When organizing fire safety for irresponsible or simply short-sighted people, the greatest difficulty is monitoring the state of fire extinguishers. Filling in paperwork, as well as fussing with the maintenance of these partitions, sometimes seems like an extra waste of time, money. And only during the inspection, having received a gigantic fine, everyone remembers the need for these procedures.
So that this situation does not happen to you, let's find out about the timing of the inspection of fire extinguishers, the features of their reloading, as well as where to document these actions.
Fire extinguishing device and its main types
Invented a little over a hundred years ago, a fire extinguisher quickly became the most affordable and convenient means of fire safety.
Regardless of the OTV (fire extinguishing substance) contained in it, the design of this device is approximately identical, and for all countries of the world.

OT is a cylinder of bright red color (there are other shades) with a trigger and a bell (or hose with a nozzle) in the upper part. All data on the use of such a device are printed on its label, and in the form of drawings and pictograms.
Following one design is made so that a person who finds himself in any country in the world, if necessary, without even knowing the language, is able to identify OT and use it for its intended purpose.
Depending on the filler, there are such main categories of fire extinguishers:
- water based (OV);
- air-foamy (ORP) and chemical-foamy (OHP);
- air-emulsion (OVE);
- powder (OP);
- carbon dioxide (OS);
- freon (OH).
It is worth mentioning right away that most often at the enterprises they use OP and OA, as they are cheaper and more durable. In car dealerships, powder devices are most often used because of their compactness.
Why is it important to know the varieties of OT
Not only what type of fires they can extinguish, but also the frequency of inspection and verification of fire extinguishers depends on what type of active substance is used.
Why is that? The thing is that although the average service life of such an instrument is ten years, due to interaction with the environment (temperature changes, humidity, physical impact), the contents of the cylinders may lose their properties (for example, powder) or even disappear due to malfunction mechanism (carbon dioxide).
To prevent this or to diagnose and correct it in time, the state standard provides for regular inspection of fire extinguishers. Its frequency directly depends on how OTV can succumb to environmental influences. Based on this, the terms of mandatory reloading of content are set.
Varieties of monitoring the state of OT
Before considering the frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers, it is worth learning about the varieties of this procedure.

Verification, depending on thoroughness, can be of two types:
- Plain. It is a surface inspection of fire extinguishers (the frequency of its implementation is indicated below). With this procedure, the condition of the OT housing (dents, corrosion, peeling of paint or varnish) and the mechanism are taken into account. It also examines the location and availability of the device in the event of a possible fire. Such control is carried out by the person responsible for fire safety at the enterprise or any other institution. In the case of a single vehicle - its owner.
- A full (thorough) inspection of fire extinguishers (the frequency of this procedure is indicated below) implies not only checking the external state, but also the parameters of the active substance inside the cylinder. Depending on the type of OTV, the methodology is different. Based on the results of a thorough examination, a conclusion is made about the fate of the device (return to the place, recharging, repairing, scrapping). Unlike a simple check, a thorough one is carried out by specialized enterprises or organizations.
What is the frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers?
Having dealt with the typology of OT control, we turn to the main issue. Next, we consider the terms of inspection of fire extinguishers at enterprises, vehicles and other institutions.

A simple surface check is done:
- when receiving FROM accounting (primary);
- every three months (quarterly);
- every six months (only for rooms with increased fire hazard);
- every twelve months (annual).
As for the full inspection, then, along with a simple one, it is carried out:
- when recharging the device due to its use for extinguishing a fire
- every six months (if the fire extinguisher is stored in rooms with increased fire hazard);
- annually.
In addition to the periods specified in GOST and SP, manufacturers can establish additional requirements for the frequency of inspection of their products. They must also be taken into account.
Another factor affecting the frequency of OT control is the frequency of use provided by the manufacturer. For reusable fire extinguishers, the same rules apply. But their one-time variety is checked only according to the instructions. Such OTs are not subject to refueling and refueling.
Types of fire extinguishers: the order and frequency of their inspection
The legislation provides for uniform periods for testing the OT of all varieties - once a year (every six months for hazardous areas). However, the order of their implementation depends on the characteristics of their contents.
The table below shows the frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers with an entry in the logbook (more about the document can be found below).
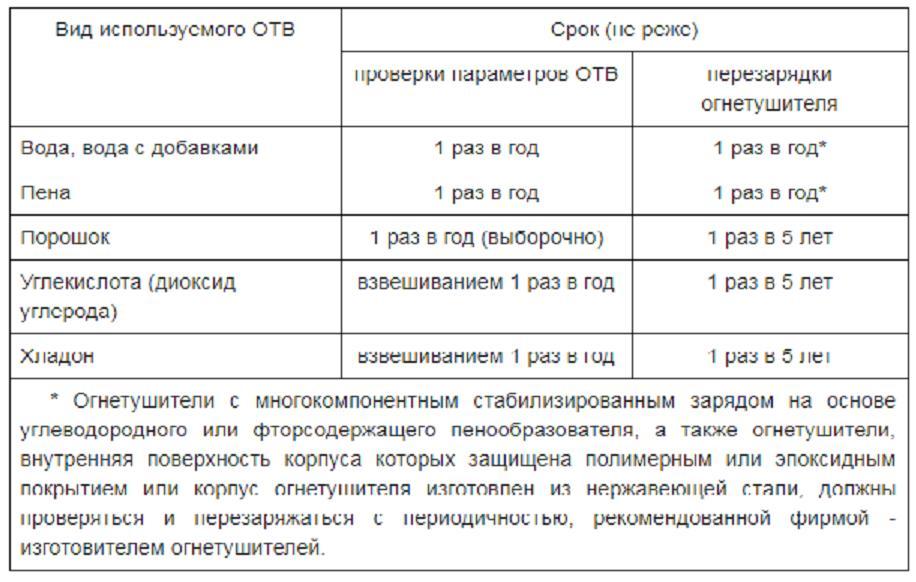
The data given here is very brief. Let's take a closer look at the features of monitoring the state of OT, depending on its contents.
Water Based Fire Extinguisher Testing

Devices (whose main content is H2O and additives) are inspected in the following way:
- The specialist disassembles the device and pours its OTV into a previously prepared container.
- Here, visually, the fluid is tested by physical parameters. If they are all normal - it regenerates (restores). If not, the cylinder is filled with a new composition, the old one is disposed of according to the instructions.
Since the standards require reloading this variety of OT annually, even if the parameters of the substance are normal, they are still sent for recovery, and the cylinder itself is recharged.
Features of checking powder fire extinguishers
Full control over the state of this type of OT is much simpler. Unlike other varieties, there is no need to disassemble each instance. The rules require that only three percent of the powder extinguishers that are in the facility pass the test. At the same time, not less than one piece.
Once a year, in the service center, the selected OPs are disassembled, and their contents are subjected to a study of the basic operational parameters:
- view;
- flowability;
- humidity;
- lumpiness;
- impurities;
- dispersion;
- destructibility of detected lumps upon shaking or falling.
To pass the test, the substance must meet absolutely all requirements. If at least one of them shows violations of the norm, not only the OT itself is recharged, but also the entire batch of powder fire extinguishers, which is on the balance sheet in the institution.
If all indicators are normal - the device is assembled and sent to serve until the next check.
According to the established rules, in any case, all OPs must be recharged once every five years, even if their OTV is normal.
How are HFC and CO2 tested
Fire extinguishers filled with gaseous substances have the property of "etching". Due to the high volatility of gas at the slightest depressurization or leaks of equipment, such OTs can escape even without activating the device itself.

It is this feature that is controlled during the annual full verification of the content. By the way, it can be carried out at the enterprise itself. For this, each cylinder is weighed. The result obtained is compared with the data of the previous inspection.
According to the standards, the annual limit for weight loss is five percent of the total OTV. Only if this limit is exceeded, such fire extinguishers are sent to a service center to check the mechanism and contents. And there is already recharging, recharging, repair or disposal.
As in the case of powder fire extinguishers, once every five years it is necessary to carry out a complete refueling of HFCs and carbon dioxide, even if their performance is normal.
Log book: what is it, what data contains
Having considered the procedure and frequency of monitoring the condition of health, it is worth learning about the design of these procedures. For this purpose, at each enterprise, a specialized logbook for the availability and frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers is started.
This document is maintained either by the head himself or by any employee of the enterprise who studied the fire-technical minimum at specialized courses, passed the exam and received a qualification certificate. OT control can be carried out without interruption from the main activity in the institution.

Such a magazine is started one for all fire extinguishers on the balance sheet of the institution. The following data is entered here:
- inventory number;
- date of commissioning;
- location;
- type of fire protection and data on the classes of fires with which it can cope;
- manufacturer;
- factory number;
- date of manufacture;
- type of OTV;
- dates of inspections;
- their results;
- dates of maintenance;
- data on the appearance and condition of the fire extinguisher;
- mass (especially relevant for carbon dioxide and chladone) or pressure (in the presence of an indicator);
- running gear condition (for mobile OT);
- measures taken to eliminate discovered shortcomings;
- position, full name and signature of the person in charge.
All this information should be in the logbook of the frequency of inspection and reloading dates of fire extinguishers. And most importantly, it must correspond to the actual state of affairs. During inspection, this document is the first thing to be checked. Based on the information contained in it and its compliance with the current state of things, conclusions are drawn about the level of fire safety in the institution.
How is this document maintained?
The legislation does not provide for any clear form of maintaining an inspection logbook and the timing for reloading fire extinguishers. The main thing is that all the above data should be clearly recorded in it and done in Russian (for Ukraine - in Ukrainian).
Usually this document contains a complete list of all fire fighting equipment that is or was available. And this is not only OT, but also other tools.
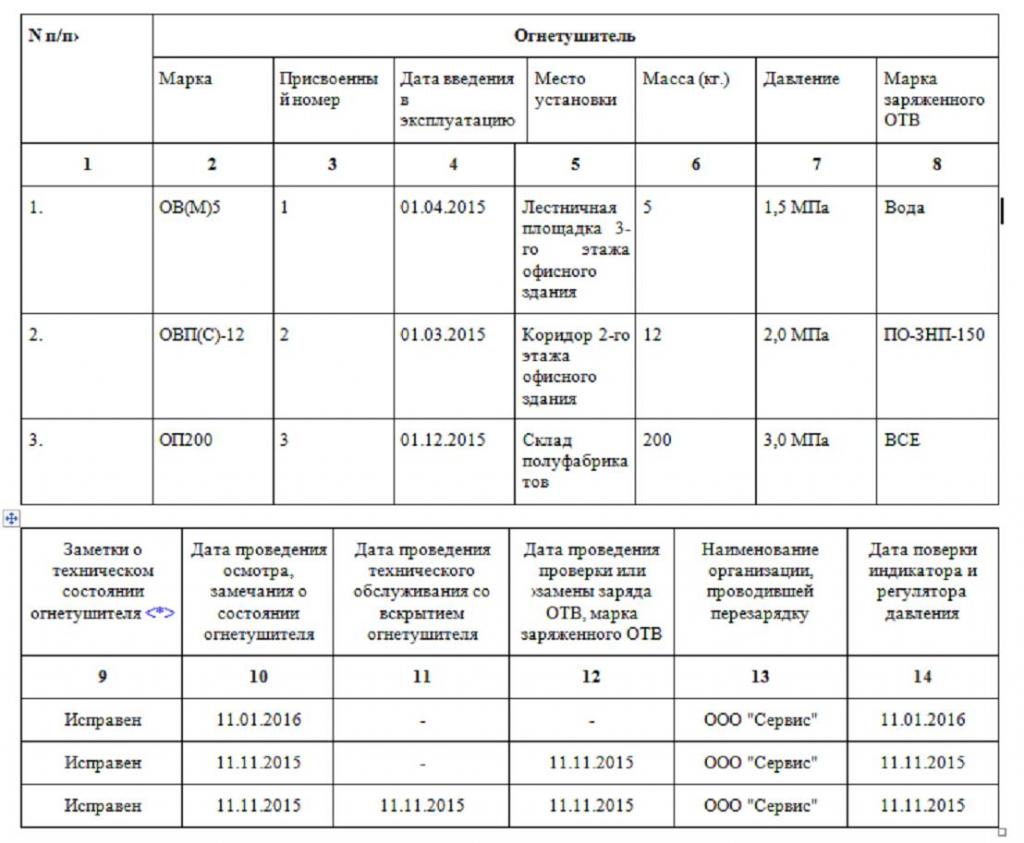
In addition, it is recommended to have a separate page for each fire extinguisher, where all data on monitoring it and recharging will be recorded.
It happens when the registration journal design form is confused with an operational passport (EP). This is the name of the paper in which all the data on the "life" of the fire extinguisher is recorded. Each OT has its own passport, which accompanies it to service centers. Information from the electronic signature is always duplicated on an individual page in the journal.
Speaking about the mandatory monitoring of the performance of a fire extinguisher, it is worth mentioning the tag (additional label). It is glued or hung on the OT after passing the first simple check at the enterprise. Data on inspections and reloads are briefly entered here.
The information on the tag must correspond to that recorded in the journal. In fact, it is a simplified version of the operating passport.
In addition to the electronic signature and tags, the magazine is also associated with the OT technical passport (it is also a factory instruction). It is from here that the initial data on the device are written (expiration date, purpose, weight, OTV, etc.).
Such a magazine can be decomposed manually or buy a ready-made form printed in a printing house. In the second case, it is worth comparing its contents with the recommendations of state standards. The best option is to coordinate its design with the local fire department. This, incidentally, applies to all documentation.
Regulations governing the frequency of inspection and recharging
In conclusion, consider where you can find all the information about the features of the operation of these devices.
Up-to-date information on the recharge times of fire extinguishers, the frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers, their placement, preparation of accompanying documentation, etc. are contained in the code of rules SP 9.13130.2009 "Fire fighting equipment. Fire extinguishers. Operational requirements."
Documentation requirements are clearly stated here. In addition, the frequency of inspection of fire extinguishers with an entry in the logbook is indicated.
In addition to this act, OT operation is regulated by GOST R 51057-2001 "Fire-fighting equipment. Portable fire extinguishers. General technical requirements. Test methods."
These two documents are standards for the Russian Federation. As for Ukraine, GOST 4297: 2004 is relevant here. Technical service of fire-extinguishing workers. Foreign technical vimogi. "