All research results in laboratories can be divided into two groups - quantitative and qualitative.
In the case of qualitative studies, the patient receives only a definite answer “yes” or “no”, for example, determination of the Rh factor or a pregnancy test. However, conclusions in this type of analysis are made on the basis of a certain number of certain components.

Quantitative studies will indicate a specific number, for example, an analysis to determine the amount of sugar in the blood.
What is the referent value in analyzes?
When a patient comes to the hospital for the results of his tests, then in them, he sees certain figures opposite the name of each laboratory test. As a rule, the patient’s indicators are described there, and next to them are the intervals in which the values are the norm. These are the so-called reference values; they are indicated in the analyzes as a “from and to” interval.
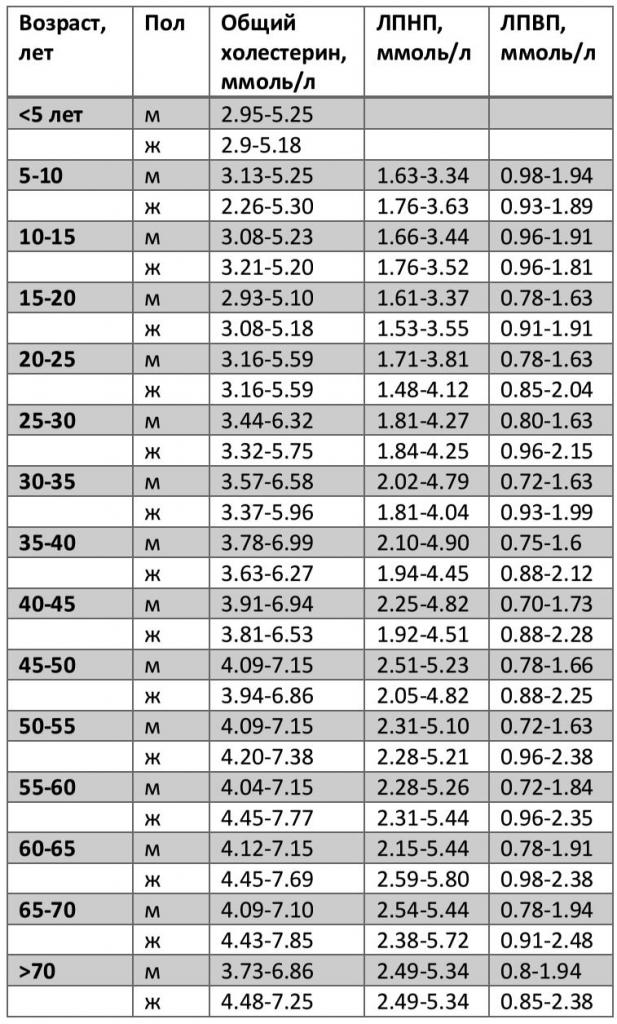
For different population groups, these indicators are different.
Factors on which norms in laboratory research depend
It is important to understand that for most examinations there is no single norm for all patients. The reference values vary depending on gender, age and other factors, sometimes you need to take into account the individual characteristics of the body. For example, in hormone tests in female patients, much is associated with physiological changes in the process of growing up the body. In addition, their standards are set in accordance with the day of the menstrual cycle.
If the analyzes revealed an increased content of alkaline phosphatase, then this is the norm for the child, since the body is in the process of bone formation, but for the adult it is a cause for excitement. In this case, further examination will be required to exclude pathologies such as metastases.
As for the patient’s gender, the rate of hemoglobin in the blood is higher for men than for women. This is due to the fact that in the male body for the production of testosterone requires a high oxygen content, in addition, their body does not undergo monthly blood loss, unlike the fairer sex.
In addition to the above factors, the result of some studies can also be affected by:
- the use of coffee, alcohol, dietary supplements, tobacco;
- stressful situations;
- diet features (vegetarianism, strict diets);
- physical activity on the eve of the tests, as well as intensive training in certain sports for many years (weightlifting, running);
- posture of the patient during the delivery of biomaterial.
How are acceptable intervals calculated?
You can definitely answer - by measuring and conducting research of a certain type in a large group of people. People of a certain age and gender are selected, always healthy (for example, women aged 30 to 40 years). After which they pass tests, based on the results of which the average value is calculated. Then, in order to obtain an interval of admissible values, a double quadratic deviation (statistical indicator) is added to and subtracted from the average value. This procedure is carried out for all population groups.
What to do if the test results are outside the acceptable range?
Do not panic if abnormalities are present in the analyzes - this does not always indicate any pathology or disease. The doctor may advise you to take the test again, as the results may vary from day to day, and some studies recommend conducting dynamically.

To determine the level of sugar in the blood, you can take a regular sugar test, which allows you to determine the content at this particular point in time. But the picture may be distorted if the patient on the eve ate a lot of sweets or, on the contrary, refrained from it for a long time, which does not correspond to his normal diet. There is an alternative to such an analysis - blood donation for glycosylated hemoglobin, which will determine the average blood sugar over the past three months.
If the results do not fall within the range of acceptable values, then the patient needs to consult an endocrinologist. In addition, the results that are the norm for most are not necessarily those for any patient. An experienced doctor must understand the physiological characteristics of his patient and make a conclusion about his state of health on the basis of this, including appointing additional examinations and consultations with specialists of a narrow profile if necessary.
HCG reference value in blood
If the patient suggests that she is pregnant, you can take a blood test for the hormone hCG (chronic human gonadotropin) and find out for sure. The production of the hormone occurs after implantation of the embryo into the uterus (approximately a week after fertilization). A pregnancy test responds specifically to this hormone, however, to get an accurate answer it is recommended to do it 2-3 weeks after conception.

The reference value of hCG during pregnancy differs in different periods of fetal development: from 25 (lower bound of normal) mU / ml in the first weeks to 200,000 mU / ml (upper bound) at 7-8 weeks, after which the hormone content decreases. In recent weeks, the hCG rate is about 30,000 mU / ml.
Chronic gonadotropin can in rare cases be present in the body of a man or a non-pregnant woman, which indicates certain health problems.