The theory of state and law includes such an extensive category as the legal system. For this section of this discipline is characterized by a combination of historical, legal and social phenomena that form it.
The study of the topic is of interest in the analysis of the compositions, forms and patterns of interaction of individual legal elements, the historical background of their formation, as well as social factors.
Any system containing a set of legal aspects of society is based on historical background, and therefore the consideration of this topic includes two large sections: legal and historical-social.

The concept of the legal structure of society
The legal system of society is a concrete historical category and is defined by a stable single set of legal institutions that form a kind of vector of social, economic, political and spiritual life of a particular society, based on historical genesis.
The legal system is also rightly called "legal reality", since, in fact, the first content of the first is the fundamental legal basis. Any national legal system, the structure of which forms a set of norms and rules of behavior in force in this society, is one of the most significant criteria that determine its development.
The concept of legal structure functions
The functions of the legal system - the impact on society, covering the entire totality of public life and expressed in the form of interaction of legal elements in this regard.
In the most general sense, they can be divided into 2 groups: socio-economic and political. It is important that the structure of the legal system is organized in accordance with a number of similar goals and objectives, respectively, the functions and structure depend on each other.

Socio-economic functions
The social and economic life of society is closely linked to the prevailing legal ideology in it, which the legal system contains. Legal institutions are created and exist within the framework of the same system, and their application is justified by its stability in time and space. It is the right-forming and ideological functions that are the most significant.
At the same time, in addition to ideological correlation and legal formation, socio-economic functions are specified:
- Identification of priority social and economic values.
- Formation of an approach to social separation.
- Modeling the behavior of subjects of social and economic life.
- Coordination of interests of persons.
Political Functions
First of all, with respect to the political life of society, the ideological function is more pronounced. The historical interaction of the legal system and political power is a symbiotic phenomenon: the resources of political power are aimed at protecting and ensuring the functioning of the legal system, while the legitimacy of power is determined by the same legal system.
For the political functioning of society, the following right functions must be performed:
- The goal setting of social development.
- The legitimization of political power.
- Organization of a system of power in society.
- Identification of the state, determination of sovereignty, national ideology.
The structure of the legal system of society
The use of law is impossible without correlation of specific categories of social relations with the corresponding legal families, institutions and sectors.With the concretization of social relations, legal differentiation arises and intensifies. The rule applies: the more voluminous one or another category of public life, the wider the area of law affecting it.
Based on this fact, the structure of the legal system is built, the scheme of which is formed on the basis of the categorization and relevance of the relevant areas of public life. The following diagram reveals the structure of the legal system.
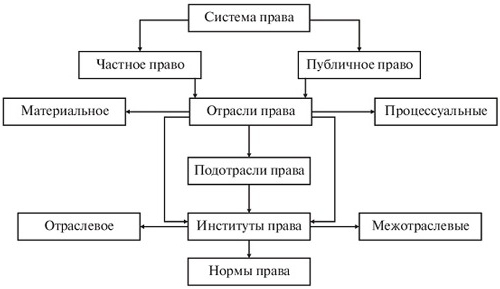
Also, the structure of the legal system is relations relating to legal practice, which directly relies on the system of existing law, and legal ideology.
Legal ideology
An integral element of the existence of the legal system of any society is the legal ideology, which is embedded in it in the course of historical and social development. The legal ideology contains the foundations that characterize the legal relationship in society, as well as distinguish it from other ideologies.
Historical concretization allows us to identify the most significant legal families today:
- Romano-Germanic legal family - European countries, Russia, Latin America.
- Anglo-Saxon Legal Family - England, United States, Australia.
- Religious legal families are states with high adherence to religious canons.
- Socialist legal family - USSR, China, Cuba.
Legal culture
The existence of law in society does not yet make it fully legal. For the normal promotion of society and law, a legal culture is necessary. Its bearer is society, it is it that expresses the attitude to law and is the main stimulus to its development.
It is generally accepted that the legal culture is expressed in the legal consciousness of people, that is, their awareness of the current norms and rules of behavior in the form of laws. The structure of the legal system of any society includes this element as an additional factor affecting its existence.

The experience of the interaction of law and society is possible only in those legal systems that are based on democratic postulates, since it is in this case that a reflection of public consciousness and feedback from the law arise. A society that meets these requirements is called civil.
The level of legal culture is also customarily attributed to one of the significant parameters that determine the development of a particular society. The higher the level of legal culture, the more laws are updated according to real social requirements, which means that the formal amount of freedom of citizens increases.
The relationship of the state and the legal system
Undoubtedly, the state is an important participant acting as an intermediary between society and the legal system. As mentioned above, the functions of the legal system include the organization and legitimization of the public administration system, which means that it is through the legal system that the grounds for exercising power are formed.
The state unites people, thereby making them citizens. At the same time, the specificity of society is determined, which consists in its historical, cultural, social and other well-established rules of life. The provision that the state acts as the guarantor of the fact that a legal system operates in its territory is fair. The concept, structure, functions and other features are formed on the basis of the historical experience of a state and form a national legal system.

National legal systems
As stated above, there is a great relationship between states and legal systems. The latter act as historical formalized experience, that is, they are a list of norms and rules of behavior acceptable by society in the territory of a given country.
National legal systems are diverse, there are many of them - up to 200 species characteristic of a particular state.Moreover, each individual system also has its own structure of the legal system, which distinguishes it from the rest.

Also, among other things, it is worth noting that among these systems there are synthetic and natural, the difference between which is based on the premises of their formation. So, synthetic systems are formed mainly by transferring legal knowledge from other states, and natural ones - by updating the legal sphere under the usual historical and social traditions.
The structure of the legal system of modern states also forms a system of functions and goals. The fact is that as a result of the genesis of national legal systems, some priorities are highlighted, which, incidentally, are specific attributes of a particular national legal system. The following examples can be attributed to the priorities identified:
- Orientation of the American, English, Canadian and other national legal systems to the judiciary. Through the use of judicial experience, legislation is expanding, and court decisions are based on an existing system case law.
- In the states of the Islamic world, the system of divine law has a number of priorities over formal law and often acts as a source of justice.
- In European countries with a socially oriented economy, for example, in Finland, law is represented primarily by socially significant provisions, and political and economic aspects are in the background.
- In Russia and a number of CIS countries, law equally exists in private and public forms, no priority is recognized, and the legislative branch acts as the main source of laws.
Russian national legal system
The Russian legal system is relatively new, its age does not exceed 30 years. And although the novelty of the Russian legal system allows us to talk about the incompleteness of the process of forming the final legal system, it can be called stand out and self-sufficient.
The structure of the Russian legal system is based on 3 fundamental principles:
- Identity and socio-historical determinism.
- The combination of the national system of law with world law adopted by the international community.
- Actualization of the legal system regarding current social, economic, political and spiritual conditions of life.
Based on the above provisions, it can be judged that the Russian system of law is complete and comprehensive. On the one hand, it complies with internationally accepted legal norms, including the UN Conventions, as well as interstate agreements acting as sources of law. On the other hand, the structure of the legal system responds to social changes taking place in the Russian Federation and changes under the influence of the legislative branch.
The structure of the legal system of the Russian Federation consists of many regulatory documents, which include: the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal and constitutional-federal laws, decrees and decrees of the Government, orders of the President, 19 codes, local laws of regions and municipalities, internal charters and rules of state and municipal institutions.

Description of modern legal systems
The modern picture of the world in relation to legal systems is quite diverse. In modernity, 4 legal families are distinguished, each of which includes up to 50 national legal systems, which are formed due to a narrower specificity compared to legal families.
Due to the division into such a large number of legal systems, the problem of the gradation of legal systems of different states, and, as a consequence, the problems of social and economic assistance, remains relevant.Although, in order to remove legal barriers to cooperation, the idea of international legislation is implemented, which includes provisions in force in all states.
However, on the other hand, as the structure of the legal system of modern states shows, modern national legal systems combine historical features and actual problems of society. This allows you to create the most effective legal system.
