Demand and supply always change under the influence of market conditions. Elastic coefficients reflect the extent to which consumers and manufacturers will respond to a new situation. Its values vary, as some products are more important to people than others. Necessary goods are less sensitive to price changes, since it is difficult to do without them. Vendors often speculate on this, as they are well aware of their benefits.

General information
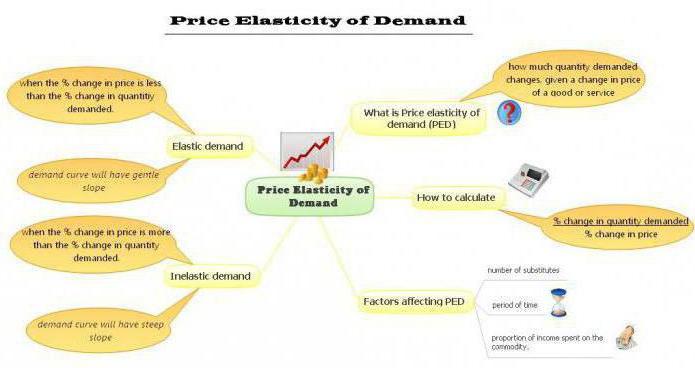
The elasticity coefficients of the goods are high if small changes in the price lead to a significant jump in demand or supply. Typically, such products are available on the market, and people do not consider them mandatory in everyday life. On the other hand, low elasticity coefficients indicate that a significant increase in prices will stimulate only a small part of consumers to abandon these products. This is due to the fact that they are necessary for the daily life of people.
Elasticity coefficient: formula
The calculation of this indicator is quite simple to implement. The ratio of changes in quantity and price is a coefficient of elasticity. The formula is as follows:
Ke= ∆Q / ∆P,
where ke Is the coefficient of elasticity of the product, and ∆Q and ∆P are the changes in the quantity of demand of the purchased (produced) and prices, respectively.
The higher this indicator, the more sensitive the product in question is to price changes.
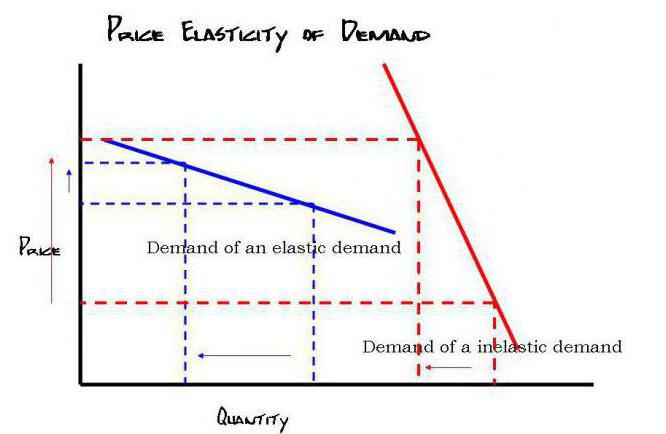
Demand elasticity coefficient
There are three main factors that influence the change in the quantity of purchased goods in the market:
- Availability of substitutes.
- Consumer income.
- The time that they are willing to do without this product.
Thus, the coefficient of elasticity is distinguished by price and cross. The first is used to assess the sensitivity of volumes of purchased goods to changes in their market value. More precisely, this indicator provides us with information on how much demand will fall as a result of an increase in prices by one percent.
Cross elasticity indicates how a change in the price of one product affects the consumption of another. It is calculated as the ratio of the percentage increase in the market value of the first to the decrease in the purchased volume of the second product. If the resulting number is greater than zero, then the goods can be called substitutes. For example, products from different manufacturers. The increase in the price of one of them leads to the fact that consumers switch to another without significant changes in their lifestyle. If the coefficient of elasticity of demand is a negative number, then the products are called complementary. For example, a car and gasoline.
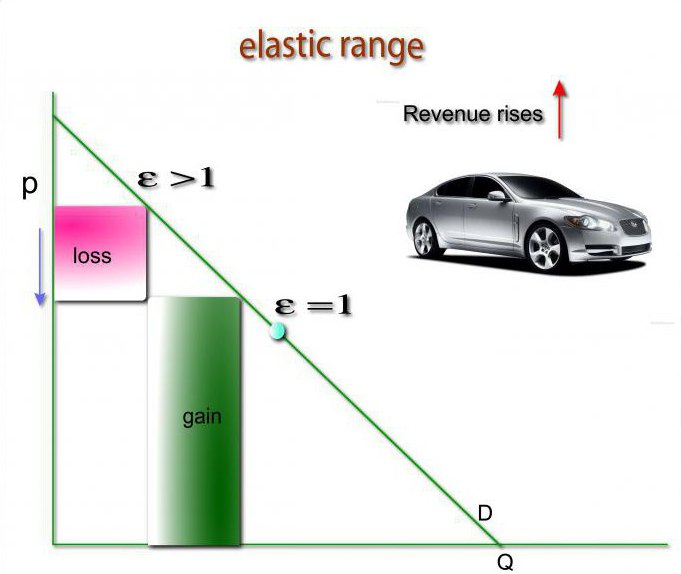
Types of demand curve
In economics, there is a graphic image called "Marshall Scissors" that show the establishment equilibrium price On the market. In general, the demand curve has a negative slope. This means that increasing the price leads to fewer buyers willing to purchase the product in question. But this does not always happen. A common option is where the curve has a positive slope. These are Giffen or Veblen products, the price increase of which only stimulates demand. If the coefficient of elasticity is low, then the angle that the curve forms with the abscissa axis will be larger. With unity, the graph would look like a vertical line.
Change offer
The elasticity factors of demand depend on the prices of the product itself and its substitutes.As for the proposal, there are also two indicators. The first is price elasticity, the second is production elasticity. Both serve to characterize the behavior of the parties in the market. Price elasticity of supply measures how the volume of a commodity changes under the influence of a new equilibrium. As in the case of demand, this indicator covers the degree of reaction of manufacturers to the establishment of various market values. If it is zero, then the goods are considered completely inelastic. This means that manufacturers will continue to produce it at any price.
Production elasticity is used in economic theory in order to show the ratio of factors and output. This formula uses such a concept as the marginal rate of substitution.

Other ways to apply the concept
Elasticity is one of the basic concepts of the economy. Without his understanding, it is difficult to understand the essence of many theories. In particular, the concept of elasticity is fundamental in the theory of market supply and demand. However, it is still used in a number of sections of the economy:
- Calculation of the effect of changes in prices on the income of firms.
- Analysis of the effectiveness of the tax burden and other government policies.
- Assessment of industry stability and future consumption characteristics based on income elasticity of demand.
- Making investment decisions.
- Calculation of the effect of international trade (Prebisch-Singer thesis, Marshall-Lerner condition).
- Analysis of the characteristics of consumption and savings (constant income hypothesis).
- Checking the effectiveness of advertising of certain groups of products.
In some cases, an indicator of semi-elasticity is used. This indicator is calculated as the ratio of changes in kind.
findings
In economics, elasticity is used to evaluate the sensitivity of indicators to changes in others. Its calculation provides the answer to the following questions:
- If I lower the price of the product, how much more can I sell?
- How will the increase in market value affect the acquisition of my products?
- If the equilibrium price of a product decreases, how will the supplier companies react to this?
Elastic variables respond more than simply proportionally to changes in the value of other indicators. Most often, this concept is used to analyze the market, that is, supply and demand. It is key to economic science as a whole and plays an important role in many theories.
