The invoice is inextricably linked with VAT - one of the budget-forming payments of the Russian tax system. Therefore, this document is one of the most important among the primary ones. By whom and when is the invoice issued? We will analyze all the nuances of this process.
Basic Document Information
Invoice - a documentary basis for accounting, calculation and deduction of VAT. An invoice is issued by a supplier - a VAT payer - to its customers: companies or entrepreneurs. In other words, any transaction for the sale of goods and services subject to VAT must be accompanied by an invoice. For the buyer, this document serves as the basis for reducing own VAT payable, that is, for a tax deduction.
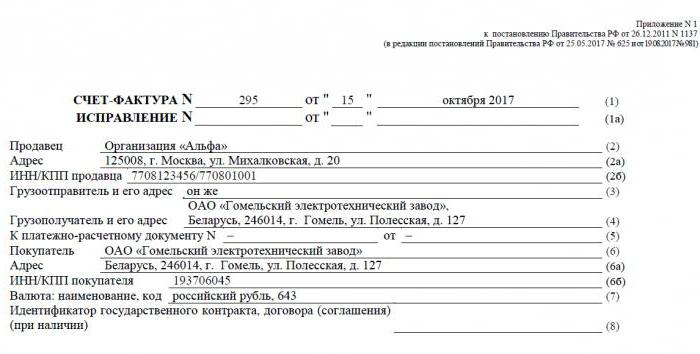
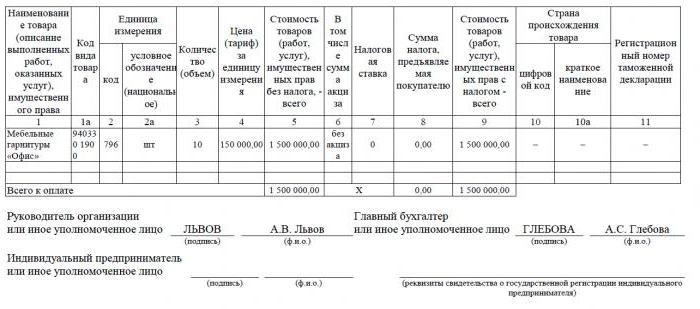
If the buyer does not pay VAT, the supplier may not issue him an invoice. However, for this, an agreement must be signed between the parties that invoices will not be issued. Suppliers who do not pay VAT are also exempted from having to draw up this document.
Normative regulation
The legal basis for the application of this document is the Tax Code. Clause 3 of Article 169 determines in which cases an invoice is issued. This is the execution of operations that fall under VAT, as well as the export of non-taxable goods from Russia to the territory of the Customs Union.
The document has a specific form, set out in Resolution No. 1137. The same act sets out the rules in accordance with which invoices should be filled. The form of the document and the procedure for filling it are constantly being improved, in connection with which the decision is amended.
Paper and electronic formats
Today, invoices are generated in a classic form, that is, on paper, or in electronic format. Such an invoice, like its paper counterpart, must be drawn up in a strictly established form and contain all the necessary details.
When is an electronic invoice issued? This is possible if the following conditions are true:
- an agreement has been concluded between organizations on the compilation of electronic invoices;
- counterparties have the technical ability to exchange documents in the established format via the Internet.
Otherwise, there are no restrictions. An electronic document completely replaces a paper one, provided that it is prepared in form and certified by a digital signature.
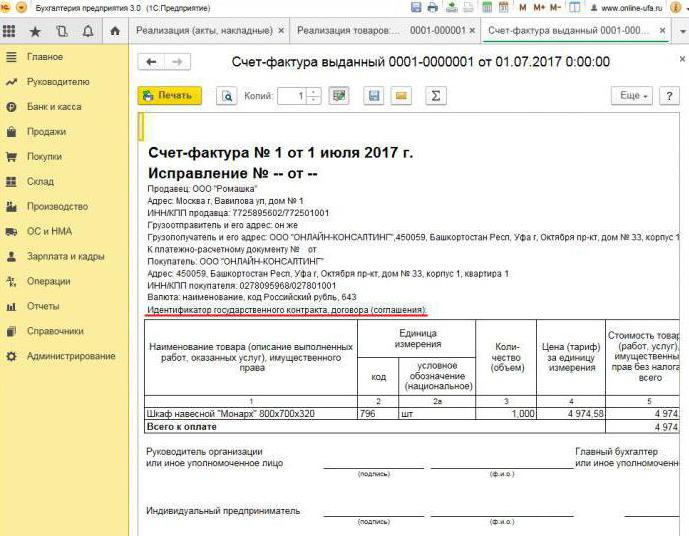
When an invoice is issued
Most often, the primary document under consideration is issued by the seller during operations that, in accordance with tax legislation, are subject to VAT. The sale of most goods and services, including gratuitous transfer, is subject to taxation. But there are exceptions - they are listed in article 149 of the Tax Code.
Also, companies and individual entrepreneurs working with VAT are required to generate invoices upon receipt of payment against future shipment. Such documents are commonly called advance invoices.
In addition, VAT payers are required to issue invoices when exporting to the EAEU countries.
There are cases when the paper is also issued by the entity that does not pay VAT. Such an obligation arises for companies and individual entrepreneurs if they, on their own behalf, sell goods belonging to another organization - a VAT payer. We are talking about mediation under a commission agreement and the like.
The procedure for issuing a document during implementation
Consider a basic example - the seller releases the goods, and the buyer makes the payment after the fact. An invoice is issued within 5 days, starting from when the shipment of the goods took place, services were sold or work was performed.
One copy of the invoice is issued for the supplier, the second for the buyer. The document must be registered in the Journal of invoices (hereinafter referred to as the Journal). In addition, the seller makes an entry in the Sales Book and indicates the details of the corresponding invoice. And the buyer, accordingly, makes a similar entry in his Shopping Book.

When an advance invoice is issued
If the buyer transfers the prepayment for future delivery, the supplier must also draw up an invoice. It doesn’t matter if the buyer paid in full or in part - the document is written out for the amount transferred. The seller charges VAT on the received prepayment, and the buyer, subject to certain conditions, can declare his input tax deductible.
When is an advance invoice issued? The deadline is 5 days, the calculation is from the date when the prepayment was received. The document is taken into account with the supplier in the following order:
- the advance invoice is reflected in the Sales Book;
- when the sale of goods takes place, a shipment is made, that is, a “real” invoice;
- the shipping document is noted in the Sales Book for the entire amount of the delivery;
- at the same time, an advance invoice entry is entered in the Purchase Book.
The buyer has a similar accounting procedure for the document, but with the opposite sign: instead of the entries in the Purchase Book, the Sales Book, and vice versa. Both the buyer and the seller documents are also subject to registration in the Journal.
When a prepaid document is not needed
When working on a prepaid basis, the following rule applies: if the shipment is carried out no later than 5 days after receipt of the prepayment, then an advance document is not necessary. After all, an invoice can be issued within five days, and during this time the goods will be delivered. So in the period allotted by law, it will be possible to immediately issue a shipping invoice, bypassing the preparation of an advance.
When an intermediary issues an invoice
We separately mention the features of working with invoices of commission agents and other intermediaries (agents, forwarders, attorneys). When selling the goods of the principal with VAT on his behalf, the commission agent must draw up an invoice and allocate the amount of tax in it. This will allow the buyer to deduct their input tax. Moreover, the invoice should also be issued if the agent himself does not pay VAT, for example, being on a simplified taxation system. The fact is that in this case the commission agent, being an intermediary between the buyer and the owner of the goods, actually assumes the function of the latter in calculating VAT and drafting documents.

The commission agent registers the submitted document only in the Journal. The second copy is intended for the buyer. The details of the document are transmitted by the commission agent to the principal, and he issues the invoice to the intermediary himself. At the same time, the document must have the same number that the commission agent assigned to it. He notes the received invoice in the Journal.
If the commission agent buys the goods from a third party for the VAT paying client, he will re-issue the invoice issued by the seller to him. In this case, the received and issued invoices should also be registered in the Journal without reflection in the Books.
If the exposed document needs to be changed
In practice, it often happens that documents have to be amended. For example, a shortage of goods has occurred or its price has changed. This is also required when an error is found in the invoice.
To change the information in the issued document, corrected and corrective invoices are compiled.The first is simply a new version of the document, which contains the correct information. The corrected invoice shall be issued within three years from the period of issuing the original document. This is due to the buyer's right to declare a deduction of input tax within the specified period. The corrected document exists independently and completely replaces the one in which the incorrect data was indicated. It is written out in cases where you need to fix a mistake that did not lead to a change in the amount. For example, the supplier incorrectly indicated the name of the buyer or the tax rate. If the incorrect information in the invoice does not make the deduction impossible, then the corrected document does not need to be drawn up.

In what cases is an adjustment invoice issued? When the transaction amount is adjusted, for example, due to a change in the value of the goods. At the same time, an agreement on changing the amount (annex to the contract, act, decision) should be concluded between the parties. An adjustment document is compiled for the amount of changes and is in addition to the original.
It happens that the supplier sold several batches of goods to one buyer and issued a separate invoice for each. However, it happened that the amount in all deliveries must be changed. How many invoices are issued for adjustment? In this situation, there is no need to draw up several documents - the seller can draw up one for all changes to the address of this buyer.
Violation of the rules and liability
What threaten companies or entrepreneurs with violations related to the described document? The law spells out when the invoice is issued, but there is no direct liability for exceeding it. But the lack of an invoice is regarded as a serious flaw in accounting. Absence refers to non-submission of the document in the quarter when the transaction took place.
For this, the taxpayer may be punished in accordance with Article 120 of the Tax Code. If this violation is detected for the first time, then the organization may receive fines in the amount of 10 thousand rubles. If the absence of invoices is revealed in several quarters, the amount of the fine will triple. And in the case when this violation led to an understatement of the tax, the fine will be 1/5 of the amount of underpayment, but not less than 40 thousand rubles.

I must say that "forgetting" about the invoice when selling a product or service is quite difficult. Even if this happens, the buyer will definitely remind you to draw up a document, because without it he will not be able to deduct VAT. With an invoice in advance, everything is different. Buyers do not always claim the VAT deduction from the advance payment paid, so they do not ask for an invoice. In such a situation, some accountants do not consider it necessary to expose them. They reason like this: receiving an advance and shipping takes place in one quarter (in most cases), so why fill out an interim document? However, the Federal Tax Service considers this a violation if more than five days elapse between the receipt of prepayment and the shipment of goods.
Why is it important to follow the design?
The document to which this article is devoted is necessary for claiming VAT deduction by the buyer. If critical errors are made in it, the tax service does not recognize the deduction. This means that the company will have to pay taxes, and in the worst case, also pay a fine. Therefore, when receiving an invoice, it is important to carefully check its main details.
In fairness, we note that not every mistake will result in a denial of deduction. There are a number of transaction parameters that must be identified by an invoice, namely:
- buyer and seller;
- object of the contract;
- cost of goods (services) or prepayment amount;
- rate and amount of VAT.
If the specified parameters are determined on the invoice, then a deduction on it can be declared, despite other errors.Having received a refusal from the IFTS, the taxpayer can safely go to court. However, if the supplier made an error when creating the invoice, for example, in the cost of goods or the amount of tax, then the buyer may not count on VAT preferences.

So, the invoice is very important for calculating the VAT from the supplier and deducting its input from the buyer. It is necessary to follow the current form of the document, because it periodically changes. And it is extremely important to observe the procedure and terms for its preparation, as well as to avoid critical errors that would entail the non-recognition of the deduction from the buyer.