Characteristic of traditional industrial society complex and multifaceted. Its foundations were formulated at the beginning of the XIX century by Saint-Simon. He put the following meaning in his definition: industrial is a society in which the basis of the economy is no longer manual production and traditional types of management (agriculture and animal husbandry), but developed industry with the corresponding development of social relations and political structure. Initially, the term was the opposite of the patriarchal (pre-industrial) society. Modern theories differ in its definition.
Historical stages of development of societies
Scientists-economists and sociologists distinguish three main stages in the development of all societies in the world. These include: pre-industrial, or patriarchal, industrial and post-industrial.
- Pre-industrial is characterized by a low level of productive forces and social relations. The economy is tied to traditional types: agriculture, livestock, fishing, crafts. In this case, the entire production cycle is carried out by manual labor without the use of automated equipment due to its absence.
- Industrial society. Its characteristic is noticeably different from the previous type. The most important difference is the development of industry, that is, industry, and its transformation into a leading branch of the economy. Other features will be discussed below.
- A postindustrial society, in contrast to an industrial one, does not put industry at the basis of its development, but the emergence and development of new technologies. In this regard, even countries poor from the point of view of a patriarchal and industrial society can become leaders in the pace of economic development. Currently, the leaders here are Japan, the USA, some states of Western Europe.
The characteristic of an industrial society has some features that distinguish it from pre-industrial and post-industrial historical types. As a result, guided by information about the historical types of human development, we can distinguish each of the three existing today.
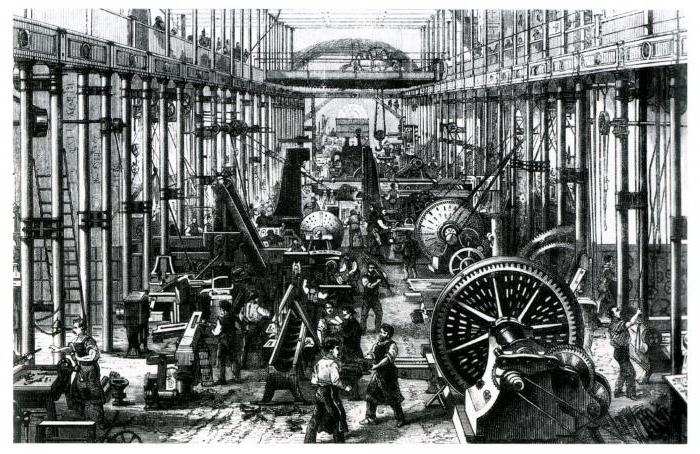
Industrial society. Characteristic of the era
The second historical stage in the development of human society has several significant differences from the first. The main characteristic of industrial society is that the industrial structure is being approved in all spheres of social life as dominant. Thus, agriculture, which previously played a dominant position, goes by the wayside. From now on, the main measure of income that determines a person’s wealth and social weight is not the amount of land (feud) available, as it was in the previous era, but the amount of capital concentrated in his hands. Regarding the approval of the technological industrial structure, it must be said that it has an impact on all areas, from the economic to the cultural.
Employment Proportions
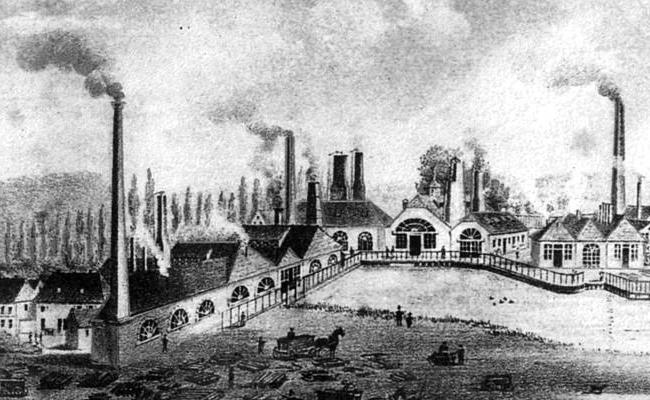
Characterization of the industrial type of society is not possible without studying the changes in the proportions of employment in various sectors. This feature follows from the first - it is inevitable. As a result of the appearance of machine labor and technology, the number of people employed in agriculture is sharply reduced - up to 3-5%; in contrast to this reduction, there is an increase in the industrial sector to 50-60% and in the services sector (40-45%).All this is inevitable if you look at the changes in public life with the advent of the industrial era.
Urbanization
The third feature is a consequence of the first two: as a result of industry growth, a large number of factories and factories that use machine labor appear. After this, there is a sharp increase in the share of people employed in industry. And where are all the industrial enterprises located? Of course, in cities and their suburbs! The result was intense urbanization. It was at that time that there was a sharp increase in cities, including due to the population arriving from the countryside due to the disadvantage of farming in the village and the attractiveness of the city.
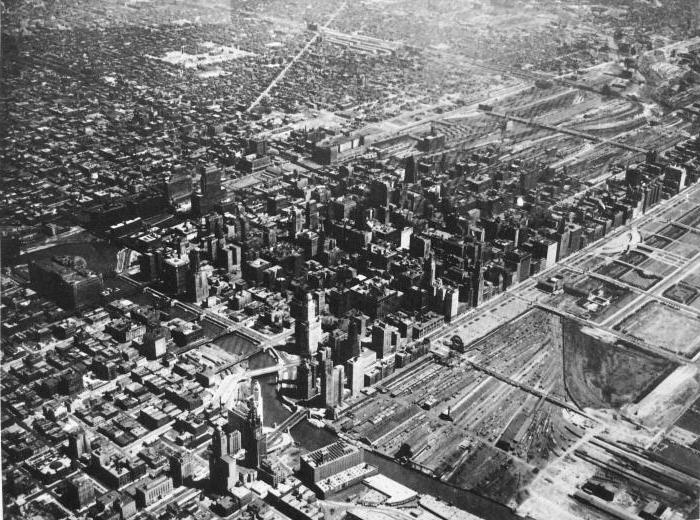

Nation states
If you are asked what an industrial society is, give a description. “Traditional industrial society is characterized by the emergence of nation-states, the basis of the rapprochement of the entire population of which is not the power of the ruler, but a common language, culture and history,” is your answer. This is the 4th feature that served to rally the population of first European countries and the USA, and then of all other states of the world. At this time, a national spirit appears, individual nations are distinguished from the entire population, and a national mentality is formed. Patriotism in the form that we know now also arises during the formation of an industrial society and the formation of nations and states.

Educational revolution
The next feature is the cultural, or educational, revolution. The characteristics of the industrial information society include such features as growing literacy of the population, as well as the formation of national education systems. Today, the fact of universal literacy may seem natural to many, but only 300-400 years ago in Western Europe, considered today advanced, only a few could read and write. On the development of technical sciences it was not necessary to speak at all. The whole “technical development” was dictated by the church, and it was in her interests to preserve the old foundations, as a result of which the church grew rich and did not see competitors for itself.
The question of the formation of national education systems was also quite acute, each advanced country tried to find its own individual way of developing education, which, firstly, would solve the need for new economic realities and, secondly, would continue the development of technology and the advent of inventions.
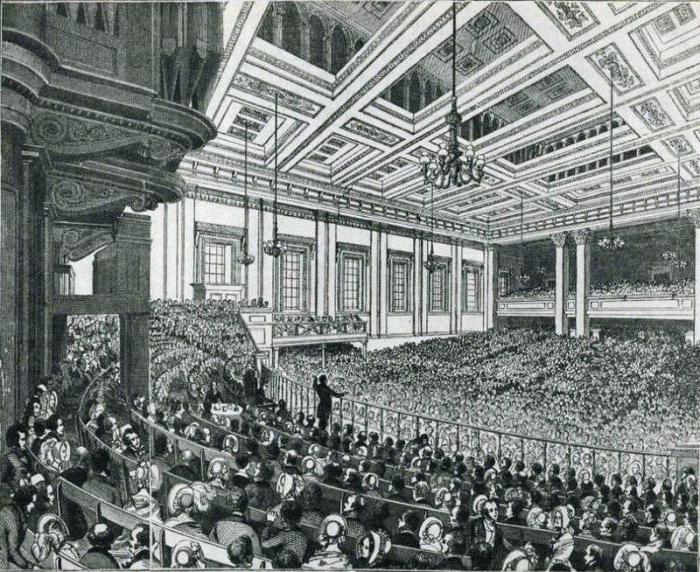
Political Rights
The cultural result was a political revolution. Oddly enough, but with a large amount of information invested in the heads of the masses, including the humanitarian direction, the population has political demands on the government, which was emerging in the era of industrial society. The characteristic of this feature allows us to conclude that most of the political rights, freedoms and duties that are vested in the citizens of modern states arose during the formation of industrial societies. The most important political law acquired by the population, was the right to vote. Of course, initially the qualification was very high - not everyone could participate in the elections, and women were not endowed with them at all, but over time, suffrage acquired a modern look and became universal.
Welfare state
The level of consumption shows a sharp increase as a result of the fact that the so-called "The state of general welfare (welfare)." At this time there is a change social status population. If earlier there was a “state-society” scheme that did not notice the importance of the abilities of individual citizens, then the industrial-state scheme distinguishes the “state-personality” scheme.This characteristic indicates that from now on the person is important for the state, and it does everything so that each person benefits to the best of his ability.

Consumer society
Following the “welfare state”, a “consumer society" appears. The growth of population incomes and the appearance of more free time have become, as it were, conductors for consumption. Individual consumption and the corresponding social attitudes have now become, one might say, the cult that gave rise to industrial society. His characteristic, of course, should include this moment. In pre-industrial society, the majority of the population in personal use had practically nothing, with the exception of shelter (most often rented), food, clothing and tools.
The growth of income and the emergence of free time led to capitalist relations, the basis of which was the accumulation of capital and its display to the whole society. At different times, various indicators became the material expression of wealth. Now they are expensive watches, sports cars, airplanes, helicopters, yachts, etc. But besides this, there is a huge amount of goods necessary for modern life, purchased by most of the population. These include the same clothes, food, household appliances and much more - you can’t list everything here.

Demographic changes
The main characteristics of industrial society include this sub-heading, the most significant in social terms. We are talking about changes in demographic development, which may include the following:
- Lower mortality due to the development of medicine and the emergence of vaccines against most diseases that have plagued the world's population for millennia.
- The result of the above fact is an increase in the life expectancy of the population of developed societies.
- Due to the fact that mortality, including children, is reduced, the need for the birth of a large number of children disappears, therefore, the birth rate is reduced.
- The consequence of these three factors is the aging of the population, that is, the proportion of older age groups becomes predominant when an industrial society is formed.

The characteristics by areas lead us to the conclusion that, on the whole, industrial society has had a positive effect on the development of mankind: the role of the individual has become higher for society, mortality has been significantly reduced, literacy is generally available, and in most countries compulsory, the standard of living is constantly growing. A man who lived only 100 years ago could not even dream of the benefits that the population of most of the globe enjoys today.
