The country's economy is a “dark forest” that is difficult for an ordinary person to understand. People usually have a general idea about it, not wanting to go into details. It is not easy for them to figure out what the shadow economy is. Similar acts in science have a lot of definitions, their functions, factors, forms, etc.
Light on the shadow
What is a shadow economy? It is worth noting that this is, first of all, the totality of some manipulations in business activities that were not registered by officially authorized departments. In fact, this is a process of illegal and unlawful events. It is known that the shadow economy includes three segments: informal, criminal and fictitious.
The functioning of this type of activity usually occurs due to government intervention. Then the size and dynamics are already determined by the number of reforms carried out by the state. For example, the shadow economy directly depends on taxation, the public benefit that the power provides, and, of course, on the stability of the economy as a whole.
Signs of Violations
It is clear that the scale of the shadow economy can be completely different. It all depends on the participants in this process, as well as on transactions and other actions. Yet the signs almost always remain the same. If a state object evades and refuses to fix a transaction, an enterprise by an official institution, or if it intentionally distorts the conditions for concluding and fulfilling this agreement, it can be confidently asserted that it is involved in the shadow economy.
Segments
So, we have already mentioned that three segments can be attributed to the shadow economy: informal, criminal, and fictitious. Now we analyze them in more detail. The first type includes the most legal type - the “gray market”. So, it can be attributed to a set of actions, the dimensions of which are hidden by the owners. An example is home teaching, employment without registration, rental of apartments, houses, etc. In principle, such actions are permissible economic operations.
The next segment should be attributed to the “black market”. The informal economy is prohibited by law in almost every country in the world. It may include drug trafficking, prostitution, racketeering, smuggling and more.

The latter is a fictitious economy. This includes bribery, individual privileges, benefits and similar types of activity, which are formed on the basis of corruption.
There is another, less official, segment - the “white-collar economy”. This type is perhaps the most common among those who allegedly conduct an honest business. So, such illegal activity implies that honest “white” workers create conditions in which the income received is distributed secretly. Usually the same white-collar workers, department heads, etc. direct this process.
Characteristics of white-collar workers
This economy has its own characteristics. It is characterized by the following factors:
- Persons who participate in such operations are representatives of a managerial position with influence in the business community and in the management sphere.
- At first glance, all actions have a legal basis, managed by economists and managers.
- Theoretically, this segment of the shadow economy is a crime, for the commission of which they often use illegal methods and official position.
- Typically, such violations occur with good technological equipment.
History reference
Of course, the shadow economy did not appear yesterday. In developed countries, it amounted to 12% of GDP, transition economies had 23%, and developing countries could boast of 39%. In the USSR, back in the early 70s of the XX century, the share of the shadow economy was only 3-4% of GDP. Most likely, this is due to the regime of the state, since similar indicators were observed under totalitarianism. Then came the crisis. And the indicators increased 3-4 times.
Russia during its development by the end of the century had indicators of 27%. A few years later, the proportion began to decline, but the fight against the shadow economy did not stop. Now the main problem is the vagueness of the boundary line between official and illegal business. This is due to the fact that leading companies operate in two directions: legal and unofficial.
What is the reason?
At first, we briefly examined the causes of the shadow economy. Now it’s worth studying them closer. The growth and functioning of the “forbidden fruit” depends directly on the state, or rather, on its intervention. So, if a country begins to regulate various areas of activity to a different extent, then problems arise with the economy. Thus, the size of taxation and the effectiveness of this administration will significantly affect the growth dynamics of the shadow economy.
Also, one must not forget about the scale of bribery and organized atrocities, which affects the "shadow" business. Those who are going to organize their business also resort to closed activities. This is because the entire bureaucratic mechanism is burdened and full of corruption. Therefore, avoiding going into the “shadow” is impossible. A striking example is that already at the end of the last century, in order to organize their business in Russia, it was necessary to turn to 54 organizations. As a parallel: in Finland everything could be solved thanks to 5 instances.
Everyone knows that when forming a business it is very important to form the initial capital. So, the shadow economy in Russia of the 90s made it possible to do this with minimal expenses, because officially the entrepreneur should have paid crazy taxes.

The crisis has also become the main reason for the development of informal financing. When the national economy suffers a “depression”, the number of unemployed increases in the country, and the standard of living of the middle classes drops sharply. Those who have suffered from the crisis are trying to recover with the help of small businesses. This, in turn, leads again to bureaucratic problems and transaction costs. So, small businessmen are forced to participate in shadow relationships or unofficially conduct their business.
Functions
It is worth saying that the shadow economy is a rather controversial process in politics. Its functions could be either stabilizing for finances or destabilizing. Such a classification refers only to the “gray market”, since other options for shadow relations are illegal.
So, the stabilizing function acts effectively on the quality of the goods. This is due to increased competitiveness. There is also a need for more staff. Thus, the informal economy works as a social stabilizer, smoothes the line of income inequality and eliminates the social tension of society.
The second side of this coin can harm the state and its society. This is due to the criminalization of economic activity. It is worth remembering that the refusal of taxation leads to the destruction of the state budget. This affects not only the country's economy, but also other areas.
Methodology
It is worth noting that the methods of the shadow economy can determine the extent of its functioning and distribution. It is worth remembering that, nevertheless, the very concept of such relations depends on the country's policy. And if in the "gray market" you can find at least some positive aspects, fraud can only lead to damage to the state and its society. Therefore, the fight against the shadow economy is so important. But to begin with, one must still determine the extent of the "catastrophe" that has been raging.

So, the first method is monetarist. It is associated with a certain assumption, in which it can be argued that cash is used for payment, and specifically large bills. Analyzing the situation on the part of this method, an increase in the specific gravity of cash should be noted. And, of course, an increase in the number of bills of high denomination. This method was already used earlier, in the early 90s, in Russia. Then the state carried out a reform, thanks to which it was able to withdraw illegal capital by exchanging a high denomination of banknotes.
The next method comes from Italy - Palermo. It is quite simple and easy to check. In order to determine the “shadow” participant, you can analyze the ratio of his declared income, the volume of purchased goods and services throughout the country. In the late 90s, Russia sought to monitor and control all major transactions, especially those related to real estate.
The third method is employment analysis. If the country has a high unemployment rate, it can be assumed that these individuals are involved in shadow relationships. The latter method can be attributed to technological factors. This option of studying the shadow economy depends on the dynamics of energy consumption and data on the industrial enterprise of goods and services. An example of this analysis is the situation that occurred in the 90s. So, the number of registered goods and services fell by 40%, but the use of electricity - only by 25%. Thus, this process showed the existence of shadow relationships in Russia.
Subjects
It is worth noting that theoretically in economic science there is no definite concept or classification for the subjects of shadow relations. Nevertheless, in practice, three groups can be distinguished.

The first is those who belong to the black market. It usually includes drug dealers, hired killers, pimps and other criminals. It also includes those who belong to state power, but practice corruption, murder, etc. The second group “hid” small businessmen. These are those entrepreneurs who know what the shadow economy is, and they hunt in this sector. The third “criminals” were people who are hired and work in various fields, whether physical or mental. Typically, these entities have illegal income.
Factors
The problems of the shadow economy are associated with the development of factors that contribute to its development. The first is economic. To a greater extent, it refers to tax increases, the crisis of the financial system, the fall of the national economy, problems with privatization, and the refusal of entities to register their organizations.
The second factor is social. The shadow economy of the state depends on the decline in living standards of the middle layer of the population, the emergence of hidden activities, a large number of unemployed people and the orientation of society on illegal income. This can also include problems with the distribution of GDP.
The legal factor significantly affects shadow relations due to imperfect legislation and problems with documents. Also ineffective law enforcement agencies that cannot control or ignore criminal illegal activities.
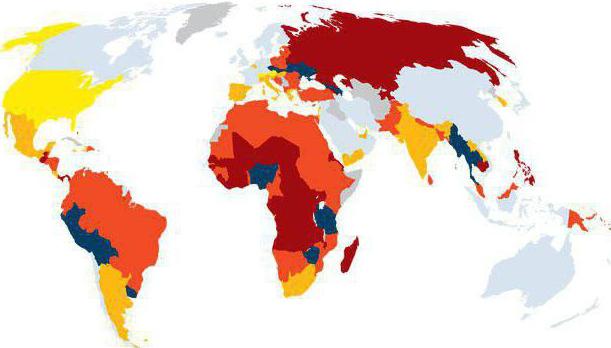
Russia and countries of the world
The shadow economy in Russia and other countries is quite diverse, because everything depends directly on the politics and society of the state.Our country has a high level of participants in illegal processes. The Ministry of Finance proposed to conduct non-cash payments for all transactions that have a value of more than 600 thousand rubles. A similar experience was used earlier in Italy. Now here, the calculation of 2 thousand euros in cash is not possible. It should be noted and the benefits of switching wages to the card account. Government employees who have finances abroad may lose them, as the government realizes that it is illegal to hide money in other countries. This means tax evasion.
The experience used in the USA is also applicable to Russia. The American government knows what the shadow economy is, and therefore has created a special organization. She reveals tax evasion from money that was later exported abroad. Russian bankers will be required to present documents or checks confirming payment. And in Latvia, they are thinking about organizing a certain mechanism that could form a database of customers who spent more than two thousand dollars in cash. If the buyer decided not to pay with a card, but with the funds available in his hands, he is obliged to present the seller with his passport so that he records personal data. Here, in Latvia, it was decided to force all residents to deposit savings in excess of 20 thousand dollars into the card account.

The shadow economy of the European Union is also controlled by the heads of state. In Spain, rates of successful taxation have improved, and the treasury has replenished by almost 2 billion euros. Italy has also approved payment by cards of goods and services in the amount of two thousand euros. In the UK, there is an organization whose composition is 200 agents who work to verify high incomes. During the crisis, Greece also pledged to fight those who refuse to pay taxes.
Switzerland, the most developed country in Europe, now has a low percentage of the shadow economy - only 7.5% of GDP. But now she is faced with the issue of illegal workers. This is especially due to the migration of residents of Asia. Now the country is taking tougher measures to capture illegal immigrants, and the employer who keeps such people in his organization will be punished in accordance with the law.