Insurance has long and tightly entered our lives. Everyone has a compulsory medical insurance policy, for those with cars - compulsory motor liability insurance. If you have made a deposit to the bank, it will already be insured, and if you fly by plane, go by train, the transport company will "voluntarily-compulsorily" arrange insurance for you. Life insurance, health insurance, property insurance are becoming more and more common. All that we have listed is divided into two large groups - compulsory and voluntary insurance. We will talk in this material in detail both about this classification and about insurance in general.
The concept of "insurance"
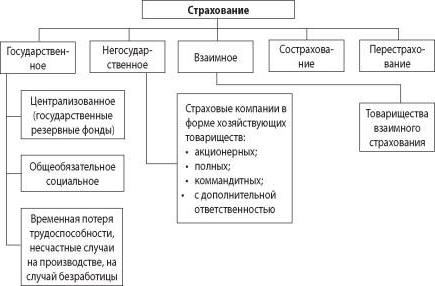
Insurance refers to the entire range of insurance activities (primary insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance, co-insurance), which is aimed at insurance coverage.
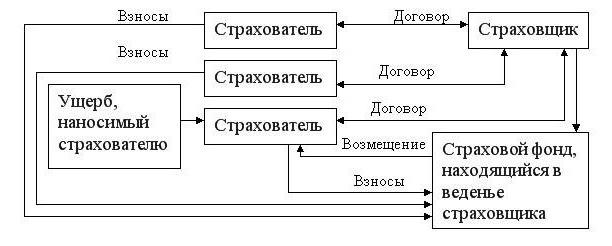
A more comprehensive definition: the relationship that is established between the insurer and the insured to protect property of both private and legal entities (meaning only the insured) in the event of an insured event against special cash funds. They are formed from premiums or contributions deducted by policyholders.
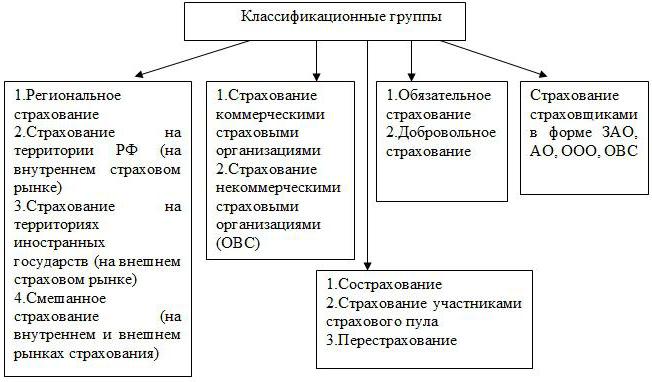
Two forms of insurance are distinguished - compulsory and voluntary. We will talk about them further, but for now we will consider the classification of the types of this phenomenon.
Types of insurance
As for the classification of species there is no consensus. In the vast majority of states, only life insurance and what is not associated with it are allocated. Civil Code of the Russian Federation prescribes property and personal. Some theorists repeat their classification according to law, others distinguish three branches - liability, personal and property, and still others say that there are already four types of insurance - property, risk, personal and liability.
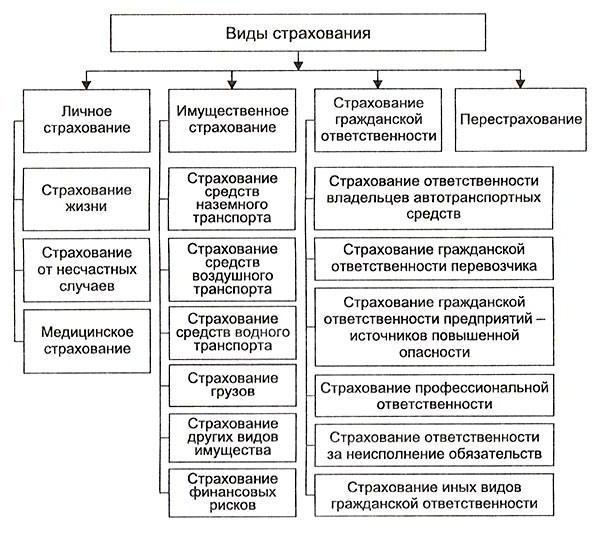
Consider the most common classification:
- Liability Insurance. It concerns cases when the policyholder must compensate the harm caused to another person. This includes civil liability of the carrier, owners of vehicles (vehicles), enterprises at which there is an increased level of danger, professional liability, responsibility for non-fulfillment of obligations undertaken.
- Property insurance. Relationships related to the disposal, possession and use of property are included. This is insurance of financial and business risks, property of citizens, organizations, enterprises, transport. Some classifications add liability insurance to this group.
- Personal insurance. This includes everything related to the ability to work, pensions, life and health of the insured. In particular, life insurance, against accidents, diseases and medical.
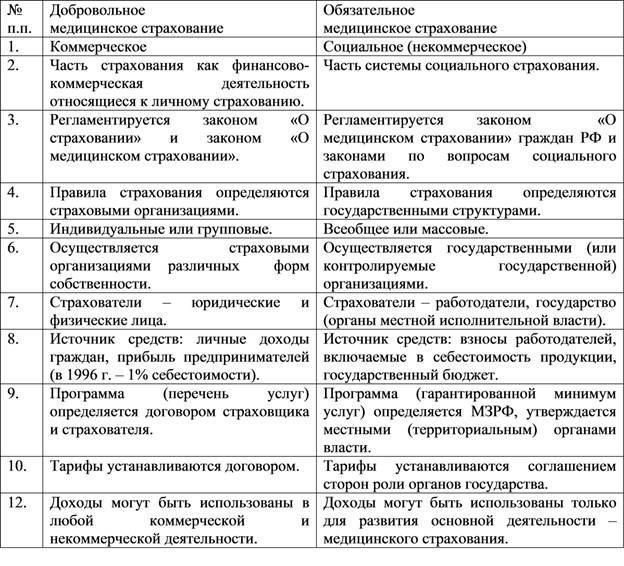
All of the above, in turn, is divided into compulsory and voluntary health insurance.
Compulsory insurance
OS is a prescription of state law for insurers, forcing them to make insurance payments. It applies to those objects and cases where the level of compensation for harm affects not only a specific person, but also a number of public interests. Separately, there is compulsory state insurance carried out at the expense of the state budget or other sources.
The main difference between a mandatory contract and voluntary insurance is that the first citizen cannot refuse. At the same time, he personally draws up only the policy of compulsory medical insurance and motor third-party liability insurance (if there is a car), all other insurance protection works automatically.
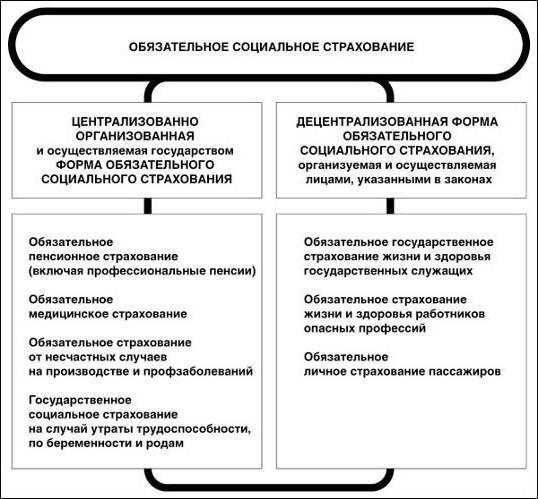
The provisions on compulsory insurance policies can be read in Art. 927 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to them, the insurer has the obligation to insure certain objects, and the insured is to pay the due payments. The law on voluntary and compulsory insurance provides:
- a list of objects that must be insured;
- insurance coverage rates;
- tariff rates, their differentiation;
- amount of responsibility;
- rights and obligations of two parties - the insured and the insurer;
- frequency of payments.
OS: types of insurance
Compulsory and voluntary insurance within themselves include a number of smaller varieties.
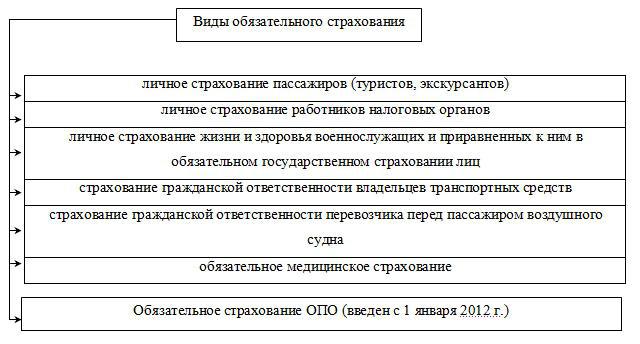
So, insurance dictated by law includes:
- Military personnel.
- Passengers
- SRO (self-regulatory organizations).
- OPO (hazardous production facilities)
- Auto civil.
- Responsibility of some specialists in the implementation of professional activities.
- Medical (compulsory and voluntary insurance).
- Bank deposits.
Principles of Compulsory Insurance
Compulsory insurance is characterized by five principles:
- Obligatory. It is dictated by the relevant legislative act.
- Continuous population coverage. For this, the insured are registered, certain deadlines for making insurance premiums are set.
- Payment Independence. If the insured person has not made the due payment, compulsory insurance does not cease to be valid. The insurance premium will be collected in court with interest for late payment.
- Perpetuity. The insurance period ends only with the death of the insured or his property.
- Fixed rate of insurance coverage. The cost of reimbursement is either an absolute value or some clear percentage of the sum insured.
Voluntary insurance
The second type of insurance is carried out exclusively on a voluntary basis. The law defines only general provisions for it, and the insurer sets the specific conditions. It should be noted that voluntariness here is the prerogative of the insured, because The broker cannot refuse to conclude an agreement with his client.
For DS (voluntary insurance) it is typical to present certain requirements that the policyholder must meet in order to receive a policy. The latter is always issued only for a certain period. You can extend the policy by concluding a second contract. Sometimes auto-renewal also works. Failure to pay the insurance premium during the indicated period leads to the termination of the contract on the DS.
Varieties of DS
Not all types of insurance contracts can be clearly divided. For example, social insurance is voluntary and compulsory, like medical insurance, one of its varieties. But specifically for the DS refers to the following:
- Life insurance - payment to relatives of the insured of certain amounts after his death.
- Pension - offers a citizen to accumulate certain amounts for his future pension.
- From accidents - disability, illness, injury, disability.
- Housing - apartments, rooms, private houses, cottages.
- Animals - typical for owners of expensive pets and livestock. In case of injury or illness of the pet, compensation is paid.
- Mortgage - protects paying a mortgage from unpleasant circumstances.
- CASCO - compensation in the event of any accident, theft, fire and other disaster that could happen to the car.
- VHI is medical insurance that partially or fully compensates for the cost of treatment.
Principles of DS
The principles of compulsory and voluntary insurance are common. DS characterizes:
- Volunteering. As we mentioned, it concerns only the insured and not the insurer.
- Selective coverage. Not all citizens consider it necessary to conclude a voluntary insurance contract.In addition, insurance companies themselves impose restrictions on policyholders - age, state of health, accident rate of property, etc.
- Urgency. The DS agreement always has a certain period of validity.
- Contribution Dependence. The insurance agreement is canceled if the policyholder has ceased to pay insurance premiums.
- Moving insurance coverage. The amount of the insured amount is established in the contract by the agreement of the insurer and the insured.
Compulsory and voluntary insurance, although they have something in common, have many fundamental differences. In addition, the same type of insurance can be both OS and DS.