The key rate was first introduced by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on September 16, 2013. She received life as a new concept in macroeconomics. Since then, the Bank of Russia has begun to use the change in the key rate in its activities. Since that time, two rates have been simultaneously used in the Central Bank policy: the key and the refinancing. At the same time, the values of these rates have been different for a long time. The refinancing rate has not changed. Its value was equal to 8.25%. The dynamics of changes in the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation was controlled by the Central Bank depending on the state of the economy. In 2016, the values of these rates were equalized.
The role of the central bank
In the context of the restructuring of the Russian economy in accordance with the new realities and its existence in the context of the sanctions policy, the main role is played by the actions of the Central Bank, which ensure the functioning of organizations, small businesses and the country's population.

Many factors depend on these actions in the economic life of the state. Carrying out its activities in accordance with the adopted monetary policy, the Central Bank regulates the activities of banks, affects inflation and many other macroeconomic processes developing in the country.
In part, this is achieved precisely by changing the key rate. The task of fixing the inflation rate at 4.0%, which is described in the “Main directions of monetary policy for 2017 and the period of 2018 and 2019,” was not only successfully achieved, but even overcome. According to official figures, the inflation rate in 2017 was 2.5%. More recently, such numbers were unattainable and seemed fantastic.
Regulatory Policy Instruments
So what are the tools that made it possible to successfully fulfill one of its main tasks in the short term, the Central Bank operates?
There are two main tools:
- key interest rate;
- refinancing rate.
As mentioned above, the key rate began to exist in mid-September 2013. From that moment, both rates exist in parallel. The dynamics of changes in key rates of the Central Bank is an indicator of the macro-financial state of the economy. Let's try to figure out what is the difference between them and what is common in them.
To begin with, they are both discount rates used by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as a tool in their policies. To one degree or another, both of them reflect the value of money for the country's economy in a certain period. Now let's move on to the differences.
Central Bank Key Rate
The key rate is the rate set by the Bank of Russia for the purpose of influencing the size of interest rates operating in the country's economy.
This effect can be either direct, through lending to commercial banks by the Bank of Russia, or indirectly. It exists in the form of an interest rate in operations for the provision and withdrawal of excess liquidity for a period of one week through an auction. To simplify, this is the rate at which the Central Bank gives money in the form of loans to banks and accepts money from them on deposit.
Thus, the key rate simultaneously plays the role of the attracting rate and the placement rate. But with some nuances. When the Bank of Russia provides loans, this rate is the minimum cost of credit funds, and when placing funds of credit banks with the Bank of Russia, it shows the maximum yield at which this can be done.
That is, banks will pay for the loan at the cost of the key rate and more, and they can place a deposit with the Central Bank at the price of the key rate and lower. Specific figures are determined by auction results. Thus, observing the dynamics of changes in the key rate, it is possible to assess the need of the economy for additional financing.
Impact on the economy
The main task that the key rate fulfills is to influence economic processes to achieve the inflation target. The impact of the key rate on the weighted average interest rates for attracting deposits and issuing loans can be monitored at any particular time period.
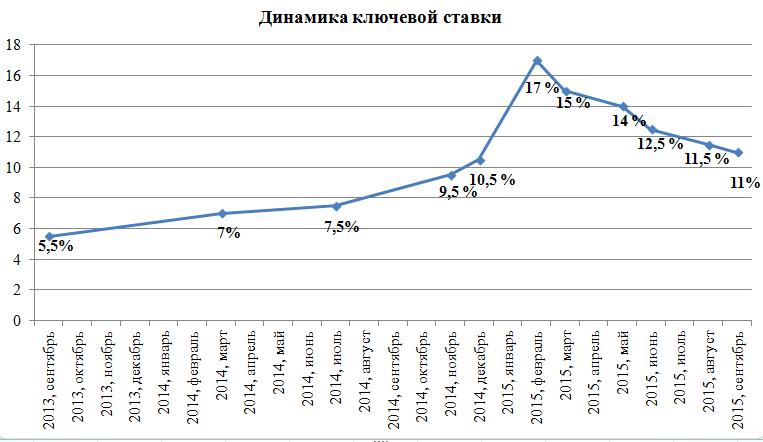
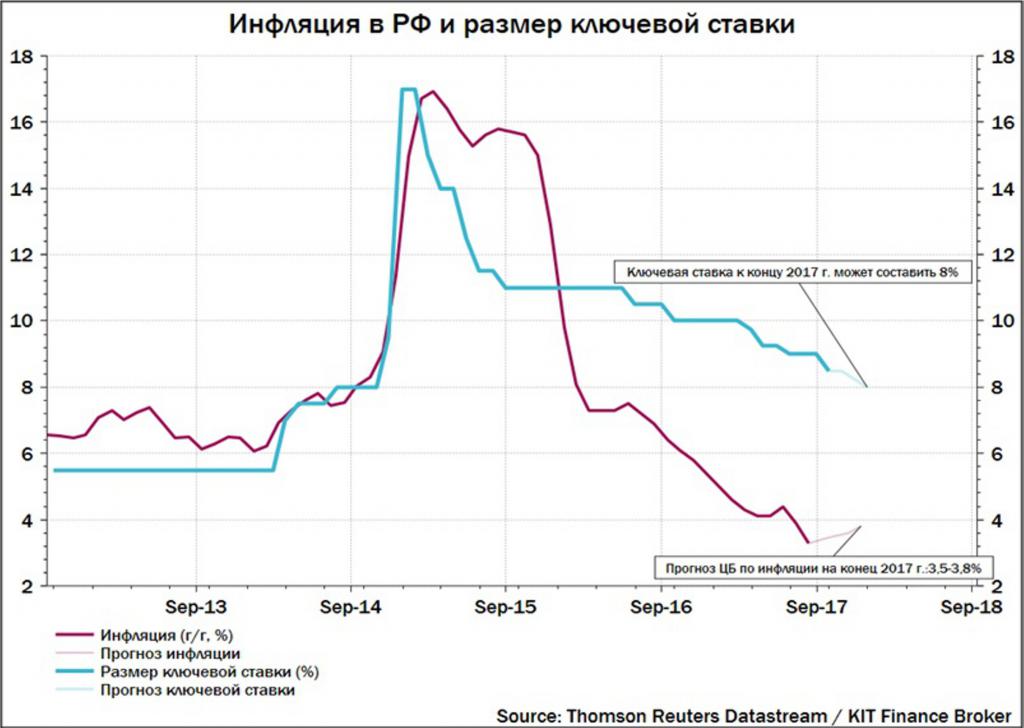
The most significant history of changes in the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation was traced from 2014 to 2017. For example, in 2015, during the period of maximum inflation, and the size of the key rate was maximum. When inflation, followed by the key rate, began to decline, so did deposit rates. You can also trace the influence of the key rate on interest on loans issued and their volumes.
Refinancing rate
Now consider the refinancing rate. It continues to play the role of the base rate in calculating various monetary compensations, subsidies, for calculating and calculating interest for late payments and installments of tax payments, penalties and fines. That is, it performs a kind of role of a national landmark in joint settlements.
Since January 1, 2016, the values of both rates have become equal at 11% per annum. This decision was made by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation following the meeting in December 2015 and enshrined in resolution No. 3894-U of 12/11/2015. Since then, the history of changes in the key rate has been consistent with the dynamics of the refinancing rate.
Background
Perhaps it’s worthwhile to dwell in more detail on the causes of the key rate. If we analyze the activities of financial systems in other states, we can see that basically one indicative rate is used there as a tool of financial policy.
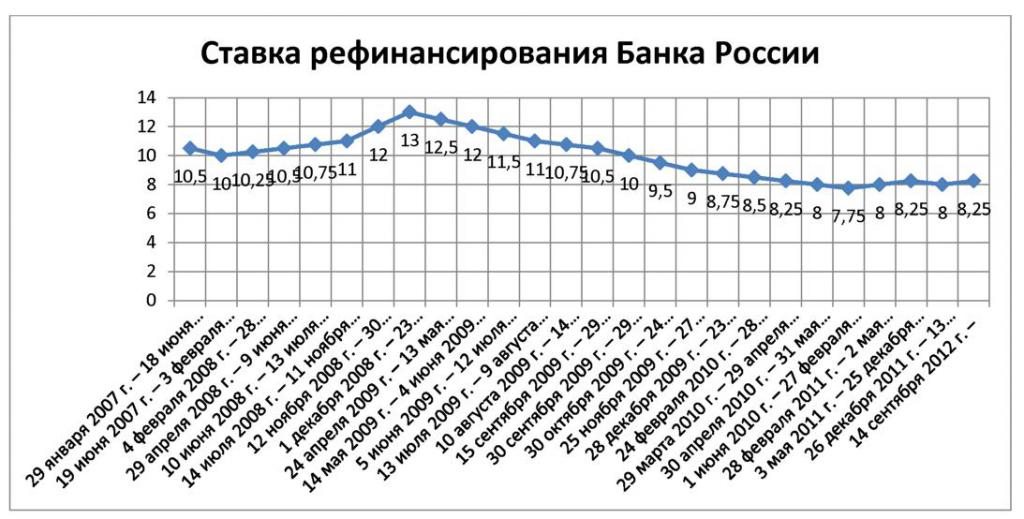
And in Russia until 2013 there was also one rate. It was a refinancing rate.
So why was the second one introduced? The fact is that during a period of relatively low, stable inflation, the rate was in the range of 7.75–8.25%. Since the events that followed since 2014 were not visible at that time, it seemed that the existing refinancing rate was at an unacceptably high level and slowed down the development processes in the Russian economy.
Both the government and public opinion demanded that the Central Bank reduce the rate more radically, so that lending would be carried out at a reduced interest rate and, thus, economic growth could be revived. The Central Bank was the main obstacle to this growth.
In fact, at this time, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, using various mechanisms, credited commercial banks at rates substantially lower than the refinancing rate.
The emergence of a key bid
In society, there was an increasing response to the position that it was the high refinancing rate that was to blame for the slowdown in economic growth. Although, at that time, it already actually performed the role of a certain interest rate for various tax, customs and other operations. And to the cost of loans issued by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, practically had no relation. Realizing the obvious absurdity of the situation, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation began to look for a way out of this situation. And he was found.
With the introduction of such a concept as a key rate, it was announced that now it is it that is a guideline in monetary relations between the main financial regulator and commercial banks. At the time of adoption, the key rate was 5.5% per annum and actually reflected the current state of affairs in the field of interbank lending. As changes in the economy occurred, a change in the key rate took place.
Present
An extreme reduction in the key rate occurred at a meeting of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on Friday, February 9, 2018. The following reasons were given as a justification for the decline:
- sustainable consolidation of annual inflation at a low level;
- decrease in inflation expectations;
- easing short-term inflation risks.
In the future, the regulator called for focusing not only on reducing inflation expectations, but also on reducing their dependence on lowering price conditions. The value of the rate decreased by 0.25%, which coincided with the expectations of analysts, including international ones. For example, both Reuters and Bloomberg predicted a rate cut just to the level of 7.5%, which ultimately happened.
In addition, the actions of the US Treasury Department, which spoke out against the ban on investing in Russian sovereign bonds for US organizations and funds, also contributed to the decline. It is worth noting that in January 2018, inflation was recorded and even at around 2.2%, which could lead to a further reduction in the rate.
Further actions of the Central Bank
Judging by the comments of the head of the Central Bank of Russia Elvira Nabiullina, it can be expected that the Central Bank of the Russian Federation can accelerate the transition to a neutral policy, which will allow fixing rates at the target level of 5-6%, while maintaining the current inflation rate.

In general, it is worth noting that the policy of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as a whole, and the adequate use of such an instrument as a key rate in particular, have made it possible to achieve serious success in reducing inflation. So, in 2015, inflation amounted to 12.9%, in 2016 - 5.4%, and in 2017 - 2.5%, which is a record for the entire history of observations.
The activities of the Central Bank not only led to a slowdown in price increases, but also significantly strengthened the basic macroeconomic mechanisms. No doubt, the change in the key rate played an important role in this.
It appears that further actions will be aimed at reducing the key rate. The consequence of this will be a decrease in interest on loans and, as a result, an increase in business activity. However, it is worthwhile to carefully monitor the behavior of prices so that these actions do not lead to a resumption of growth in inflationary processes.
Perhaps, other mechanisms to increase the availability of financial resources of economic entities will also be involved. For example, reducing reserve requirements, which will lead to the release of additional resources without changing the key rate. Which way the regulator will go will be seen in the near future. It will depend on both internal and external factors. We just have to wait a bit.
