Almost every multinational company today is such an organization, which at the moment is the main and driving force of the process of the so-called internationalization of the economy in the world, and this applies both to regionalization and globalization. This suggests that the dominance in the modern world economy of several hundred of the largest transnational corporations determines the basic proportions of world sales and production.
What it is?
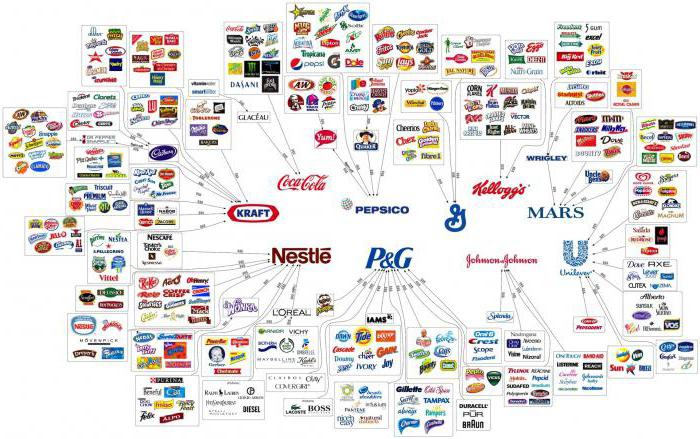
The term "multinational company" itself appeared as a compromise that was reached in the process of negotiating the mandate of the UN activities in the issue of setting the boundaries of various international monopolies in any developing countries. In particular, in 1974, they tried to terminologically separate their own multinational companies from specific Western companies, the formal features of which were quite similar to companies in developing countries, but had two rather important distinguishing features:
- Source of origin of capital. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the origin of capital was within the same country and, accordingly, the prefix “trans” could very well reflect the main line of operations of a given company in relation to a certain headquarters.
- The scale of the technological and financial base, as well as the possibility of legal, political or any other cover for the operations. Subsequently, such political distancing began to fade over time, as a result of which the international monopolies of various countries constantly began to be called "transnational."
By the definition of the United Nations itself, a multinational company is an internationally operating company that operates in two or more countries, and at the same time manages these units from a certain center (or several).
At the same time, it is worth noting the fact that UN experts refer to various international companies operating in any sales or production activity, and the main parameter of this definition is that their activity is carried out outside the boundaries of a certain state. However, in reality, such a definition can hardly be called exhaustive, since in this case the most important features of this modern international subject, which could distinguish it from other subjects of the international economic activity and the international economy, are not taken into account. For this reason, before you understand what a multinational company is, it is worth deciding on the main features of such organizations.
Corporatism
Such firms are an association of a private parent company, as well as branches and capital located in the home country, which belong to it, but are actually located in other countries.
Multinational companies, the list of which is supplemented by the most influential organizations, can work in any number of countries, but, depending on the scale of their activities, they begin to influence the world economy in different ways.
The division of such a company is a relatively independent enterprise that operates in the economy of this country, and at the same time takes part in strengthening its external economic relations to ensure goals and directions in accordance with the interests of the parent company. Moreover, such units, depending on their legal status, may act as branches, associations or subsidiaries.
Branch

It is worth noting that the branch that multinational companies have is unique in this chain.The list of such divisions includes various organizations for the creation of which the parent company allocates its own funds, and the national businessman, in turn, is engaged in the creation of the company and then registers it as a national legal entity, thereby gaining wide opportunities for work inside this country, as well as participation in its foreign economic relations.
All kinds of managerial, financial and many other relations of this unit with the parent company are more or less transparent, but due to the fact that this company has a national status, the parent company has a lot of advantages.
What are these benefits?

It is worth noting several positive aspects from doing such work:
- Excellent knowledge of local economic conditions, as well as the current legislation of the country and the practice of government influence on the work of private entrepreneurs.
- Personal ties of various national leaders, as well as other responsible employees, allow them to fit their activities into the framework and directions of the current state policy.
Ultimately, in the economy of the host country, this branch, as a foreign national, begins to work as a national economic entity, which allows it to significantly reduce both political and commercial risks.
In the same way, the strategy for the location of branches works, which ensures their closest approximation to labor, technological, natural, financial and other resources, and also allows the use of advanced branch management technologies that provide greater independence in the field of marketing. It also provides concentration and centralization of financial flows and cash management. For example, quite often multinational companies in the world prefer to use the so-called divisional branch management scheme. Units may operate as branches, associations or subsidiaries, depending on their legal status.
Regardless of how the branch operates, which is managed by multinational companies (examples above), it is always an immanent part of the corporation that performs the assigned functions in its country. Moreover, the creation of such units can only be carried out in the order established by the current legislation of the host country.
The line of the parent company also defines the watershed between the branches owned by multinational companies. Examples of the work of such units show that this determines the general degree of legal independence of the branch, as well as the rigidity of control over its work by the main headquarters.
Subsidiary company

In this case, a legal entity having its own balance is considered. The creation of such organizations provides an opportunity to ensure the management of this unit by the parent company, and legally it cannot be responsible for the activities of a subsidiary beyond the nominal price of the controlling stake that it contains. Between a subsidiary and a parent company, any transactions that meet the basic interests of the latter may be concluded. All profits of the subsidiary can be artificially concentrated in the parent company, even to the extent that such a unit will be partial or even complete bankrupt.
Thus, a global or Russian multinational company can realize the possibilities of a capital participation system, and it can be multi-stage, which allows the parent company, which is at the top of the whole pyramid, to provide control over huge funds.In the overwhelming majority of cases, the parent organization retains more than 50% of the shares or units of this branch, as a result of which it has the right (which is most often practiced) to ensure full control over its activities, that is, to dismiss or appoint the overwhelming majority of members of the bodies management and administration.
In relation to their branches, global multinational companies can also use a more significant participation system compared to subsidiaries in order to have centralized control over the entire work of such an organization. In this case, various branches of the parent company begin to be created in the host country, or the subsidiaries that are currently operating there begin to transform into full-fledged branches. In particular, this situation occurred with subsidiaries of various US TNCs after the Second World War ended.
Among the distinguishing features of such a branch, it is worth highlighting that all its shares belong to the parent company, which deprives him of the right of a legal entity, as well as any economic independence. It is in this way that the activity of multinational companies is most often built.
Associative companies
The third version of the units is the so-called associates. In this case, multinational companies and corporations have only 10-50% of the total number of shares and units, which makes control over their work somewhat limited compared to other branches.
Thus, the corporate system of such companies is based on the participation system, the main meaning of which is that the joint-stock company has securities of other branches, on the basis of which a multi-stage dependence of a large number of other organizations on the parent is ensured. Due to this, multinational companies (TNCs) can achieve the interweaving of capital in corporations and subsequently pump profits from their branches.
Domestic market

The presence of a special international domestic market within TNCOs, which appears as a result of various special economic ties between branches and the parent organization, is very important. The regulation of this market is carried out by the leaders of the parent company and, accordingly, of all its branches in a variety of ways, including barter, transfer prices, planning and many others. As a result of this, the overwhelming majority of financial, trade, and formally international operations become internal firms.
Mono-ethnicity
Another distinguishing feature of TNCs is that both small and large multinational companies have a predominance of capital in a particular home country. It is on this basis that in the specialized literature and on practical examples, the definition that TNCs belong to a certain country is preserved. In the vast majority of cases, a controlling stake is in the hands of the parent company, which is based in the original country.
Unlike transnational corporations, multinationals can have a multinational core, that is, a controlling stake belongs to several states at once.
Monopoly

In this case, we are talking about the monopoly and international nature of the company. This feature determines the system, as well as the way they act in the global economy, as well as the availability of opportunities to turn MEOs and MRIs in areas that provide the opportunity to secure a leading position in major markets, and thereby ultimately begin to make a profit on all advanced capital.
TNCs and their work in the international market

The world community is very carefully watching how international multinational companies are strengthened.The thing is that TNCs can not only positively but also negatively affect the economy of the host countries. World practice includes a huge number of examples of the fact that if certain things are beneficial for transnational corporations, then this will not necessarily mean that they are beneficial for the national economy of the host and exporting countries. However, the power that any large multinational company has, the types of its activities and available tools make it possible to completely ignore such discrepancies. Thus, we can say that today, modern TNCs are practically uncontrollable, which is a rather serious problem, which they have been trying to solve for more than 30 years.
Already in 1972, the UN Center first appeared, which was exclusively engaged in work on transnational corporations. The main goal of this unit was to study the activities of multinational companies, as well as how they affect the global and national economies, as a result of which a fairly large amount of information was published about the leading TNCs and, thus, the most significant trends in their development were identified.
Ultimately, after such observations, a conclusion emerged in which the tremendous power of TNCs was recognized, as a result of which the world community has extremely limited opportunities to influence them. In particular, the special report of the UN Economic and Social Council includes a record that the power that is concentrated in the hands of transnational corporations, as well as the actual or potential use of this power, can change demand and significantly change values, including the ability to influence people's lives and the conduct of policies of various governments. It is for this reason that many began to worry about their role in the modern world.
With the beginning of decolonization, the UN, as well as other international companies, began to look for new ways of how to achieve a new international economic order so that those countries that were free from colonial oppression and began to develop could do this without any restrictions. At the same time, the ILO, UN, UNESCO and a number of other international organizations ultimately came to the conclusion that for the normal development of third world countries additional external assistance was required, as a result of which it was necessary to find a compromise between the introduction of foreign capital (especially in the form of TNCs) and developing countries.
In regulating the work of multinational corporations in developed countries of a market economy, the “Charter of Duties and Economic Rights of States”, the creation of which was thought in 1972, was to play a major role. In accordance with the second article of this charter, each state had the right:
- Ensure control and regulation of foreign investment within the boundaries of national jurisdiction in accordance with its laws and regulations. In accordance with their priorities and national goals, no countries could be compelled to receive any benefits from foreign investment.
- Fully control and regulate the work of transnational corporations within the boundaries of accessible national jurisdiction, and at the same time take measures to ensure that such activities can not contradict its norms, laws and regulations, and also fully comply with the social and economic policy of the state. Transnational corporations could not in any way interfere in any internal affairs of the host countries.
However, at the initiative of the United States, the role of this charter gradually decreased, and in 1993 the UN Center for TNCs ceased to work, which turned into another department, and the host countries agreed to weaken control over the activities of such corporations, as well as create more favorable conditions FDI admission.
