The fundamental rights and freedoms enshrined in the Constitution of the Russian Federation include the human right to work. Moreover, working conditions must meet all safety requirements and hygiene standards. Concern for labor protection and the health of citizens, as well as the protection of all forms of property recognized in the state, are the basis of the constitutional system of the Russian Federation. This article will address liability. Examples will also be described in detail.
About labor relations
Labor relations are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with Article 21, every citizen has the right to own a workplace, which must comply with state standards and safe working conditions. All this should be reflected in the collective labor contract.
It also provides for compensation for harm that may occur in the performance of labor duties, including compensation for moral damage. Labor relations mean that you need to be careful both with the property of employers and employees. Article 238 of the Labor Code of Russia establishes the liability of a citizen who caused damage directly to the property of the employer, as well as the damage that the employer is forced to compensate for the fault of the employee to third parties. An example of employee liability will be given below.
Material liability
It occurs due to violation of labor duties, which led to damage. Along with disciplinary, it is one of the types of legal liability. Therefore, it has all the signs of legal liability, in addition, it has signs of a compensatory nature (such as violation of obligations stipulated by the Civil Code of Article 25 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), and finally, mat. responsibility has features that are unique to it.
This type of liability provides for mutual agreement between the parties (employer and employee) in case of damage compensation for the injured party. This is reflected in the legislation in article 232 of the Labor Code of Russia.
Types of mat. responsibility
Based on the foregoing, there are two types of mat. responsibility:
- The employer in front of his employee.
- A worker in front of his employer.
Common symptoms
According to the employment contract, a liability arises between the employer and the employee, characterized by common features:
- mat. liability having a bilateral orientation and stipulated by the existing labor contract;
- parties to the contract become its subjects;
- liability occurs only when mutual obligations stipulated in the employment contract are violated;
- each subject of the contract bears mat. liability only for those violations of their duties that caused damage to the second party;
- both parties to the agreement voluntarily indemnify the damage to the other party.
Differences
Along with the general signs of liability, there are differences. As a rule, an employee who is considered an individual and, on the other hand, an employer, most often a legal entity, is involved in signing an employment contract. And, of course, they are not equal in their economic and other opportunities. The employer is endowed with organizational and organizational powers in relation to employees. The presence of these distinctive factors makes adjustments to the mat.liability of the parties to the contract: if the employee is provided with a partial or limited mat. responsibility, then for the legal entity or the employer full responsibility is provided.
Example of limited liability
Robbers stole a computer from the office of the company. It happened at night. But an employee who is materially liable under the contract will not indemnify. After all, everything happened due to circumstances beyond his control. But if he accidentally broke it, while intoxicated, or took it home, then he would have to reimburse the head of the company the cost of the computer in full.
About the contract
In addition to legislative consolidation mat. responsibility between the parties, it can be stipulated by the contract itself or by agreement to it. Responsibilities of the parties are established by Part 2 of Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, guaranteeing the fulfillment of obligations undertaken. The Labor Code and federal laws govern the liability of the parties. The responsibility of the employee may not exceed, and the employer may not be lower than the liability prescribed by law. An example of a collective liability agreement is presented below.
The obligations and rights of the parties to the employment contract are valid only for the period of its validity.
This rule does not apply to material liability that arose during the term of the contract, after causing damage to one of the parties and terminating the contract. This provision is stipulated by Part 3 of Art. 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Examples of employee liability:
- When an employee intentionally causes harm, and he knows about the consequences. For example, the cleaner does not like the accountant, and therefore broke her computer so that she would not be able to submit reports in a timely manner. But it is necessary to prove the presence of malicious intent.
- When the employee was intoxicated or drunk. In such circumstances, the damage caused must be fully compensated.
- There was a commission of criminal acts, and the court proved it.
- When the manager sold the list of regular customers and their contacts to competitors.
Conditions for the offensive. responsibility
To come mate. Responsibility for parties to an employment contract requires the following conditions:
- causing damage;
- violation of legal norms of behavior (inaction or action) of the party that caused the damage;
- if there is a causal relationship between the unlawful inaction (action) of one of the parties to the contract and the damage that arose;
- the fault of the person who caused the damage.
When calculating the amount for compensation for damage under labor law, lost profits, i.e., unearned income, are not taken into account (Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and are not subject to recovery.
Actual damage
According to established practice, the amount of cash property that the organization has lost as a result of damage should be considered as actual damage. Deterioration of property and decrease in property value, this also includes the costs of restoring or acquiring the lost, as well as excessive payments made (Article 244 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, this may include shortages, costs of repairing damaged property, damaged values. Excessive payments mean fines recovered, it can also be wages paid to the dismissed employee, but did not receive the work book on time due to the fault of the employer, etc. Each of the parties claiming compensation for damage must prove the extent of the harm caused to it (Article 233 of the Labor Code RF).
A slightly different understanding of actual damage is accepted in civil law, and the term “damage” itself is different, in monetary form it will be called a loss.Article 15 of the Civil Code of Russia states: a loss is understood to mean expenses incurred by one of the parties, or which it must pay in order to restore a violated right, lost or damaged property (real damage). This also includes lost profits or lost profits, that is, those funds that a person could receive by participating in a civil circulation with normal conditions, if his right had not been violated. In this case, the person who caused damage to the property or identity of the citizen, as well as to the damage to the legal entity, must compensate for this damage in full (article 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This provides for a liability agreement (an example of filling can be seen in the article).
An action (inaction) is considered illegal if it violates the obligations of one party to the labor contract assigned to it by legal norms.
The rules of the internal routine, labor contract, instructions of the employer imposed on the employee shall not be at variance with the rules provided for by the Labor Code. For employers in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also developed certain responsibilities.
The damage that has occurred and the actions of one party have a causal relationship. Accidentality in the occurrence of damage is impossible, and its occurrence is a consequence of the action (or inaction) of the causer.
Forms of guilt
As a rule, someone is to blame for the damage. Guilt can be highlighted by negligence or in the form of intent. Regardless of the form of guilt, the person who committed the damage is liable for compensation. But on whether the fault was intentional or through negligence, the size of the recoverable loss will be covered. This implies the liability indicated in the job description (examples above).
There is no general wording to declare a party not guilty in labor law. In paragraph 1 of Article 401 of the Civil Code of Russia there is a wording of innocence that is quite applicable to labor relations: a person, employer or employee is recognized as innocent if, with the proper performance of his duties, he took all measures to prevent damage.
To mate. liability for damage caused by either party to the other employment contract has occurred; all conditions listed above must be present at the same time. If at least one condition is absent, liability does not occur. Examples from life will help to figure this out.
Functions of the agreement on a mat. responsibility
The employer entrusts one of the employees with the safety of their property, and the latter, acting in accordance with his official duties, monitors its safety.
Caring for the integrity of their property, and as a person interested in the rational and proper use of it, the employer concludes with such an employee (employees) an agreement or an agreement on the full mat. responsibility (article 244 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An example of a liability agreement is in our material.
An agreement of this kind is concluded with the aim of:
- To increase the degree of responsibility of the employee for property that does not belong to him.
- Collect compensation in full for the damage caused by the employee.
The legislation does not oblige employers to draw up such agreements, this is one of the rights of the employer. However, if such an agreement is absent, then even in the case of proven and obvious guilt of the employee, the employer will be able to recover from him the amount of losses incurred, which is not more than his average monthly salary (article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What are the types of mat. responsibility?
All employees have a liability to the employer. However, it has different types:
- Limited, in which they do not conclude an agreement on mat. responsibility, the employer may recover damages from the employee, but to a limited extent.Recovery from the employee of an amount greater than established by law only through the court.
- Complete individual. The employee has the corresponding responsibility. The volume of property assigned to the employee is easily specified, and there is the possibility to control it. An example of an agreement on full liability is available.
- Complete collective. In this type of liability, a specific amount of property is controlled by a group of persons. And the responsibility lies with all the people in the group.
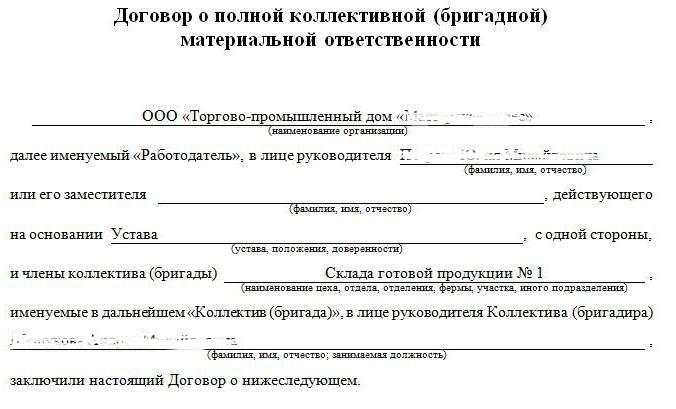
In both cases, a complete mat. responsibility between the employer: for the first case with each financially responsible person, and for the second with all members of the group, a written agreement is made on the mat. responsibility (articles 244, 245 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The material values transferred to them according to the inventory are periodically inventoried. An example of a collective liability agreement can be found above.
Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85 provides a list of jobs and positions in which one of the types of materials may arise. responsibility. For example:
- Individual - cashiers, storekeepers, freight forwarders, drivers.
- Collective - a team of storekeepers or builders, a team of sellers.
We give an example of collective liability.
This type of responsibility is borne by a team of sellers in any department of the store or a team of builders is responsible for the safety of materials.
It is more advisable to draw up an agreement on liability immediately upon the appointment of an employee to a position involving such liability. Or perhaps just before the start of work related to liability. Persons under the age of 18 do not enter into such agreements.
To systematize the relationship between the employer and the employee in relation to the mat. responsibility, internal regulations are drawn up.
Circumstances precluding employee liability (examples)
These circumstances include the following:
- Damage due to force majeure (natural disasters, earthquakes, floods, hostilities, embargoes).
- Normal economic risk (accidental death or damage to property).
- Extreme need or necessary defense (for example, an employee was attacked, and defending himself, he ruined the laptop belonging to the company).
- The employer violated the conditions for the normal storage of property entrusted to the employee (if the cashier has lost material assets, and the warehouse or office is not properly equipped, that is, there is no alarm, bars on the windows, an unreliable lock on the door). In these cases, neither limited nor full liability can come. Examples may be others.

Where to get the agreement form for the mat. responsibility?
When developing your own agreements that take into account the requirements for specific positions, types of work, teams and certain situations, you should be based on standard forms developed by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation.
Such documents must necessarily contain the following information:
- Parties to the contract.
- Duties of the parties. So, it is the employer's responsibility to provide the employee with the conditions under which he can ensure the safety of property.
- The subject of responsibility of the employee.
- Date of conclusion of the contract.
For employers who are very interested in the safety of their property, the issue of registration of a contract on a mat is extremely important. responsibility with the employee who will be entrusted with the work with the mat. values. When preparing such a document, one should be guided by the current legislation and adhere to the rules established by it.
We examined what is liability, examples are also described.