An enforcement or award claim is a special form of presentation of certain material or legal claims of the plaintiff against the defendant. Its purpose is not to declare the existence of rights, but to prompt the defendant to take specific actions or, conversely, to prompt the defendant to inaction.
A claim for awarding by a court decision must be necessarily executed; moreover, enforcement of a court decision by force is also possible here. This is possible if the defendant reacts incorrectly - delays or does not want to execute the court decision. Of course, before the decision on the defendant’s obligations is made, the court comprehensively examines the plaintiff’s legal rights in relation to the requirement of any action by the defendant. Only after this the defendant receives a claim for award.

Thing
The subject of such a lawsuit is mainly for the sake of which the plaintiff started a given trial, which is precisely the basis for a court decision. A claim for award is in all cases the restoration of the plaintiff's violated right, which is the subject of the lawsuit. It is necessarily aimed at protection, which differs from, for example, claims for recognition, where the subject is relations in themselves, legal or material. In this case, securing the claim guarantees the execution of the award. This is because the award is always based on certain facts that are absolutely specific when the rights of the plaintiff are violated, as well as on facts that confirm the actions of the defendant, if the latter does not fulfill his duties or violates the legitimate interests or rights of the plaintiff. The executive claim necessarily contains the plaintiff's requirements for the defendant to take specific actions or to abstain from them, and securing the claim guarantees the execution of the award. That is why they have a different name - it is always a synonym for enforcement claims.
Almost all types of award claims, which are considered in courts of all levels, are classified as executive, since they are the main tool for legal protection of citizens and always affect the most diverse aspects of material and legal relations. For example, they may require the defendant to return the debt, vacate the living space, pay child support, remove obstacles when entering the apartment, and much, much more. Also, a claim for an award, an example of which will be given below, will necessarily be comprehensively examined by the court. This is a lawsuit of the owner of a thing or property in which he asks the court to recover it from the possession of unauthorized persons, or to evict from an apartment owned by him an unauthorized person who has settled unlawfully, as well as if he has lost the right to reside in this residential area. And there can be many such examples.

Filing a lawsuit
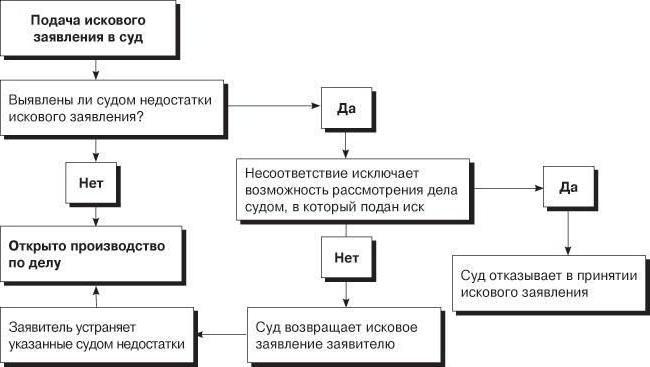
The Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation does not highlight any special requirements for enforcement claims. The types of award claims are far too diverse for individual rules to exist. They are common to all. Applications must be submitted to the court to the representatives of the plaintiff or to the plaintiff himself, they must be drawn up in writing and meet all the requirements in the form that are set out in the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation (Article 131). At the same time, certain documents are submitted to the already drawn up and signed statement of claim, a list of which is contained in the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation (Article 132). Those who intend to file awards claims must carefully examine these articles.In court, all incoming claims are reviewed within five working days, after which the judge makes his decision. Either the claim is accepted for production, and on the basis of this, a civil court case is instituted, or the claim is rejected.
It must be borne in mind that in any case, the judge has the right to do so - he can refuse the lawsuit, and the application will not be accepted, he can return the statement to the plaintiff for revision, or he can even leave it without movement. He does this not of his own free will, but strictly based on the provisions of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, in particular on articles from 134th to 136th. The widest range of conflicts, both material and legal, reveal enforcement claims. Therefore, the claim for the award of the example of the only true execution does not have. In each statement of claim, the plaintiff in the most detail, openly and intelligibly must state all the circumstances of the situation and his own requirements. They must be aimed at restoring legitimate interests and violated rights. It is the latter that differ in drawing up a lawsuit for recognition and a lawsuit for award. The following sample can be considered as one of the possible options for writing such a statement.

Statement of claim
Justice of the peace (hereinafter indicated the number of the plot, district, city).
Plaintiff: last name, first name and patronymic.
Address: name of the city, street, house number, building, apartment where the plaintiff lives.
Defendant: last name of the individual, name and patronymic or name of the organization.
Address: city name and detailed postal address of the respondent.
Statement of claim for protection of rights (for example, consumer).
Further, the plaintiff describes in detail the situation in which his rights were violated. For example, on such-and-such date of such-and-such month and such-and-such year, he acquired some goods in a store owned by the defendant. The full name of the goods, their value according to the attached cash receipt are indicated. The warranty period for this product is also indicated, also according to the attached warranty card. Next, the date of failure of this product is indicated so that it can be accurately determined that the warranty period has not yet expired, the nature of the malfunction and the reasons for the impossibility of its further use are described in detail. On such and such a month of such and such a year, the plaintiff handed over the goods for repair (the exact name and address of the repair organization is indicated, which is also confirmed by the attached receipt in the receipt of goods for repair). The product was not repaired at the appointed time, and therefore the repair organization set a new deadline for the work, which also was not completed for such and such reasons. However, in accordance with the law, the rights of consumers must be protected (clause 1, article 20): the period for eliminating defects in the goods may not exceed forty-five days. In this case, the law was violated.
It must be recalled that this award is a model for a process in a civil court, it concerns one specific case, and in each other other circumstances must be described accordingly.

The main part of the statement
If the consumer’s requirements are not satisfied within the time periods specified in the articles from the 20th to the 22nd inclusive of the "Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights", for the latter there is article 18. It affirms the consumer’s right to make other claims of her choice. He can refuse the goods and demand compensation for losses that were caused to him by the fact that the defendant sold him a product of inadequate quality, and the defects of this goods were not agreed upon with the consumer. Therefore, the consumer has the right to apply to this organization or to this person with a written claim and a demand to return the entire amount paid by check. The exact date of payment must be indicated.
However, the money for the purchased and turned out to be defective goods were not returned.Ten days later, according to the same law (Article 22), if the seller does not satisfy the buyer's demand, he will also have to pay a daily penalty, that is, a penalty - one percent of the value of the goods. In addition, the seller is obliged to compensate the buyer for non-pecuniary damage, which primarily consists in the fact that the buyer could not use the purchased product for its intended purpose, and this caused him some discomfort. A role is also played by the fact that a lot of time was lost and inconvenience was experienced due to the very long time that I had to ask the seller to fulfill his obligations stipulated by law, and the most important inconvenience is that they all turned out to be inconclusive.
Conclusion of a claim
Based on all of the above and, accordingly, the requirements of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Protection of Consumer Rights" (Articles 23, 22, 20, 18, 15, 13, 4), I ask: to recover from the defendant the cost of this product in favor of the plaintiff (indicate the amount on the check); recover from the defendant a forfeit in the amount (indicate), recover from the defendant in favor of the plaintiff compensation for the non-pecuniary damage (indicate the amount). The total price of the claim is such and such. The following are attached: calculation of the penalty for each day of delay in payment after the requirement to return the principal amount of the value of the goods; copy of the statement of claim; copy of cash receipt; copy of warranty card; a copy of the receipt from the repair organization about the acceptance of the goods (all with the date of receipt on hand); copy of the claim.
Something like this is a lawsuit for the award in civil proceedings. Naturally, all descriptions should relate to a strictly defined case and describe specific circumstances.
Classification
We examined a sample of a claim for awarding only one of the branches of law. And such disputes are classified much wider. Of the most common in legal proceedings, claims differ in substantive grounds. They can relate to labor, housing, family and many more. Each section of this classification has its own subsections. For example, the basis of a claim for award is civil law. Then from them we can distinguish:
- claims under separate agreements - leasing, leasing and the like;
- relating to the protection of property rights;
- copyright infringement claims;
- on restoration of inheritance rights.
All of them relate to civil suits. It is the substantive classification that helps to establish the correct subject of the award.
At the first stage, this is the most important, since the scope and direction of judicial protection, the subject composition of the dispute and its jurisdiction are determined, the specificity of procedural actions and the features of a particular dispute are revealed. The procedural legal attribute may also have its own classification, because the plaintiffs have completely different goals, according to the content of each claim. Claims for awards in civil law are extremely rarely alike, except in fine detail. From the content of the dispute, from its purpose, both the method of protecting the law and the very nature of court decisions depend. That is, the plaintiff formulates what he wants to receive by court order. The legal process divides claims into three types:
- on recognition (which are called installation);
- on awarding (executive);
- transformative (these are not universally).

The essence of the award
The most common lawsuit in judicial practice is a lawsuit for awarding in a civil proceeding. It represents the requirements of the plaintiff, the subject of which will be such characteristic methods of protection as the compulsory or voluntary performance of the duties of the defendant, which are confirmed by a court decision. Turning to the court with a request to protect his rights, the plaintiff asks, first of all, to recognize the disputed right for him and to award the defendant to perform certain actions or, on the contrary, to refrain from performing certain actions. Each dispute combines these two requirements, which is their characteristic feature. This recognition of the disputed law and the subsequent award to the performance of the duties of the defendant.
The form of protection is always determined by the nature of the violation of rights that the plaintiff asks for protection.Therefore, a claim for award falls under this classification only when the protection of the right is carried out solely by awarding the defendant to certain actions or refraining from them. A claim for award in an arbitration process can be aimed at economic disputes and other cases that arise from civil legal relations, administrative or public relations, bankruptcy cases, judicial review, complaints, and so on. The decision is confirmed by a writ of execution. That is why the claims themselves are often called executive.
Ground of action
The basis of the award is only legal facts. They can indicate either the emergence of the right (purely facts: for example, the conclusion of a transaction or the certification of a will), or, conversely, a violation of a certain right (for example, failure to fulfill obligations upon the expiration of the contract).
There can be countless examples here: from a claim for the recovery of the value of a share to a lawsuit for eviction from a certain living space and relocation of a defendant to where he is registered. The claim for recognition (administrative) has a completely different purpose. It establishes the certainty of law and eliminates its debatability. The defendant to whom this lawsuit is brought cannot be forced to commit certain actions, that is, the plaintiff will not receive any benefit from a positive decision of the judge.
Previous lawsuit
However, installation lawsuits have their own tasks, which have unconditional and most important value. A lawsuit for recognition establishes the absence or existence of a disputed right, and also in a number of cases serves as the surest means of protecting violated rights, if it is necessary not only to determine the disputed legal relationship, but also to eliminate violations of the subjective rights of the plaintiff. If the claim for recognition is satisfied, then the claim is satisfied by the court. That is, his rights will be restored. But at the same time, no one is obliging the defendant to commit certain actions in relation to the plaintiff. Although the value of recognition claims is more likely to be of prophylactic value, they surely serve as a means of establishing both a disputed duty and a disputed law. After all, contesting certain rights will certainly create a threat of their violation in the future.
Recognition claims are presented to prevent this threat to the rights of the plaintiff. Very often, a search action precedes an award. Especially indicative are cases where these statements are interrelated. In this case, the court, satisfying the claim for recognition, thereby cannot but satisfy the claim for award. Recognition claims have their own classification, which is also highly branched. After all, the circumstances prompting the filing of such a claim can have a lot of options. One of the most common types are disputes about the recognition of positive (where recognition of the disputed law is carried out) and negative (when the court determines the absence of legal relations).

Do conversion suits exist?
Theorists in civil procedural law discuss the existence of transformative claims, that is, a third type according to their classification. They should be aimed at terminating or changing the existing legal relationship between the plaintiff and the defendant. This can happen for various reasons and can be accomplished in various ways, including as a result of a unilateral expression of the will of the plaintiff. The examples show that almost all perfect judicial acts on claims that are presented in theory as transformative, in fact, are either awarding claims or recognition claims. So, the establishment of paternity or divorce - claims for recognition, and the division of property acquired together - a lawsuit for the award. Most leading lawyers believe that in this classification there should be only two sections, determined solely by the procedural purpose.
Now the science of civil procedural law asserts that there is no need to highlight such transformative lawsuits as an independent institution. There are a number of reasons for this. First of all, the courts do not have the function of eliminating rights by their own decision, as well as creating rights and obligations, especially if both parties did not have them before the trial. Only claims for recognition and awards are satisfied, despite the fact that in the legal literature there are references to the existence of lawsuits of group or defending an indefinite circle of persons, as well as indirect, that is, derivative claims are also mentioned. The basis of the classification is still disputes with a pronounced nature of the protected interests. In a class action, there is a synthesis of two procedural concepts at once - representation and complicity, and therefore this type stands apart in this classification. A procedural remedy for protecting the interests of the plaintiff is a court to which a specific claim has been transferred with a specific indication of the plaintiff and defendant.