If a couple of centuries ago no one even thought about introducing legislation on copyright and related rights in the Russian Federation, now, in the age of technical, cultural and scientific progress, this issue has worried many people. With the development of the Internet, it has become very difficult to secure intellectual property rights, therefore, authors prefer to attend to this issue prematurely, in order to subsequently reserve copyright, the right to reproduce the results, to pay, and many others. It is the question of what the legal protection of copyright and related rights in Russia is, as well as what lawmakers directly mean by terms, and will be discussed in this article.
The foundation

Until the advent of the Fourth part of the Civil Code in the Russian Federation, namely chapter 71, the violation of copyright and related rights, as well as their protection, did not have a single consolidation. Indeed, there were several federal laws that in some of their parts at some level could help the authors to individualize their work, but in practice they were so fragmented that they could hardly be used normally.
For example, the law of the Russian Federation "On Copyright and Related Rights" was adopted on July 9, 1993. After him, several others appeared who tried to control activities in this direction. They were constantly trying to adapt them to the current situation, so new additions were gradually introduced, but they could not completely solve the situation. That is why on November 24, 2005, the State Duma adopted a new chapter of the Civil Code, which replaced the current laws on copyright and related rights.
In a certain way, Russia became a pioneer, combining regulation of the entire turnover of intellectual products and means of individualization of authors into a single whole. The norms that are enshrined in this document are the same for all that are listed in the chapter "General Provisions".
History reference

In order to fully understand what the legislative system means by copyright and related rights in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is worthwhile to first examine the history of their consolidation in the country.
In fact, the first attempts to consolidate copyright in Russia began in the early 19th century. This term was formulated quite simply, due to which the creator or translator of books was assigned the right to use and sell their works for the rest of his life, adding another 25 years after death. After that, any work was recognized by the public.
Almost a century later, in March 1911, a special law on copyright and related rights appeared, which absorbed all the achievements of the then existing legislation in Europe in this area. Moreover, it should be pointed out that to some extent he even surpassed European regulations, since he expanded their existing types and gave a number of concepts. Unfortunately, the coming to power of the Soviets overturned existing legislation, and the new government revised existing decrees. They nationalized almost all classical literature, saying that absolutely anyone can publish books without the permission of the state in those cases if the author died before 1917. Gradually, copyright passed from the domain of private to public property.
Only gradually, by the time of the collapse of the USSR, authors began to recognize much more rights, but in reality all this was miserable crumbs.In addition, the rights adjacent to copyright were directly enshrined in the legislation only again from 1991, after which a new round of development of this sphere began.
The concept
It is clear that the protection of copyright and related rights is currently very important, because it allows you to assign to a person the results of his intellectual property. But in order to understand exactly how it is carried out, you first need to give them clear concepts.
So, copyright refers to intellectual rights to works of science, literature and art. As you can see, this list is exhaustive, and it is enshrined in article 1255 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The concept “intellectual rights” introduced for the first time includes the results of intellectual activity, which include not only the exclusive right, but also a number of personal non-property and other rights.
Kinds

Before proceeding directly to the consideration of rights adjacent to copyright, one should consider what is customarily attributed to them. This list is enshrined in the same article and includes:
- The exclusive right to the work created.
- The right to personal authorship.
- The right to indicate your name on the result.
- The right to inviolability of the work created.
- The right to free disclosure.
In some cases, this list may also include some other rights that are enshrined in the Civil Code.
Subjects
Before proceeding to clarify what relates to rights related to copyright, we will also talk about the subjects of copyright. By them are meant the direct creators. However, in addition to this, successors, as well as other persons who, according to the law or the contract, acquire exclusive copyright, may be included in the subjects.
In fact, it doesn’t really matter to the law whether the subject of this right is a natural or legal person, since the publishers of magazines and newspapers have the same number of rights as the person who wrote the book at home.
You should always remember that all the rights of the author to the work are with him as the creator directly because of the very fact of creation. This is what distinguishes copyright from patent, as it does not require pre-registration or other formalities.
Copyright mark
As a confirmation of his exclusive right to the result of intellectual activity, the owner of the work may use (although he may not do so if he wishes) the sign of copyright protection. It consists of three special elements:
- Letters With a Latin alphabet drawn in a circle. This is the first letter of the word copyright.
- Indications of the name or nickname of the owner of the exclusive right.
- The year of first publication of this work.
This mark serves an informational role only, and its placement is optional. In practice, this sign identifies cases of unauthorized use of rights.
Rights Related to Copyright
Now we will directly proceed to what is meant by legislation as related rights. It is customary to relate to them, as the name implies, rights that are quite similar to copyright. Due to similar similarity, they have an identical legal regime.
In many ways, the emergence of related rights is considered to be the result of progress, as they enable third parties to perceive new trends. The creation of the cinema by the Lumiere brothers, and Thomas Edison, photography at the time, significantly expanded the types of copyright and related rights. When the real technological progress of the 20th century began, it became clear that the legislative framework was simply not able to keep up with it, and therefore it was necessary to highlight a special group of relations that possessed a certain specificity, which could not fully relate to the copyright.
Types of Related Rights

So, at present, all these concepts are fixed in article 1304 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It is customary to relate to them:
- The right to perform - is directly given to the performing artists and conductors, as well as to other persons, recognizing them the exclusive right to be called the author of the performance and indicate their name or nickname on copies of the phonogram.
- The right to a phonogram - prohibits in any way distort the phonogram, and if you wish, you can publish it or indicate your name on the copies.
- The right of broadcasting and cable television organizations to any created program or message broadcasting can be used in any way that does not contradict existing legislation.
- The right to databases - the manufacturer can extract from it any data depending on his desire and reuse it.
- The publisher’s right to works previously protected by copyright after their transfer to public ownership.
In fact, all related rights are reduced to the fact that without the permission of organizations, artists or other holders of these rights it is impossible to use any phonograms, television programs, creative results of activities.
Sign of protection
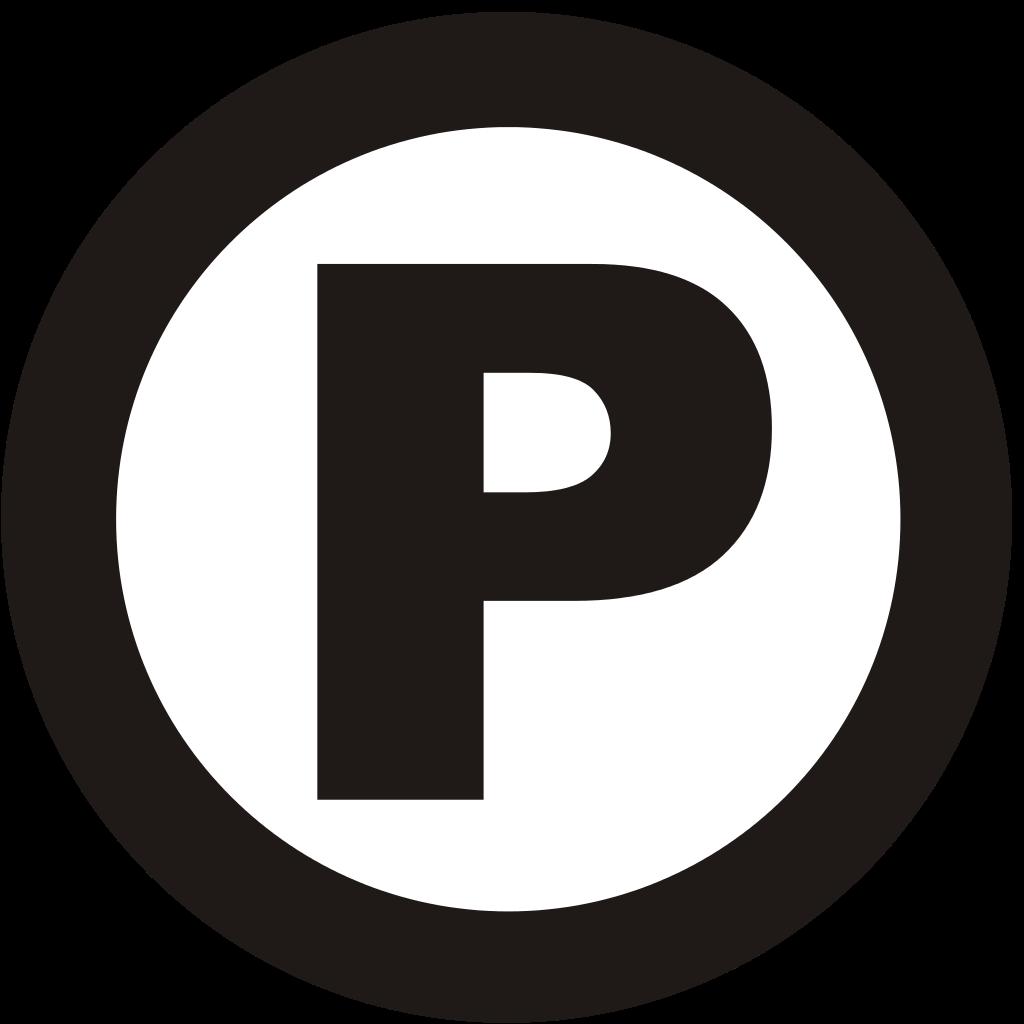

Like copyrights, related ones also have their own special protection mark. It is usually placed on each copy of the phonogram, and in cases where this is not possible, then on the case. It consists of the following elements:
- The letters P are in a circle.
- Names of the owner of the exclusive right.
- The year in which this phonogram was first published.
As you can see, this protection mark is very similar to the one that copyright has. Their only difference is that the letter changes, because the word used to describe them is different, namely phonorecord.
Protection

Free civil circulation is primarily aimed not only at the fact that the authors will be assigned certain civil rights, but also at the fact that they will be under strict legal protection. Currently, the term protection in this area provides for a whole set of various measures that ensure the normal implementation of the law, so this includes not only legal norms, but also economic, political and organizational measures that help fully establish all the necessary conditions for in order for subjective rights to be realized.
Based on this, we can say that the protection of rights has a fairly broad understanding. However, in addition to this, there is a more narrow sense of this concept. It includes only those measures that are provided for by law. They aim to help the owner protect his civil rights in cases where they have been challenged or violated. Such rights, for example, include the possibility of the author to turn to the court for unlawful actions of the violator to restore his legitimate interests, as well as many others.
Conclusion
The issue of copyright and related law is currently one of the most central issues in both the Russian and international legislative systems. It has a huge number of nuances that are difficult to consider in one article, since they are largely subjective. But in fact, it is worth remembering one main idea of all legal norms in this area: copyright and related rights are exclusive by virtue of their nature, so that they can only belong to the holder and no one else. It should also be remembered that the creator has a single copyright, which may subsequently slightly change depending on the conditions.
