Such is the reality that the activities of domestic individual entrepreneurs are also associated with filling out a large number of a wide variety of papers. Especially tax reporting is highlighted here. Some sections in the forms of documents raise questions not only for beginners, but also for entrepreneurs who have long been engaged in business. For example, is there a checkpoint for IP? Let's first understand what it is.
PPC is ...
You saw in the form a field where you need to enter your checkpoint. Of course, the first thing you do is open a certificate of registration and you won’t find such information there. Where to see the checkpoint at the IP?
This is the abbreviation for the registration reason code. What does it mean? The reason why this or that taxpayer was registered with the Federal Tax Service. Some codes will encrypt in this way organizations, their units, real estate. Hence, such a cipher is the necessary information for reporting, therefore, a field for it is available in many forms.

What is the registration reason code? This is a nine-character combination in which information about a particular organization is encrypted. In contrast, say, to the TIN, which stores data specifically about the person, the owner-taxpayer. A checkpoint must be assigned when registering a legal entity along with the same TIN.
The code is needed for a wide range of payment, legal and accounting documents. By the way, one organization may have several such codes, if, for example, it conducts activities both at the place of main registration and in other regions. Therefore, 9 PPC symbols encrypt the following information:
- 1-4 - code of the authority of the Federal Tax Service, where the legal entity is registered.
- 5-6 is the reason code for registration.
- 7-8 - ordinal figures of accounting in tax territorial authorities.
When is a gearbox assigned?
Note: the owner of a checkpoint can only be a legal entity, but not a physical person. Here are a number of reasons that are the basis for obtaining such code:
- Registration of a new legal entity. The gearbox is assigned with the TIN.
- When changing the legal address of the company.
- When opening a new branch, a separate division in another region.
- When changing the location address of a separate division of the organization.
- By location of vehicles or real estate owned by this legal entity.
- Other reasons specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.

But is the checkpoint number determined by the IP? The answer here is quite simple.
Does the IP (individual entrepreneur) have a checkpoint?
By registering an IP, an individual receives only the TIN. An individual entrepreneur does not have a checkpoint! The lack of it is explained simply: the reason for registration with a tax individual is one. Moreover, registration always takes place at the place of registration. Hence the need for the assignment of the checkpoint disappears.
Why is there a field for the checkpoint in the IP documents?
A logical question arises: if the entrepreneur does not have such a code, why is the SP contained in the payment order in the checkbox? The fact is that many documents and reporting forms are standard for both legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. Therefore, both those and others are given the same forms to fill out.
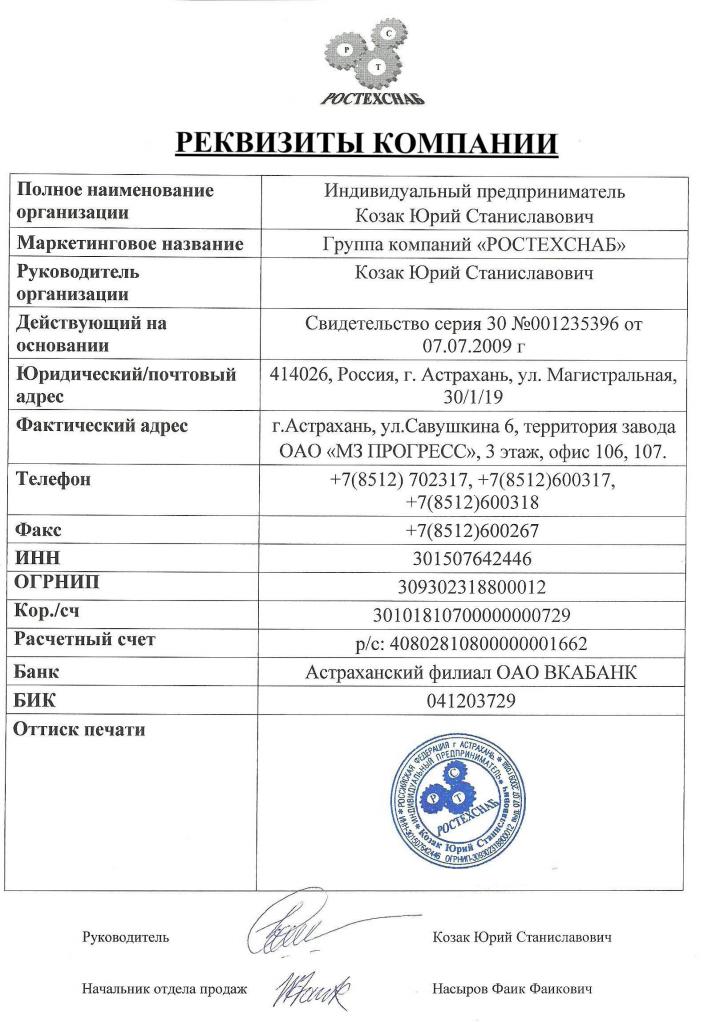
If you, IP, have come across such a form, then you no doubt put a dash or zero (0) in the "PPC" field. You can leave it blank - ask the tax officer or other organization how to correctly indicate the absence of this code. But the legal entity in this section will be required to put its registration code.
If they require a checkpoint ...
Sometimes the bureaucratic machine itself can fail by answering the question "Is there a checkpoint at the IP?" in the affirmative. What to do if any organization asks the entrepreneur to indicate in the document this code, which he does not have?
It is necessary to substantiate your objection by current legislative norms and official explanations of the representatives of the Federal Tax Service in this regard. An exhaustive answer will be the sending to this letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation: document dated 02.28.2013 No. 03-02-08 / 14. Here is a complete answer to the question "Is there a checkpoint at the IP?"
Note that even in relation to legal entities, the checkpoint is not significant information for identifying them as taxpayers. The requisite has a purely technical function - it is needed by the Federal Tax Service for accounting, which is why it has the status of an additional indicator. And now the entrepreneur's TIN helps to perform identification.

General details
We also note that the checkpoint does not apply to general details even for legal entities. For most operations, identifying the IP will help to indicate the following information:
- The name of your brand (if any).
- The legal structure of doing business.
- Head structure.
- Information from your certificate of registration of IP: the number of this document, the date of registration, the authority of the Federal Tax Service that issued the paper.
- Actual address.
- Contact number.
- The address of your own site.
- Email inbox.
Indication of oneself and its activity of the following information is also considered standard for IP:
- FULL NAME.
- Bank account.
- Checking account.
- Legal address.
- INN
- OGRIP.
- OKPO.
- OKATO.
- Contact phone number.
If the form implies the indication of a personal category code, then in this column you just need to put a dash.

Bank details
To make non-cash banking settlements in the accompanying documents of the IP, it is sufficient to indicate the following information:
- Its official name is from the registration certificate.
- Own 20-character bank account.
- Name of the bank where the r / s is open.
- Correspondent account.
- On the standard form there will also be graphs for writing PPC, TIN and OKPO. An individual entrepreneur here only enters his TIN - such data is sufficient for the implementation of this non-cash transfer, and for all the functional activities of entrepreneurs in general.
When the counterparty is persistent ...
If everything is clear with documents for the tax service and bank payment orders, then it is not so simple with counterparties. The partner may not accept the objection that the entrepreneur cannot have a substitution code for registration. But it also happens that the situation does not allow you to dispute about "There is a checkpoint at the IP or not."
In this case, experienced entrepreneurs offer to go for a little trick - come up with this code for the counterparty yourself! Of course, such a combination can in no case be entered in official papers. Generating a checkpoint is simple:
- The numeric code of your region.
- The code of the tax office at your place of residence.
- The code for legal entities used for registration thereof is 01001.
The result is nine numbers, which can be specified for a persistent, but unenlightened counterparty.

The main conclusion from all that has been said: An individual entrepreneur does not and cannot have a checkpoint under Russian law and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The main information for identifying an individual entrepreneur as a taxpayer is considered a TIN.
