Direct debit, what is it? It is faced by many citizens who have debts. And they have questions, is it allowed to use it in the case of them, or are such actions illegal? How is such a procedure regulated?
The essence of the phenomenon
Direct debit of funds is a procedure carried out by a bank without a client’s command. His consent is almost always required, which is expressed, for example, in actions with an ATM or card or electronic service.
It is assumed that situations where the cancellation is made for other reasons. In accordance with the provisions of the law, court decision or clauses of the contract.
Purpose of use
Consider the use of the tool under discussion in terms of business relations. If a court decision is made or a decision is made in the enforcement proceedings, no questions arise. But how do they act with mutual agreement on such things? The agreement of direct debit of funds gives the bank the right to manage the money of the client, having previously agreed to certain operations.
Everything is done under the conditions agreed by the parties. For example, a client took a loan from a bank through which he simultaneously receives a salary, pension or other official and regular payments. At the agreed time, the bank automatically writes off. There is no need to spend time visiting a bank, filling out securities or other manipulations to pay off a debt.
In business, more complex forms of interaction are used: the parties agree in advance on automatic payments for the goods or services provided, or which will be provided in the future. First, an agreement is made with the relevant condition with a partner, and then with the bank.
Normative regulation
- GK - contains the main provisions on maintaining a bank account;
- regulations of the Central Bank.
The code contains a basic rule, it is developed in other provisions of the law. For example, the law on enforcement proceedings, bankruptcy, etc.
To find out whether a bank has the right to conduct direct debit of funds, one should turn to the regulatory framework governing disputed relations. It is impossible to say unequivocally whether a bank has such a right. A positive or negative answer will be given to the question, depending on the rule of law to be applied in a particular situation.

The rules of service approved by banks are also important. They do not have the status of a normative act, but the client cannot refuse to fulfill them in any way. By signing the application for opening an account, the client puts a note on familiarization and consent to act in accordance with them.
At the same time, if it is possible to prove in court a contradiction of bank rules or an agreement to the norms of the law or acts of the Central Bank, then they do not apply. Then the law directly applies.
Reasons for surgery
Consider some of the reasons for direct debiting of funds:
- receipt of a court decision or an executive document issued on the basis of a judicial act to the bank;
- a claim from the tax service (on the payment of insurance premiums, tax charges and interest on them);
- claim for payments from the customs service;
- the lessor's claim in case of delay, which took place more than 2 times;
- clause of the contract concluded with the client giving the bank the right to write off without the prior consent of the client.
The condition of the contract is the basis for write-off if the payment is delayed or the credit limit is exceeded.
Write-off
Direct debit of funds from the client’s account is limited, first of all, by the norms of the law. The ban applies to the grounds for writing off, and the amount of funds. It is forbidden to write off if:
- funds on the broker's account belonging to the client company are affected if claims are presented to the broker;
- debit card funds are repaid for repayment of credit debt.

Accounts for social payments (except for pension payments) are protected from the requirements of bailiffs. Penalizing them is permitted in exceptional cases.
If we are talking about a card on which a salary or pension is transferred, the amount debited cannot exceed 50% of the amount of each receipt. Sometimes it is allowed to write off 75%. The debtor or his representative has the right, through higher bailiffs, to reduce the amount of deductions by complaint.
Right or obligation
From time to time the question arises: direct debit of funds from the account - the right or obligation of the bank? Courts give opposite answers on this issue.
If a bailiff's request or a court decision, duly executed, arrives at the bank, it is impossible to evade their execution. If the cancellation is connected solely with the contractual relationship of the bank's client with third parties, the bank, without having indisputable grounds, is obliged to refuse the request.
Relationship of the parties
Let's talk about a direct debit agreement. As such, it is concluded with the bank servicing the accounts of the parties to the agreement. This agreement is significant if the parties have secured the right to demand write-offs in agreements between themselves.

In the agreement, participants prescribe additional clauses. In particular, among the rights of the creditor, a request to the bank for direct debit is indicated. The reasons, terms and other nuances that protect the interests of the parties are prescribed.
The debtor undertakes to sign an agreement with the bank on direct debit of funds, enabling the creditor to promptly carry out such operations. If there is no such clause in the agreement, the parties shall have the right to either amend it or sign additional documents.
Relations with the Bank
Now we will consider the agreement on direct debit of funds from the current account. The structure of the document is approximately as follows:
- name of agreement;
- settlement or place of signing of the agreement;
- preamble (between whom the contract is concluded);
- description of the obligation (the bank is obligated to write off from the client’s account in favor of the agreed person);
- the contract is indicated in accordance with which the cancellation is made;
- the clauses of the agreement giving the right to direct debiting are indicated;
- comprehensive information about the person entitled to claim;
- The purpose of the payment is described (for example, repayment of a loan debt);
- indicates the obligation of the person having the right to demand to submit a payment order that fully meets the requirements of the law or the contract;
- the bank undertakes to inform the client about the write-off (the message is sent either to the phone number or e-mail);
- the agreement is considered effective from the moment of signing or from another date;
- details of the parties.
Third party involvement
Judicial practice implies the conclusion of an agreement only between the bank and its client, the presence of a third party as a participant is impossible.

If a bank client withdraws its consent to direct debit, then its partner does not have any leverage. It remains only to refer to the clause of the contract concluded by the parties about the obligation to ensure such a transfer of funds.
Bank actions
The Bank is obliged to fulfill the order to be written off when all the conditions of the agreement or the norms of the law are fulfilled, especially if the demand is presented by the authorities.Doubts about the legitimacy of the request give the right to provide additional or new documents if those submitted for the first time do not meet the law.
So, for example, a party requiring cancellation on the basis of a court decision is obliged to present a properly executed and certified copy of the judicial act. The right of direct debit of funds proceeds from the norms of the law and is documented.
Practical example
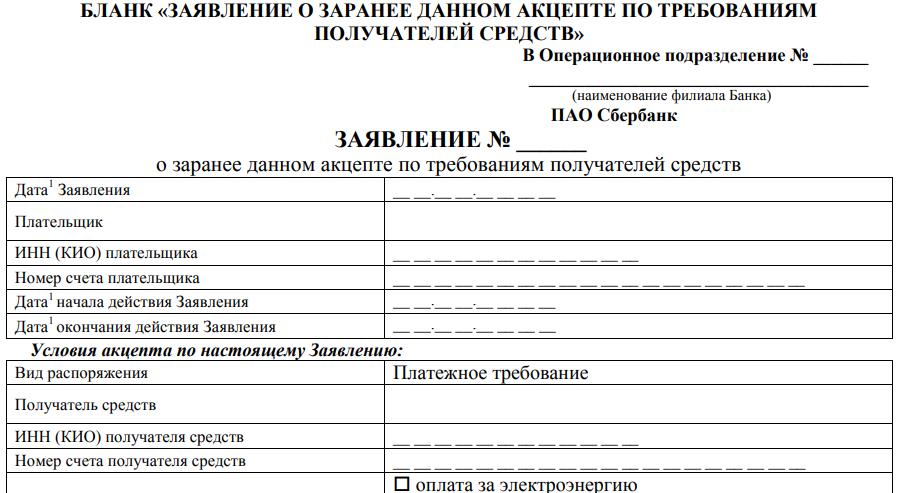
What are the features of the direct debit of Sberbank funds? When concluding an agreement with a financial institution for servicing, the client is entitled to pre-issue an acceptance for debit in the future. A special form is issued listing the following items:
- indicate the number of the application, information of the operating department where the application is submitted;
- date of writing or submitting an application to the bank;
- TIN of the client;
- his account number;
- date the permit begins and expires.

Similar information shall be indicated in relation to the person to whom the right of claim is granted. Following in the form are graphs:
- type of order, the payment order is immediately indicated in the form;
- recipient of funds;
- TIN or KIO;
- payer's obligation (payment of utility bills, telephone is offered; it is permissible to indicate another option);
- contract number and date;
- the amount that is allowed to be debited;
- formula for calculating the allowable charge amount;
- the possibility of incomplete or partial execution due to insufficient funds in the account.
The client has the right to allow partial execution. He is offered another option - the requirement is fulfilled after transferring funds to the account in order of priority. Execution is permitted during the period of validity of the application submitted by the client.
Finally
Management of money by opening accounts is considered normal and even habitual. The law also allows you to allow the bank to write off money from them in specified cases.

The grounds are provided for by legislative acts and an agreement with the bank. There are restrictions that cannot be circumvented by the terms of the agreement, in conflict with the law, they are automatically canceled.
