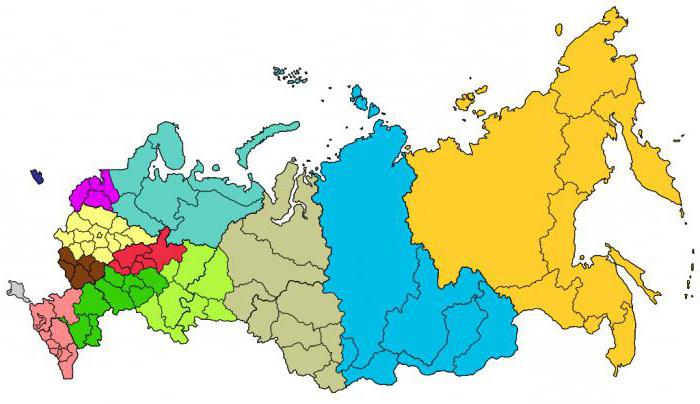
The Russian Federation is a huge state with different levels of economic development and area specialization. As a result, historical zoning of the territory of Russia took place. The economic regions of the Russian Federation are represented by 12 entities that differ in their specialization of development, national characteristics and administrative structure.
Basics of Economic Zoning
The division of the whole territory into individual areas is carried out with the aim of division of labor and the convenience of communication between them. Thus, the subjects of the Russian Federation by economic regions are divided not just like that, but on the basis of certain economic or other factors that can improve the economic situation and specialize individual regions for specific industries.
Zoning Principles
Currently, there are three main principles of zoning of the territory of Russia:
1. Economic. This division specializes individual parts of the state according to the principles National economy. Based on economic considerations, this method leads to lower labor costs, as well as other means of production. At the same time, production within a given economic region should be more efficient than outside it, and for this purpose, specialization of economic regions of the Russian Federation is carried out.
2.National. The borders of the economic regions of the Russian Federation are outlined on the basis of national composition and historically established forms of management.
3. Administrative. This principle determines the unity of the territorial structure of the state and economic zoning.
The above principles of zoning are today fundamental in the theory and practice of economic science in the field of zoning.

Northern
The main economic regions of the Russian Federation are of great importance not only for the state, but also for the entire CIS and part of Europe. In this regard, the Northern region is indicative. It is the largest in area, at the same time, the natural conditions here are very difficult, and in some places even extreme. The area is rich in resources such as oil, coal, gas, metals, rich in forest and water resources. Forestry engineering, shipbuilding, and fishing industry are developed. The more developed center of the region is the Vologda region with its dairy cattle and, therefore, cheese production and oils. Of great importance are the ports of Arkhangelsk and Murmansk. It should be noted that the region is sparsely populated and most of the population is concentrated in large cities.
Central
The oldest district of the Russian Federation. This is where our statehood came from. Already in the 19th century, it was distinguished by a high degree of development of the textile industry. A high degree of population and at the same time a small amount of natural resources forced the development of "non-resource" production here. The central economic region of the Russian Federation is a place for the development of general engineering, chemical and light industry. Because it is a “metropolitan region”, it is here that the majority of new discoveries and inventions appear on the territory of the country and only then spread to other regions. Moscow is important as a central transport hub across the entire continent and especially for the CIS and Eastern and Central Europe.
Volgo-Vyatka
This area can be called transitional from the center to the Urals and the Volga region. The area is poor in mineral resources, but rich in forest and water resources.It has developed engineering and machine tools, automotive and electrical engineering. The chemical industry mainly plays the role of processing the Volga-Ural oil and wood chemistry. The basis of industrial development is the forest industry, where both mining and processing of timber with its full complex are concentrated. Here is the third center of the Russian Federation in industrial potential - Nizhny Novgorod.
Northwestern
The economic regions of the Russian Federation are highly dependent on each other - some from the raw materials of neighboring regions, others from its processing, and others from transportation. St. Petersburg, located in the Northwest Economic Region, plays a huge role as a transport hub connecting Russia with other states. It should be noted that the agglomeration of the Northern capital is the basis of economic potential. Here microbiology, the chemical industry, metallurgy, and light industry are developing. In this area, shipbuilding of a wide profile is developed from passenger ships to nuclear icebreakers and tankers, mechanical engineering, carriage building, tractor manufacturing, etc. In agriculture, the intra-regional orientation in dairy and beef cattle breeding is pronounced.

Central Black Earth
Industrial-agrarian region. The main forms of economic development are engineering, machine tools, metallurgy, instrument making. There is a full range of agricultural production, both agricultural and livestock. In this area is located one of the largest iron ore basins in the world - KMA (Kursk Magnetic Anomaly).
Volga region
The economic regions of the Russian Federation are heterogeneous, both in terms of economic potential and territory. The Volga region has a distinctive feature - a significant elongation from north to south and concentration in the Volga valley. As a result, while timber industry is developing in the north, the south of the region is occupied by semi-deserts. The Volga region is one of the most developed economic regions of Russia - machine building (Togliatti, Ulyanovsk, Naberezhnye Chelny), chemical industry, machine tool building, and equipment manufacturing. A large accumulation of resources, such as oil, gas, chemical raw materials, agro-climatic resources, table salt. There is access to the Caspian along the Volga River, and from there to the North Caucasus Economic Region.

North Caucasian
The district is concentrated on a variety of natural resources such as gas, oil, coal, non-ferrous metals, raw materials for building materials and industry. In industry, the predominance of mining and processing industries is observed, mechanical engineering is inferior in this regard, although there are also large centers such as Rostov-on-Don, Taganrog, Pyatigorsk. Commodity agriculture is strongly developed - rice, viticulture, tobacco growing, vegetable growing, etc. The most developed region of Russia in terms of resort tourism.
Ural
Some economic regions of the Russian Federation played a huge historical role for the formation of the country's economy. In this regard, the Ural region is one of those. This region is located at the junction of the Center and Siberia, Western and Eastern economic zones. The area is resource, there are deposits of iron ore, non-ferrous metals, salt, oil, gas, coal, the north is rich in forest. Heavy engineering, non-ferrous metallurgy, timber and chemical industries are developed.

Eastern Economic Zone
The composition of the economic regions of the Russian Federation of the East represents 3 regions: West Siberian, East Siberian and Far Eastern. The common features of these areas include a vast territory with a small population; the severity of natural conditions that create difficulties in development; greater importance of water and air transport in the south - railway; contrast of the territory of production and its “shifting” to the south; exorbitant resource potential, while its use today is at a relatively low level.
West Siberian region It is the largest resource center, especially in terms of fuel resources. According to the specialization of the economy, the whole region can be divided into three component parts: the “oil center”, “the coal-engineering and grain south”, and the “gas north”.
East Siberian region. The basis of economic development is the generation of electricity through hydroelectric power stations and thermal enterprises operating on cheap coal. The region is rich in graphite, wood, mica, asbestos. The so-called "Underutilization" of resources in relation to their use.
Far Eastern region. The leading sectors of economic development here is mining, it should be emphasized the extraction of diamonds in Yakutia and gold; metallurgy; engineering; fishing and forestry industries; Here are located the largest ports of the Russian Federation in the Pacific Ocean - Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Nakhodka, Vladivostok.
Economic Regions, Federal district of the Russian Federation in the Eastern Economic Zone they have a huge territory, with a low population, this is probably the reason for the low level of use of the richest resources of the Trans-Urals.

Kaliningrad region
As a result of its remoteness from other regions of the Russian Federation, it represents a separate business unit. The economy of this region is directly connected with the sea - Kaliningrad is a large commercial and industrial center of Russia. In addition to trade, reserves of natural gas, oil, rock salt were discovered here. Amber, brown coal, building materials, peat are mined. The basis of the market is the extraction and processing of fish, amber, pulp and paper, machine-building industry.

The economic regions of the Russian Federation, in addition to 11 main and 1 regions, consist of two self-governing cities - St. Petersburg and Moscow. The significance of each economic region for the overall management of the country is very great. Each region is specialized either in the extraction or processing of raw materials. However, today there are still significant problems in terms of the level and quality of use of natural resources of individual regions of the country.









