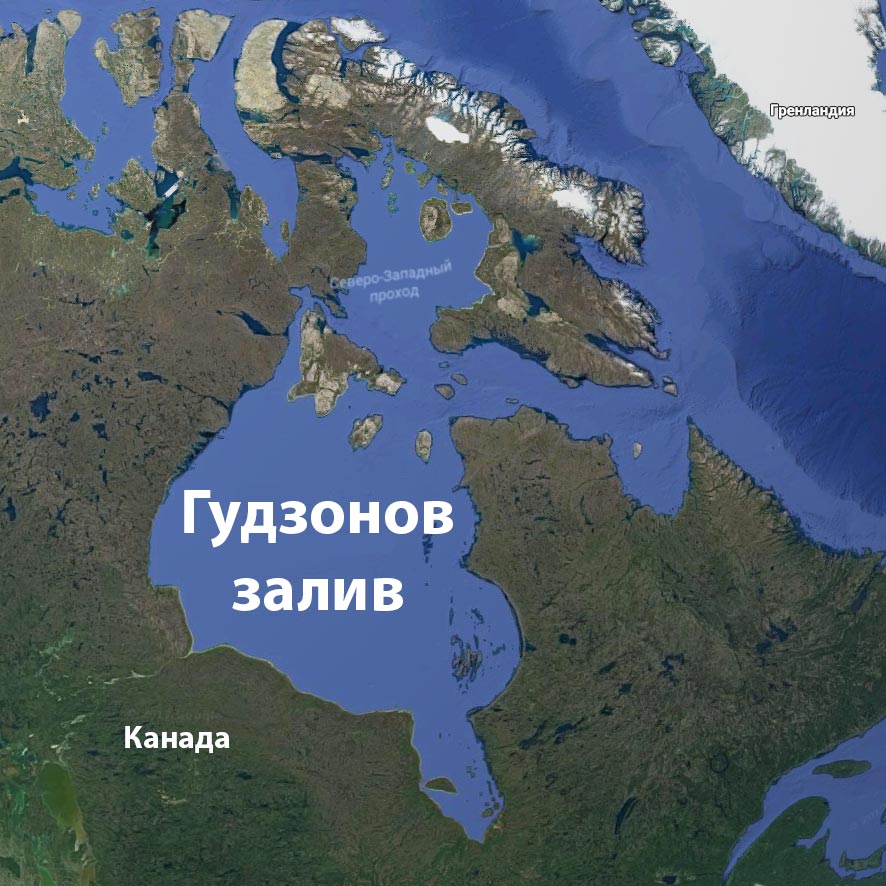
Another example is the Hudson Bay, which Canada considers its historical territory. Thus, Norway claims to be the Varangerfjord, and Tunisia considers the Gulf of Gabes to be its own.
Legal regime of inland waters
Laws in these waters are established at the discretion of the state. The laws of the coastal state regulate shipping and fishing, scientific research in its inland sea waters. Foreign ships and vessels may enter the territorial waters of a country only with the permission of its government. An exception may be a ship entering in emergency situations due to a natural disaster or entering open ports. Usually, without special permission, foreigners are forbidden to engage in any kind of fishing, scientific activity in these sea waters.
Legal regime in ports
The sea territory of the ports is also included in the internal sea waters. The state in whose territory these ports are located has the right to control access to them and determine the order of stay there for ships of other countries. This right is confirmed by the Convention establishing the regime of seaports.It was signed in 1923 in Geneva. It includes 40 states with inland sea waters. Some countries have made open access in their ports for foreign ships to improve and develop relations and trade between states.
According to the 1974 convention on the protection of human life at sea, nuclear ships of other states, before entering the seaport, must first warn and provide information that their call does not pose a nuclear threat.
Warships belonging to other countries must have a special permit or invitation from the coastal state to enter the port. All ships are required to comply with the rules and laws of the state on issues of sanitary, customs and border regimes, port charges. As a rule, countries conclude agreements and agreements on shipping and trade with each other, establish a certain procedure for calling at the port and the legal regime, including for merchant ships.
What is the territorial sea
Inland seawater and the territorial sea (territorial waters) are distinguished by the fact that the latter concept refers to a strip of 12 nautical miles, extending from the baseline along the entire coast.
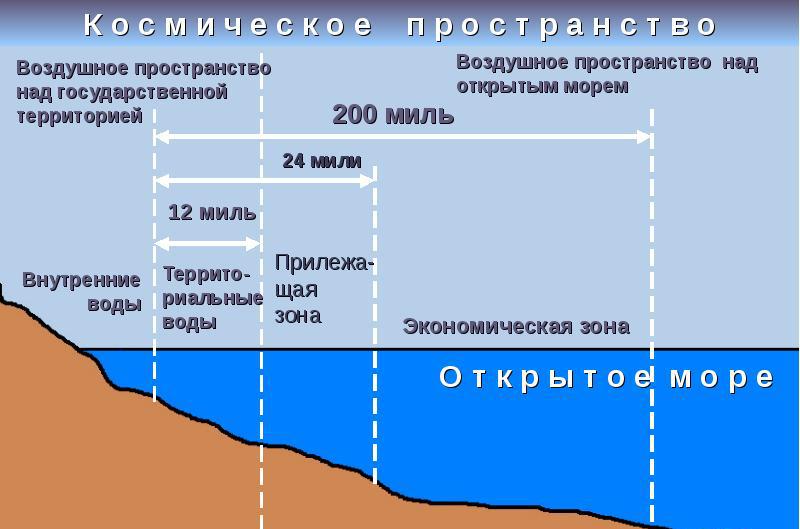
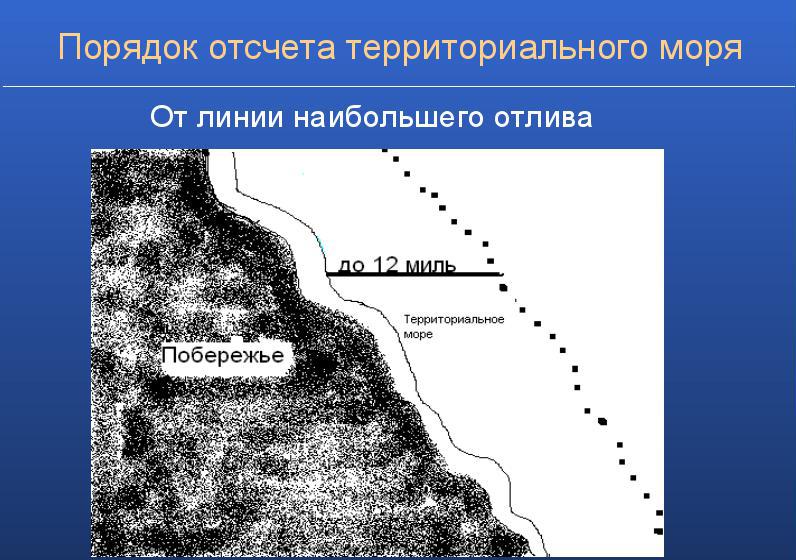
The width of this strip is counted from the coast line, which is formed at maximum tide. In those places where the coastline is uneven, rugged and has many bends, the countdown is from the straight source line, which passes through certain points.
The above methods of reference are used in the Russian Federation.
Legal regime in territorial waters
The legal regime has its own specifics. It is explained by the fact that the coastal state extends its sovereignty to territorial waters, but at the same time, all vessels have the right to peacefully pass through these waters. A peaceful passage is considered a passage that does not violate the world, does not threaten the safety of citizens, and does not violate public order. Nevertheless, within this zone, the state may establish its own laws and regulations governing shipping. Thus, it seeks to make the passage of ships safe, to protect navigation aids and equipment, to protect and preserve the ecology of the sea coast.
Some sites may become completely closed to shipping. Foreign vessels entering territorial waters are required to comply with state rules, laws and traditions.
Criminal and civil cases
Criminal and civil cases involving seafarers who are aboard a ship in a port or in the territorial waters of a coastal state are resolved by the judicial authorities of that same state. But most often, the country's authorities refrain from interference, unless the crimes committed that occurred on a merchant ship of another country are serious and do not harm the citizens of the coastal state. And also, if these offenses do not violate public order and tranquility in the state, people who do not belong to the crew of a foreign vessel are not disturbed.
The state may exercise criminal jurisdiction in order to stop the drug trade. At the international level, it has become customary that on foreign ships the routine inside the ship’s crew is determined by the laws, customs and rules of the state whose flag flies above the ship.
Facilitation of shipping between states
To make international shipping simpler and easier, a special convention was signed in 1965. It contains recommended specific standards designed to simplify and reduce the number of formalities and documents required for vessels to enter ports of other states, stay and leave them.
For starters, warships that are legally in the port of another state are immune from the jurisdiction of that state.But this does not exempt them from compliance with the laws and regulations adopted in this country, and from following the norms of international law.
According to historical tradition, non-military ships, including sea merchant ships, could also enjoy immunity from the jurisdiction of foreign states at sea. But after the Geneva Convention in 1958 (on territorial waters, the adjacent zone and the high seas) and the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, immunity is recognized only for state ships that are operated without commercial purposes.
Inland sea, territorial waters of the Russian Federation
In 1998, the Federal Law (Federal Law) on Inland Sea Waters, Territorial Waters and the adjacent zone was issued. According to him, the internal waters of the seas, as in other countries, spread from the baseline to the coast. These include water bodies of ports, as well as small bays, sea bays, estuaries (with a magnitude of entry of less than 24 miles), historic bays and other marine areas near the coast.
The territorial sea of Russia adjoins either the shores or the internal sea waters of the state. This belt is 12 miles wide, measured from the baseline, which are indicated in the Federal Law. The borders of inland sea waters and the territorial sea are applicable to all island territories of the Russian Federation. The adjacent zone is located beyond the territorial sea and is no longer part of the Russian Federation.
Thus, where territorial waters end, the border of the state of the Russian Federation passes. The sovereignty of Russia also extends to the space above territorial waters, the seabed and the bowels of the earth beneath it. At the same time, peaceful ships of other countries can pass through the territorial sea. Their passage through this water strip becomes possible and regulated in accordance with the applicable Federal Law and established Navigation Rules, including for warships and other non-commercial vessels.
Warships of other states can enter these waters with the aim of peaceful crossing them along specially designed routes without entering the internal sea waters of the Russian Federation. To enter the inland waters you need to get a special permission of the authorities of the Russian Federation. This rule does not apply to ships on which heads of state are present, and those warships that accompany them. Also, this rule may not be observed during natural disasters and during calls to avoid shipwrecks.
